You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: XP_001904222.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: XP_001904222.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Podospora anserina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Podosporaceae; Podospora; Podospora anserina | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | XP_001904222.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA7 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Chitinase [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:B2AEY3] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119357 | GH18_zymocin_alpha | 0.0 | 346 | 701 | 2 | 345 | Zymocin, alpha subunit. Zymocin is a heterotrimeric enzyme that inhibits yeast cell cycle progression. The zymocin alpha subunit has a chitinase activity that is essential for holoenzyme action from the cell exterior while the gamma subunit contains the intracellular toxin responsible for G1 phase cell cycle arrest. The zymocin alpha and beta subunits are thought to act from the cell's exterior by docking to the cell wall-associated chitin, thus mediating gamma-toxin translocation. The alpha subunit has an eight-stranded TIM barrel fold similar to that of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases such as hevamine, chitolectin, and chitobiase. |
| 214753 | Glyco_18 | 1.23e-56 | 346 | 700 | 2 | 333 | Glyco_18 domain. |
| 395573 | Glyco_hydro_18 | 4.65e-46 | 348 | 700 | 4 | 306 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 18. |
| 119351 | GH18_chitolectin_chitotriosidase | 1.61e-42 | 357 | 704 | 12 | 344 | This conserved domain family includes a large number of catalytically inactive chitinase-like lectins (chitolectins) including YKL-39, YKL-40 (HCGP39), YM1, oviductin, and AMCase (acidic mammalian chitinase), as well as catalytically active chitotriosidases. The conserved domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel fold belonging to the family 18 glycosyl hydrolases. The fold has a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The chitolectins lack a key active site glutamate (the proton donor required for hydrolytic activity) but retain highly conserved residues involved in oligosaccharide binding. Chitotriosidase is a chitinolytic enzyme expressed in maturing macrophages, which suggests that it plays a part in antimicrobial defense. Chitotriosidase hydrolyzes chitotriose, as well as colloidal chitin to yield chitobiose and is therefore considered an exochitinase. Chitotriosidase occurs in two major forms, the large form being converted to the small form by either RNA or post-translational processing. Although the small form, containing the chitinase domain alone, is sufficient for the chitinolytic activity, the additional C-terminal chitin-binding domain of the large form plays a role in processing colloidal chitin. The chitotriosidase gene is nonessential in humans, as about 35% of the population are heterozygous and 6% homozygous for an inactivated form of the gene. HCGP39 is a 39-kDa human cartilage glycoprotein thought to play a role in connective tissue remodeling and defense against pathogens. |
