You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: XP_001906534.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: XP_001906534.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Podospora anserina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Podosporaceae; Podospora; Podospora anserina | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | XP_001906534.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH12 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Podospora anserina S mat+ genomic DNA chromosome 1, supercontig 6 [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:B2AS32] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 277993; End:280351 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MEAGCFKRDH DPPLSVLWRE RYEIGTKSPP PQTLIMKFSP ATLLPLLMAA GSNAAPSQNS | 60 |
| PRQTKPPTVY LAGDSTMART NSPHNGWGEY LSRYLTISVV NKAISGRSAR SFTNEGRFAE | 120 |
| IERLVVPNDI VIISFGHNDG SSPNSANDNG RSACPGTGNE VCRSGKTGET VYTYNHYLQT | 180 |
| AGRALIAKGA KVVFSAQTPK NLWQNGQWSG NYEPPRFVPY AAAAARNVGS GASFVDHYQA | 240 |
| VTKTYQRLGS QKVNSFYPVD YTHTSPEGAD VIAQAFAQAV SRDFNGTTAV KPYLRNPVPN | 300 |
| PSAAIGICMT RVGVVVARGV CDAGRCCLRV AGSDIGHLFF FQSPIQFSVP GIHQFSSPAK | 360 |
| AVQRTMAKVL ITGINGYIAA HTAARFLQAG FSVRGTVRNK TSPNVESLLR ALSAPQKAGG | 420 |
| GKVEIVEVPD ITIEGAFDNA VQAHLASPVS MADGDPAPMM KAAVDGTTSL LASAVEAPTK | 480 |
| FKSVAFMSSI SAVYSPPPYR SPDHVFTSAD WNQEAEAKVA ELGDNTPGYI TYQASKTAAE | 540 |
| KALWKIVDDK NDPRWKAVNV TTFCPSPVLG PPLFMPSPLS GLSMRVKDIW DVMHGGDVPE | 600 |
| ASVIRGTFVD VRDVAEVVVK TVANDLAVGD GEEKRRERLL LVAQDNVSPG QMAQVLREEV | 660 |
| GDNLRGVIRE ASAGKVEEVK KTRAAMKKFN SEPARKVLGR DWVMFRDSVV DSARFFVSFE | 720 |
| ETEAII | 726 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 68 | 279 | 9.5e-45 | 0.9904761904761905 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187538 | AR_SDR_e | 1.01e-55 | 368 | 699 | 1 | 301 | aldehyde reductase, extended (e) SDRs. This subgroup contains aldehyde reductase of the extended SDR-type and related proteins. Aldehyde reductase I (aka carbonyl reductase) is an NADP-binding SDR; it has an NADP-binding motif consensus that is slightly different from the canonical SDR form and lacks the Asn of the extended SDR active site tetrad. Aldehyde reductase I catalyzes the NADP-dependent reduction of ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate to ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
| 238859 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like | 2.50e-53 | 67 | 280 | 1 | 198 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like subgroup of SGNH-hydrolases. Rhamnogalacturan acetylesterase removes acetyl esters from rhamnogalacturonan substrates, and renders them susceptible to degradation by rhamnogalacturonases. Rhamnogalacturonans are highly branched regions in pectic polysaccharides, consisting of repeating -(1,2)-L-Rha-(1,4)-D-GalUA disaccharide units, with many rhamnose residues substituted by neutral oligosaccharides such as arabinans, galactans and arabinogalactans. Extracellular enzymes participating in the degradation of plant cell wall polymers, such as Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase, would typically be found in saprophytic and plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. |
| 187661 | FR_SDR_e | 2.81e-30 | 369 | 616 | 1 | 227 | flavonoid reductase (FR), extended (e) SDRs. This subgroup contains FRs of the extended SDR-type and related proteins. These FRs act in the NADP-dependent reduction of flavonoids, ketone-containing plant secondary metabolites; they have the characteristic active site triad of the SDRs (though not the upstream active site Asn) and a NADP-binding motif that is very similar to the typical extended SDR motif. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
