You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: jhhlp_001539-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: jhhlp_001539-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Lomentospora prolificans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Microascaceae; Lomentospora; Lomentospora prolificans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | jhhlp_001539-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA7 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2178567; End:2182689 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MYQKVLGLLG APTFLLFAPN ILTAQPDAGS LLTSPNGSVE DFIAWERPIA LENILCNIGP | 60 |
| ECVDFYTWTR DAALVFKGLV EIFAANQTTD LQTEIHNYIQ AQARLQAVEN LSGSLRDGSG | 120 |
| LAEPKFHVDS TAFTDNWGRP QRDGPPLRAI AMMAYANWLV EQGEKPLALD KIWPVIQNDL | 180 |
| SYVVQHWNKT GFDLWEEVEG SSFFTTASQY RALIEGGTLA KALGFSCPHC DIVAPQILCF | 240 |
| LQQYWSPSQG YALSNINDHS DRSSKDVNAI LASIHSFDPS VGCDGNTFQP CSSRMLATHK | 300 |
| ILADSFKDEY PINSGVAPGK AMAIGRYPED VYYGGHPWYL ATLAAAEQMY DALYVWQENG | 360 |
| YIEVTDVDVP FFHDFSHELQ TGKHLNDSAE FAALMNSIAN YADGFIDIVA EYIHPNGSIA | 420 |
| EQYTRDTGTP TSARDLTWSY AAFLSAVARR DKQVPRSWLN AQVVTPPNKC VPTSIVGYYA | 480 |
| AADPSPFPLP RGNEKAPGDG QGPGGSCPET RYVVVNFQVR VVTSWGEKIK MVGNTDILGG | 540 |
| WEPGLGVELN AAGYSEEDPI WRVSIVLLAG QEIEYKFVRV GEDGQQVSWE SDPNRRYSAP | 600 |
| AECETTATVH PSSPIRIAAS PRESPKPRNG LADPTSRHPP AGTAQARPLR TRVVLHHPTL | 660 |
| PLLATSHGRT VTVFSLTSLT PHSTVTNGHE RSIRCTAWKP NLDPGRLCLV SGSFDSTAGL | 720 |
| WRWEGASEER DHATDMTARS AAGSDDERRE DEDDEEEDTD WQFTLVLEGH DSEIKGVAFS | 780 |
| PSGAHLATCS RDKSVWIWED VGADEDDDEW ETVAVLNEHE GDVKAVAWCP DVPGRNARRS | 840 |
| YSADVLASAS YDDTVRIWRE DDDGEWVCVA VLSGHEGTVW GIAWEGTERA DGAFPRLASC | 900 |
| SADGTIRVWK LKVDDEDDAP TATLGGIPNT MRRSLREDWV CEAVLPKAHT RDIYSVTWSP | 960 |
| RTGLLASTGS DGVIALYREE DEPEPAKAAD PGAGGDEAAG SKKWKLVATY DRGHGPYEVN | 1020 |
| HVTWCPRYDS EKKPGEEMLV TTGDDGQVRT WRVSVPDA | 1058 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.3:94 | 3.2.1.1:13 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH15 | 65 | 447 | 2.2e-73 | 0.8836565096952909 |
| CBM20 | 513 | 605 | 6e-24 | 0.9777777777777777 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395586 | Glyco_hydro_15 | 2.41e-111 | 48 | 446 | 1 | 415 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 15. In higher organisms this family is represented by phosphorylase kinase subunits. |
| 238121 | WD40 | 1.51e-38 | 657 | 1052 | 18 | 289 | WD40 domain, found in a number of eukaryotic proteins that cover a wide variety of functions including adaptor/regulatory modules in signal transduction, pre-mRNA processing and cytoskeleton assembly; typically contains a GH dipeptide 11-24 residues from its N-terminus and the WD dipeptide at its C-terminus and is 40 residues long, hence the name WD40; between GH and WD lies a conserved core; serves as a stable propeller-like platform to which proteins can bind either stably or reversibly; forms a propeller-like structure with several blades where each blade is composed of a four-stranded anti-parallel b-sheet; instances with few detectable copies are hypothesized to form larger structures by dimerization; each WD40 sequence repeat forms the first three strands of one blade and the last strand in the next blade; the last C-terminal WD40 repeat completes the blade structure of the first WD40 repeat to create the closed ring propeller-structure; residues on the top and bottom surface of the propeller are proposed to coordinate interactions with other proteins and/or small ligands; 7 copies of the repeat are present in this alignment. |
