You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: YALI0_E21021g-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: YALI0_E21021g-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Yarrowia lipolytica | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Saccharomycetes; ; Dipodascaceae; Yarrowia; Yarrowia lipolytica | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | YALI0_E21021g-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT20 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | YALI0E21021p | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.34:56 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT48 | 838 | 1624 | 0 | 0.9891745602165088 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396784 | Glucan_synthase | 0.0 | 838 | 1663 | 1 | 819 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component. This family consists of various 1,3-beta-glucan synthase components including Gls1, Gls2 and Gls3 from yeast. 1,3-beta-glucan synthase EC:2.4.1.34 also known as callose synthase catalyzes the formation of a beta-1,3-glucan polymer that is a major component of the fungal cell wall. The reaction catalyzed is:- UDP-glucose + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N+1). |
| 405046 | FKS1_dom1 | 2.18e-45 | 326 | 435 | 1 | 111 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase subunit FKS1, domain-1. The FKS1_dom1 domain is likely to be the 'Class I' region just N-terminal to the first set of transmembrane helices that is involved in 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis itself. This family is found on proteins with family Glucan_synthase, pfam02364. |
| 367362 | Glutenin_hmw | 0.002 | 27 | 177 | 171 | 300 | High molecular weight glutenin subunit. Members of this family include high molecular weight subunits of glutenin. This group of gluten proteins is thought to be largely responsible for the elastic properties of gluten, and hence, doughs. Indeed, glutenin high molecular weight subunits are classified as elastomeric proteins, because the glutenin network can withstand significant deformations without breaking, and return to the original conformation when the stress is removed. Elastomeric proteins differ considerably in amino acid sequence, but they are all polymers whose subunits consist of elastomeric domains, composed of repeated motifs, and non-elastic domains that mediate cross-linking between the subunits. The elastomeric domain motifs are all rich in glycine residues in addition to other hydrophobic residues. High molecular weight glutenin subunits have an extensive central elastomeric domain, flanked by two terminal non-elastic domains that form disulphide cross-links. The central elastomeric domain is characterized by the following three repeated motifs: PGQGQQ, GYYPTS[P/L]QQ, GQQ. It possesses overlapping beta-turns within and between the repeated motifs, and assumes a regular helical secondary structure with a diameter of approx. 1.9 nm and a pitch of approx. 1.5 nm. |
| 407550 | Trnau1ap | 0.002 | 97 | 140 | 5 | 48 | Selenocysteine tRNA 1 associated proteins. This entry represents the C-terminal region of Selenocysteine tRNA 1 associated proteins (Trnau1ap also known as Secp43). Family members found in Eukaryotes have been shown to serve an essential role in the synthesis of selenoproteins, which have critical functions in numerous biological processes. Selenium deficiency results in a variety of diseases, including cardiac disease. Trnau1ap proteins harbor RNA recognition motifs (RRM) pfam00076 and Tyr-rich region found in the C-terminal. The Tyr-rich region (amino acids 185-225) is conserved among several mammals, including human, chimp, dog, cattle, mouse and rat. Furthermore, constitutive deletion of exons corresponding to the Tyr-rich region in mouse resulted in embryonic lethality. |
| 407550 | Trnau1ap | 0.010 | 96 | 135 | 1 | 32 | Selenocysteine tRNA 1 associated proteins. This entry represents the C-terminal region of Selenocysteine tRNA 1 associated proteins (Trnau1ap also known as Secp43). Family members found in Eukaryotes have been shown to serve an essential role in the synthesis of selenoproteins, which have critical functions in numerous biological processes. Selenium deficiency results in a variety of diseases, including cardiac disease. Trnau1ap proteins harbor RNA recognition motifs (RRM) pfam00076 and Tyr-rich region found in the C-terminal. The Tyr-rich region (amino acids 185-225) is conserved among several mammals, including human, chimp, dog, cattle, mouse and rat. Furthermore, constitutive deletion of exons corresponding to the Tyr-rich region in mouse resulted in embryonic lethality. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 57 | 1934 | 57 | 1934 | |
| 0.0 | 57 | 1934 | 58 | 1935 | |
| 0.0 | 57 | 1934 | 83 | 1961 | |
| 0.0 | 209 | 1934 | 1 | 1726 | |
| 0.0 | 67 | 1868 | 103 | 1924 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 165 | 1852 | 126 | 1781 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component FKS1 OS=Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii serotype A (strain H99 / ATCC 208821 / CBS 10515 / FGSC 9487) OX=235443 GN=FKS1 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 0.0 | 75 | 1903 | 84 | 1880 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component FKS1 OS=Aspergillus niger (strain CBS 513.88 / FGSC A1513) OX=425011 GN=fksA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 175 | 1911 | 15 | 1775 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component FKS3 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=FKS3 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 128 | 1896 | 103 | 1852 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component FKS1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=FKS1 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 0.0 | 130 | 1896 | 119 | 1871 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component GSC2 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=GSC2 PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000044 | 0.000001 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
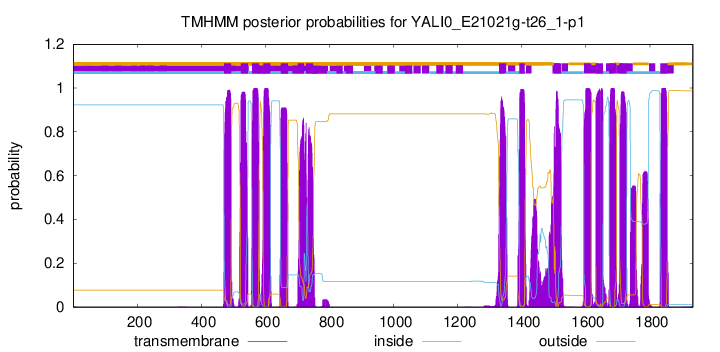
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 471 | 493 |
| 523 | 545 |
| 558 | 580 |
| 593 | 615 |
| 648 | 670 |
| 701 | 720 |
| 727 | 749 |
| 1329 | 1351 |
| 1392 | 1409 |
| 1501 | 1523 |
| 1594 | 1616 |
| 1631 | 1653 |
| 1673 | 1695 |
| 1705 | 1727 |
| 1832 | 1854 |
