You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: sr11248-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: sr11248-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Sporisorium reilianum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Ustilaginomycetes; ; Ustilaginaceae; Sporisorium; Sporisorium reilianum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | sr11248-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | conserved hypothetical protein (fragment) | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 162 | 371 | 6.4e-49 | 0.9746192893401016 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 404513 | Glyco_trans_2_3 | 1.07e-47 | 161 | 374 | 1 | 194 | Glycosyl transferase family group 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferases, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
| 224136 | BcsA | 8.57e-08 | 159 | 461 | 138 | 426 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| 133045 | CESA_like | 2.05e-07 | 159 | 269 | 79 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| 133034 | Glucan_BSP_MdoH | 0.004 | 163 | 249 | 100 | 187 | Glucan_BSP_MdoH catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of glucan. Periplasmic Glucan Biosynthesis protein MdoH is a glucosyltransferase that catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of glucan, requiring a beta-glucoside as a primer and UDP-glucose as a substrate. Glucans are composed of 5 to 10 units of glucose forming a highly branched structure, where beta-1,2-linked glucose constitutes a linear backbone to which branches are attached by beta-1,6 linkages. In Escherichia coli, glucans are located in the periplasmic space, functioning as regulator of osmolarity. It is synthesized at a maximum when cells are grown in a medium with low osmolarity. It has been shown to span the cytoplasmic membrane. |
| 133057 | CESA_NdvC_like | 0.006 | 160 | 283 | 86 | 198 | NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. Bradyrhizobium japonicum synthesizes periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans during growth under hypoosmotic conditions. Two genes (ndvB, ndvC) are involved in the beta-(1, 3), beta-(1,6)-glucan synthesis. The ndvC mutant strain resulted in synthesis of altered cyclic beta-glucans composed almost entirely of beta-(1, 3)-glycosyl linkages. The periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans function for osmoregulation. The ndvC mutation also affects the ability of the bacteria to establish a successful symbiotic interaction with host plant. Thus, the beta-glucans may function as suppressors of a host defense response. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 545 | 1 | 545 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 545 | 528 | 1072 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 545 | 684 | 1230 | |
| 5.86e-264 | 1 | 545 | 385 | 878 | |
| 1.22e-263 | 1 | 545 | 387 | 879 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
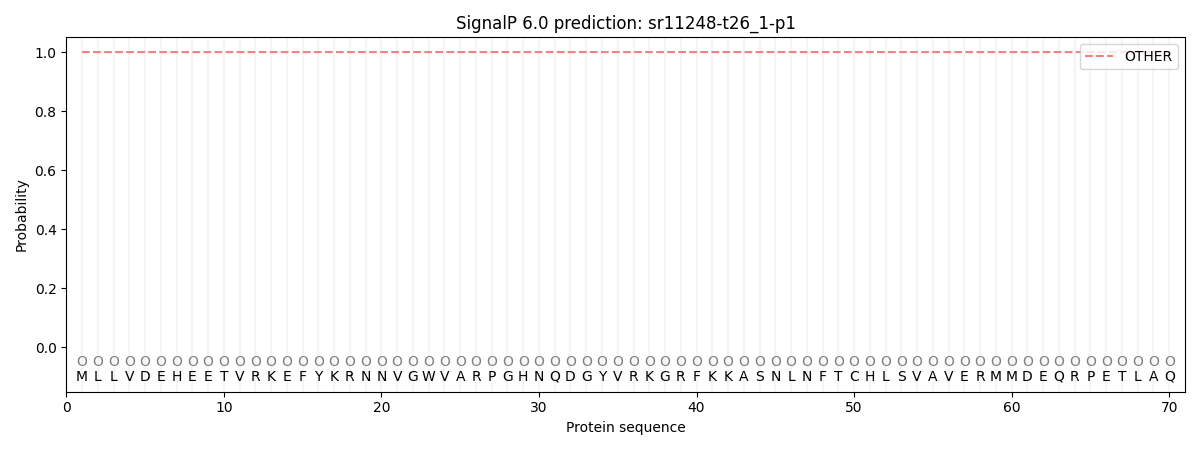
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000045 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
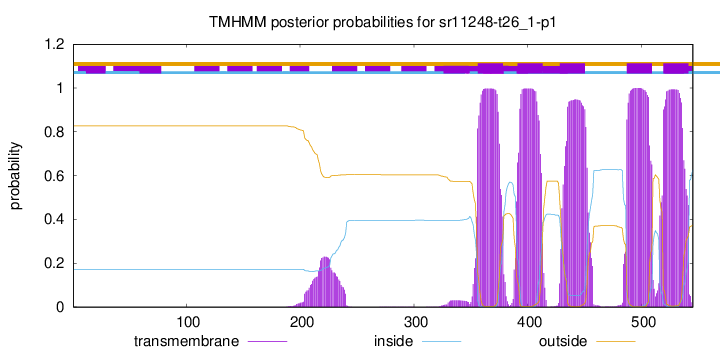
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 356 | 378 |
| 391 | 413 |
| 428 | 450 |
| 487 | 509 |
| 519 | 541 |
