You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: evm.model.AC2VRR_s00053g38-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: evm.model.AC2VRR_s00053g38-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Albugo candida | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Albuginaceae; Albugo; Albugo candida | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | evm.model.AC2VRR_s00053g38-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH17 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.34:28 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT48 | 846 | 1590 | 1e-272 | 0.9634641407307172 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396784 | Glucan_synthase | 0.0 | 847 | 1529 | 3 | 701 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component. This family consists of various 1,3-beta-glucan synthase components including Gls1, Gls2 and Gls3 from yeast. 1,3-beta-glucan synthase EC:2.4.1.34 also known as callose synthase catalyzes the formation of a beta-1,3-glucan polymer that is a major component of the fungal cell wall. The reaction catalyzed is:- UDP-glucose + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N+1). |
| 405046 | FKS1_dom1 | 1.44e-30 | 150 | 243 | 6 | 106 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase subunit FKS1, domain-1. The FKS1_dom1 domain is likely to be the 'Class I' region just N-terminal to the first set of transmembrane helices that is involved in 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis itself. This family is found on proteins with family Glucan_synthase, pfam02364. |
| 395036 | Sugar_tr | 7.06e-21 | 1769 | 2147 | 24 | 432 | Sugar (and other) transporter. |
| 340916 | MFS_GLUT6_8_Class3_like | 3.63e-18 | 1783 | 2148 | 40 | 418 | Glucose transporter (GLUT) types 6 and 8, Class 3 GLUTs, and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This subfamily is composed of glucose transporter type 6 (GLUT6), GLUT8, plant early dehydration-induced gene ERD6-like proteins, and similar insect proteins including facilitated trehalose transporter Tret1-1. GLUTs, also called Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporters (SLC2A), are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). Insect Tret1-1 is a low-capacity facilitative transporter for trehalose that mediates the transport of trehalose synthesized in the fat body and the incorporation of trehalose into other tissues that require a carbon source. GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. They belong to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 340873 | MFS_GLUT_like | 1.43e-13 | 1769 | 2153 | 21 | 360 | Glucose transporters (GLUTs) and other similar sugar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This family is composed of glucose transporters (GLUTs) and other sugar transporters including fungal hexose transporters (HXT), bacterial xylose transporter (XylE), plant sugar transport proteins (STP) and polyol transporters (PLT), H(+)-myo-inositol cotransporter (HMIT), and similar proteins. GLUTs, also called Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporters (SLC2A), are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. The GLUT-like family belongs to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 3 | 2224 | 5 | 2225 | |
| 0.0 | 5 | 2219 | 8 | 2232 | |
| 0.0 | 6 | 2221 | 11 | 2224 | |
| 0.0 | 6 | 2224 | 4 | 2242 | |
| 0.0 | 11 | 2218 | 10 | 2241 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.40e-230 | 69 | 1735 | 241 | 1939 | Callose synthase 3 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS3 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 1.35e-225 | 69 | 1735 | 237 | 1934 | Callose synthase 2 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS2 PE=2 SV=3 |
|
| 4.61e-223 | 69 | 1735 | 237 | 1934 | Callose synthase 1 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS1 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 1.75e-219 | 48 | 1735 | 238 | 1918 | Callose synthase 7 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS7 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 2.27e-217 | 69 | 1730 | 258 | 1961 | Putative callose synthase 8 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS8 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000038 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
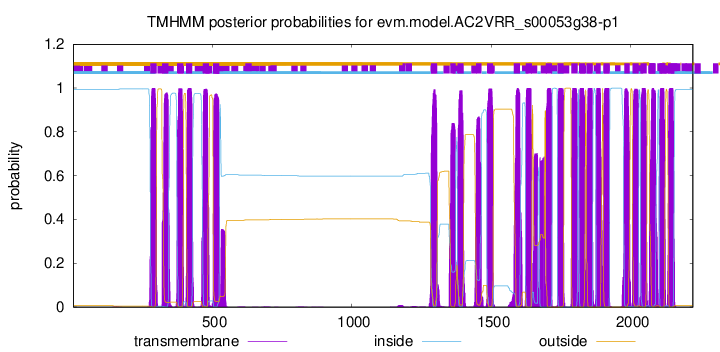
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 277 | 299 |
| 319 | 341 |
| 373 | 395 |
| 405 | 427 |
| 465 | 487 |
| 502 | 524 |
| 1284 | 1306 |
| 1353 | 1372 |
| 1379 | 1401 |
| 1446 | 1465 |
| 1485 | 1507 |
| 1581 | 1603 |
| 1624 | 1646 |
| 1696 | 1718 |
| 1738 | 1760 |
| 1788 | 1810 |
| 1815 | 1837 |
| 1842 | 1864 |
| 1876 | 1893 |
| 1903 | 1925 |
| 1978 | 1997 |
| 2007 | 2029 |
| 2036 | 2058 |
| 2068 | 2090 |
| 2103 | 2125 |
| 2135 | 2157 |