| 187536 | AR_like_SDR_e | 8.90e-27 | 369 | 658 | 1 | 266 | aldehyde reductase, flavonoid reductase, and related proteins, extended (e) SDRs. This subgroup contains aldehyde reductase and flavonoid reductase of the extended SDR-type and related proteins. Proteins in this subgroup have a complete SDR-type active site tetrad and a close match to the canonical extended SDR NADP-binding motif. Aldehyde reductase I (aka carbonyl reductase) is an NADP-binding SDR; it catalyzes the NADP-dependent reduction of ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate to ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate. The related flavonoid reductases act in the NADP-dependent reduction of flavonoids, ketone-containing plant secondary metabolites. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
| 223528 | WcaG | 4.61e-24 | 368 | 699 | 2 | 290 | Nucleoside-diphosphate-sugar epimerase [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP67203.1|CE12 | 0.0 | 1 | 726 | 1 | 726 |
| CDP24616.1|CE12 | 0.0 | 1 | 726 | 1 | 726 |
| AEO61153.1|CE12 | 2.06e-109 | 47 | 299 | 12 | 260 |
| AEO64902.1|CE12 | 4.32e-105 | 43 | 299 | 8 | 260 |
| QPC78219.1|CE12 | 1.68e-86 | 68 | 300 | 22 | 255 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1DEO_A | 3.27e-64 | 68 | 280 | 2 | 212 | RHAMNOGALACTURONAN ACETYLESTERASE FROM ASPERGILLUS ACULEATUS AT 1.55 A RESOLUTION WITH SO4 IN THE ACTIVE SITE [Aspergillus aculeatus],1DEX_A RHAMNOGALACTURONAN ACETYLESTERASE FROM ASPERGILLUS ACULEATUS AT 1.9 A RESOLUTION [Aspergillus aculeatus],1K7C_A Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase with seven N-linked carbohydrate residues distributed at two N-glycosylation sites refined at 1.12 A resolution [Aspergillus aculeatus],1PP4_A The crystal structure of rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase in space group P3121 [Aspergillus aculeatus],1PP4_B The crystal structure of rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase in space group P3121 [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
| 3C1U_A | 1.72e-63 | 68 | 280 | 2 | 212 | Chain A, Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
| 5GMO_A | 1.87e-19 | 369 | 714 | 5 | 327 | Chain A, Protein induced by osmotic stress [Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054],5YW4_A Chain A, Protein induced by osmotic stress [Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054] |
| 5YWL_A | 1.87e-19 | 369 | 714 | 5 | 327 | Chain A, Protein induced by osmotic stress [Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054],5YWN_A Chain A, Protein induced by osmotic stress [Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054] |
| 1Y1P_A | 4.65e-15 | 369 | 581 | 14 | 220 | X-ray structure of aldehyde reductase with NADPH [Sporidiobolus salmonicolor],1Y1P_B X-ray structure of aldehyde reductase with NADPH [Sporidiobolus salmonicolor],1ZZE_A X-ray Structure of NADPH-dependent Carbonyl Reductase from Sporobolomyces salmonicolor [Sporidiobolus salmonicolor],1ZZE_B X-ray Structure of NADPH-dependent Carbonyl Reductase from Sporobolomyces salmonicolor [Sporidiobolus salmonicolor] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q00017|RHA1_ASPAC | 2.88e-63 | 68 | 280 | 19 | 229 | Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase OS=Aspergillus aculeatus OX=5053 GN=rha1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q5BAA2|RHA1_EMENI | 9.62e-56 | 68 | 280 | 19 | 224 | Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=AN2528 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9UT59|YKJ7_SCHPO | 3.16e-22 | 369 | 659 | 6 | 279 | Putative uncharacterized oxidoreductase C513.07 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPAC513.07 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|O94563|YGD4_SCHPO | 8.44e-21 | 369 | 620 | 5 | 250 | Putative uncharacterized oxidoreductase C1773.04 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPBC1773.04 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|O31528|RHGT2_BACSU | 9.48e-17 | 69 | 280 | 5 | 202 | Probable rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase YesY OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yesY PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
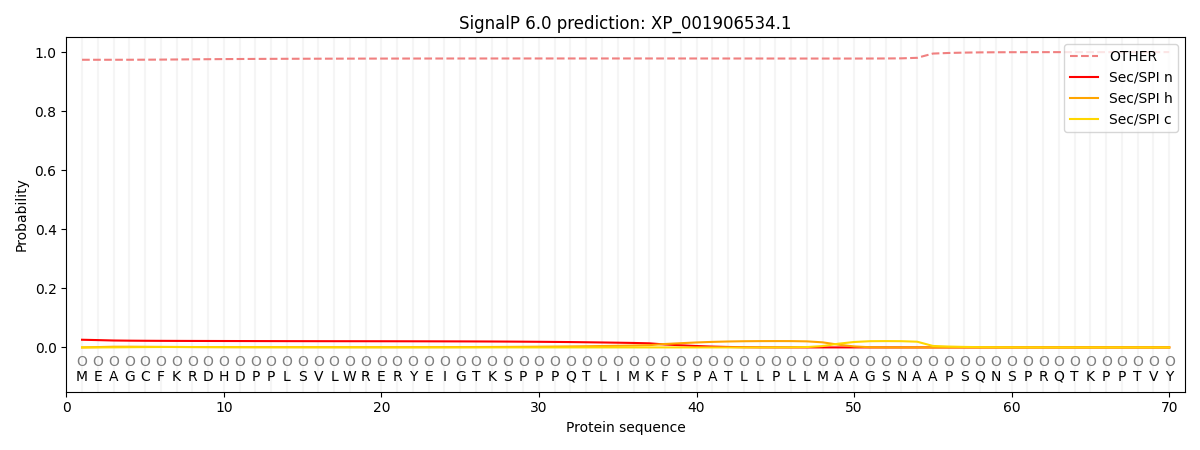
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.975628 | 0.024377 |