| 405536 | Hce2 | 3.49e-36 | 1182 | 1282 | 1 | 103 | Pathogen effector; putative necrosis-inducing factor. The domain corresponds to the mature part of the Ecp2 effector protein from the tomato pathogen Cladopsorium fulvum. Effectors are low molecular weight proteins that are secreted by bacteria, oomycetes and fungi to manipulate their hosts and adapt to their environment. Ecp2 is a 165 amino acid secreted protein that was originally identified as a virulence factor in C. fulvum, since disruption reduces virulence of the fungus on tomato plants. We have recently determined that Ecp2 is a member of a novel, widely distributed and highly diversified within the fungal kingdom multigene superfamily, which we have designated Hce2, for Homologs of C. fulvum Ecp2 effector. Although Ecp2 is present in most organisms as a small secreted protein, the mature part of this protein can be found fused to other protein domains, including the fungal Glycoside Hydrolase family 18, Glyco_hydro_18 pfam00704 and other, unknown, protein domains. The intrinsic function of Ecp2 remains unknown but it is postulated by that it is a necrosis-inducing factor in plants that serves pathogenicity on the host. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 1299 | 1 | 1299 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1299 | 52 | 1350 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1299 | 128 | 1430 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1296 | 123 | 1467 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1296 | 128 | 1484 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.14e-25 | 342 | 705 | 4 | 355 | Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 [Ostrinia furnacalis],5Y2B_A Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 in complex with HEPTA-N-ACETYLCHITOOCTAOSE (NAG)7 [Ostrinia furnacalis] |
|
| 1.38e-25 | 342 | 705 | 4 | 355 | Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 in complex with a piperidine-thienopyridine derivative [Ostrinia furnacalis],6JAW_A Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 in complex with a napthalimide derivative [Ostrinia furnacalis],6JAX_A Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 in complex with chitooctaose [(GlcN)8] [Ostrinia furnacalis],6JAY_A Crystal structure of Ostrinia furnacalis Group II chitinase catalytic domain 1 in complex with a dipyrido-pyrimidine derivative [Ostrinia furnacalis] |
|
| 4.08e-25 | 347 | 703 | 4 | 344 | High resoultion crystal structure of human chitinase in complex with allosamidin [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 4.15e-25 | 347 | 703 | 4 | 344 | Crystal structure of human chitinase in complex with glucoallosamidin B [Homo sapiens],1HKJ_A Crystal structure of human chitinase in complex with methylallosamidin [Homo sapiens],1HKM_A High resolution crystal structure of human chitinase in complex with demethylallosamidin [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 5.28e-25 | 345 | 704 | 3 | 351 | Chain A, Probable endochitinase [Caenorhabditis elegans] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.12e-81 | 221 | 699 | 272 | 710 | Killer toxin subunits alpha/beta OS=Kluyveromyces lactis (strain ATCC 8585 / CBS 2359 / DSM 70799 / NBRC 1267 / NRRL Y-1140 / WM37) OX=284590 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.64e-24 | 341 | 703 | 19 | 365 | Chitotriosidase-1 OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=CHIT1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.85e-24 | 347 | 741 | 25 | 409 | Acidic mammalian chitinase OS=Rattus norvegicus OX=10116 GN=Chia PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.61e-23 | 347 | 703 | 25 | 367 | Acidic mammalian chitinase OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=CHIA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.98e-23 | 342 | 704 | 51 | 402 | Probable endochitinase OS=Caenorhabditis elegans OX=6239 GN=cht-1 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
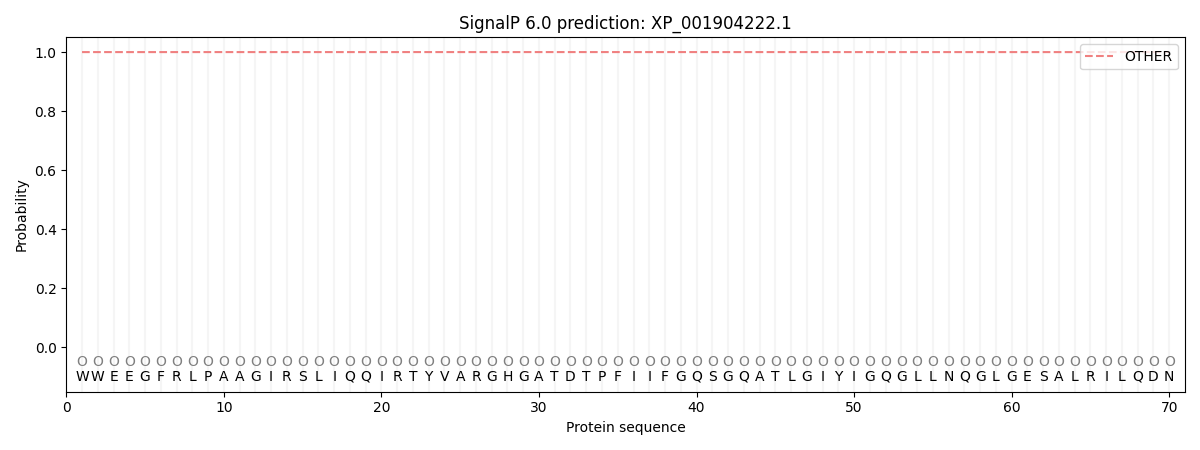
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000059 | 0.000000 |