| 99886 | CBM20_glucoamylase | 1.07e-32 | 523 | 612 | 17 | 105 | Glucoamylase (glucan1,4-alpha-glucosidase), C-terminal CBM20 (carbohydrate-binding module, family 20) domain. Glucoamylases are inverting, exo-acting starch hydrolases that hydrolyze starch and related polysaccharides by releasing the nonreducing end glucose. They are mainly active on alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds but also have some activity towards 1,6-glycosidic bonds occurring in natural oligosaccharides. The ability of glucoamylases to cleave 1-6-glycosidic binds is called "debranching activity" and is of importance in industrial applications, where complete degradation of starch to glucose is needed. Most glucoamylases are multidomain proteins containing an N-terminal catalytic domain, a C-terminal CBM20 domain, and a highly O-glycosylated linker region that connects the two. The CBM20 domain is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 293791 | 7WD40 | 3.79e-31 | 777 | 1051 | 4 | 200 | WD40 repeats in seven bladed beta propellers. The WD40 repeat is found in a number of eukaryotic proteins that cover a wide variety of functions including adaptor/regulatory modules in signal transduction, pre-mRNA processing, and cytoskeleton assembly. It typically contains a GH dipeptide 11-24 residues from its N-terminus and the WD dipeptide at its C-terminus and is 40 residues long, hence the name WD40. Between the GH and WD dipeptides lies a conserved core. It forms a propeller-like structure with several blades where each blade is composed of a four-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet. The WD40 sequence repeat originally described in literature forms the first three strands of one blade and the last strand in the next blade. The C-terminal WD40 repeat completes the blade structure of the N-terminal WD40 repeat to create the closed ring propeller-structure. The residues on the top and bottom surface of the propeller are proposed to coordinate interactions with other proteins and/or small ligands, allowing them to bind either stably or reversibly. |
| 238121 | WD40 | 1.83e-29 | 766 | 1053 | 4 | 248 | WD40 domain, found in a number of eukaryotic proteins that cover a wide variety of functions including adaptor/regulatory modules in signal transduction, pre-mRNA processing and cytoskeleton assembly; typically contains a GH dipeptide 11-24 residues from its N-terminus and the WD dipeptide at its C-terminus and is 40 residues long, hence the name WD40; between GH and WD lies a conserved core; serves as a stable propeller-like platform to which proteins can bind either stably or reversibly; forms a propeller-like structure with several blades where each blade is composed of a four-stranded anti-parallel b-sheet; instances with few detectable copies are hypothesized to form larger structures by dimerization; each WD40 sequence repeat forms the first three strands of one blade and the last strand in the next blade; the last C-terminal WD40 repeat completes the blade structure of the first WD40 repeat to create the closed ring propeller-structure; residues on the top and bottom surface of the propeller are proposed to coordinate interactions with other proteins and/or small ligands; 7 copies of the repeat are present in this alignment. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEO61583.1|CBM20|GH15|3.2.1.3 | 3.33e-204 | 25 | 598 | 16 | 608 |
| AEO64596.1|CBM20|GH15 | 1.16e-201 | 38 | 609 | 35 | 632 |
| QSZ31699.1|CBM20|GH15 | 2.17e-201 | 38 | 609 | 68 | 671 |
| APA12357.1|CBM20|GH15 | 6.51e-201 | 19 | 609 | 52 | 673 |
| UPK89675.1|CBM20|GH15 | 9.60e-201 | 39 | 608 | 67 | 663 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2VN4_A | 8.08e-194 | 38 | 609 | 1 | 592 | Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei],2VN7_A Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei] |
| 6FRV_A | 5.06e-174 | 65 | 609 | 49 | 611 | Structure of the catalytic domain of Aspergillus niger Glucoamylase [Aspergillus niger] |
| 6FHV_A | 1.22e-167 | 37 | 603 | 6 | 582 | Crystal structure of Penicillium oxalicum Glucoamylase [Penicillium oxalicum 114-2] |
| 3EQA_A | 8.39e-153 | 65 | 488 | 49 | 467 | Catalytic domain of glucoamylase from aspergillus niger complexed with tris and glycerol [Aspergillus niger] |
| 1AGM_A | 7.74e-150 | 65 | 488 | 49 | 466 | Refined structure for the complex of acarbose with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. x100 to 2.4 angstroms resolution [Aspergillus awamori],1DOG_A REFINED STRUCTURE FOR THE COMPLEX OF 1-DEOXYNOJIRIMYCIN WITH GLUCOAMYLASE FROM (ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI) VAR. X100 TO 2.4 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION [Aspergillus awamori],1GLM_A REFINED CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF GLUCOAMYLASE FROM ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI VAR. X100 [Aspergillus awamori],3GLY_A REFINED CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF GLUCOAMYLASE FROM ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI VAR. X100 [Aspergillus awamori] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|P14804|AMYG_NEUCR | 1.31e-193 | 38 | 609 | 36 | 621 | Glucoamylase OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=gla-1 PE=1 SV=3 |
| sp|P36914|AMYG_ASPOR | 7.02e-179 | 65 | 609 | 76 | 606 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=glaA PE=2 SV=2 |
| sp|P69327|AMYG_ASPAW | 2.88e-173 | 34 | 609 | 22 | 635 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus awamori OX=105351 GN=GLAA PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P69328|AMYG_ASPNG | 2.88e-173 | 34 | 609 | 22 | 635 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus niger OX=5061 GN=GLAA PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P22832|AMYG_ASPUS | 7.34e-170 | 34 | 609 | 22 | 634 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus usamii OX=186680 GN=glaA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
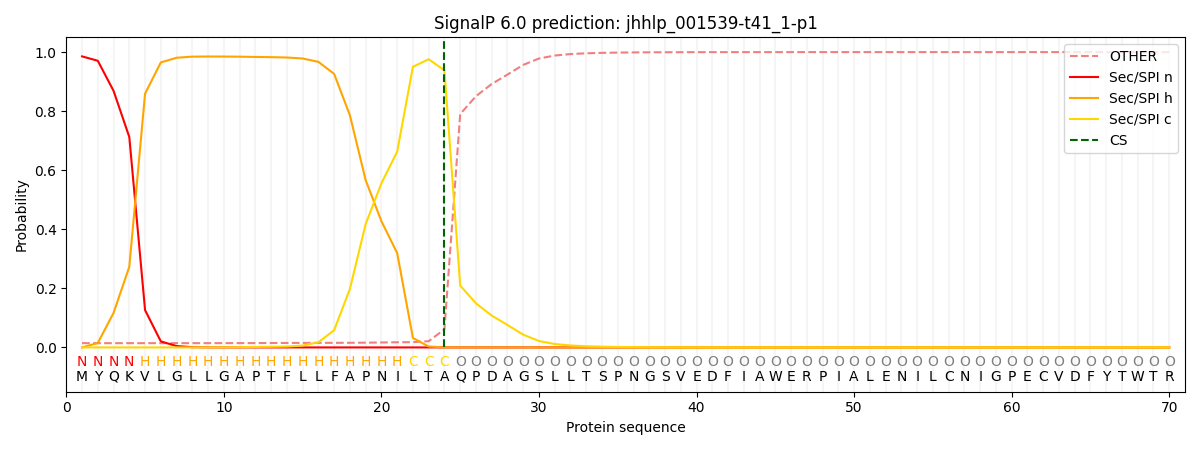
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.018942 | 0.981030 | CS pos: 24-25. Pr: 0.9385 |
