You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: TSTA_082450-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: TSTA_082450-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Talaromyces stipitatus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Trichocomaceae; Talaromyces; Talaromyces stipitatus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | TSTA_082450-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH36 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | multicopper oxidase, putative | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA1 | 41 | 325 | 7.9e-57 | 0.7597765363128491 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 132431 | ascorbOXfungal | 5.13e-123 | 24 | 352 | 8 | 334 | L-ascorbate oxidase, fungal type. This model describes a family of fungal ascorbate oxidases, within a larger family of multicopper oxidases that also includes plant ascorbate oxidases (TIGR03388), plant laccases and laccase-like proteins (TIGR03389), and related proteins. The member from Acremonium sp. HI-25 is characterized. |
| 259941 | CuRO_2_AAO_like_2 | 1.39e-68 | 149 | 314 | 1 | 161 | The second cupredoxin domain of plant Ascorbate oxidase homologs. This family includes plant laccases similar to ascorbate oxidase. Ascorbate oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of ascorbic acid to dehydroascorbic acid. It can detect levels of ascorbic acid and eliminate it. The biological function of ascorbate oxidase is still not clear. Ascorbate oxidase belongs to multicopper oxidase (MCO) family which couples oxidation of substrates with reduction of dioxygen to water. Although MCOs have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats that include one mononuclear and one trinuclear copper center. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 2 of 3-domain MCOs has lost the ability to bind copper. |
| 259916 | CuRO_1_AAO_like_2 | 4.53e-40 | 25 | 138 | 1 | 117 | The first cupredoxin domain of Ascorbate oxidase homologs. This family includes fungal proteins with similarity to ascorbate oxidase. Ascorbate oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of ascorbic acid to dehydroascorbic acid. It can detect levels of ascorbic acid and eliminate it. The biological function of ascorbate oxidase is still not clear. Ascorbate oxidase belongs to multicopper oxidase (MCO) family which couple oxidation of substrates with reduction of dioxygen to water. MCOs are capable of oxidizing a vast range of substrates, varying from aromatic compounds to inorganic compounds such as metals. Although the members of this family have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. |
| 274555 | ascorbase | 1.27e-31 | 40 | 317 | 17 | 300 | L-ascorbate oxidase, plant type. Members of this protein family are the copper-containing enzyme L-ascorbate oxidase (EC 1.10.3.3), also called ascorbase. This family is found in flowering plants, and shows greater sequence similarity to a family of laccases (EC 1.10.3.2) from plants than to other known ascorbate oxidases. |
| 177843 | PLN02191 | 1.25e-26 | 40 | 307 | 39 | 312 | L-ascorbate oxidase |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.72e-168 | 1 | 357 | 1 | 379 | |
| 6.02e-138 | 24 | 357 | 31 | 380 | |
| 1.65e-111 | 25 | 357 | 29 | 379 | |
| 1.48e-86 | 24 | 351 | 29 | 354 | |
| 1.81e-83 | 24 | 351 | 34 | 357 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.66e-16 | 23 | 347 | 2 | 346 | Crystal Structure of the Zea Mays laccase 3 [Zea mays],6KLI_A Crystal Structure of the Zea Mays laccase 3 complexed with sinapyl [Zea mays],6KLJ_A Crystal Structure of the Zea Mays laccase 3 complexed with coniferyl [Zea mays] |
|
| 1.89e-12 | 27 | 277 | 70 | 315 | Structure of the L499M mutant of the laccase from B.aclada [Botrytis aclada] |
|
| 1.89e-12 | 27 | 277 | 70 | 315 | Crystal structure of laccase from Botrytis aclada at 1.67 A resolution [Botrytis aclada],4X4K_A Structure of laccase from Botrytis aclada with full copper content [Botrytis aclada] |
|
| 4.17e-12 | 42 | 350 | 42 | 330 | Crystal structure of laccase from Lentinus sp. at 1.8 A resolution [Lentinus],3X1B_B Crystal structure of laccase from Lentinus sp. at 1.8 A resolution [Lentinus] |
|
| 1.71e-11 | 42 | 277 | 22 | 247 | Chain A, LACCASE 1 [Coprinopsis cinerea] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.13e-86 | 83 | 360 | 11 | 286 | Multicopper oxidase terE OS=Aspergillus terreus (strain NIH 2624 / FGSC A1156) OX=341663 GN=terE PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 5.02e-79 | 24 | 360 | 27 | 360 | Multicopper oxidase aurL2 OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=aurL2 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 8.35e-71 | 25 | 351 | 31 | 392 | Laccase-like multicopper oxidase 1 OS=Myceliophthora thermophila (strain ATCC 42464 / BCRC 31852 / DSM 1799) OX=573729 GN=LMCO1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.51e-22 | 48 | 338 | 54 | 349 | L-ascorbate oxidase OS=Nicotiana tabacum OX=4097 GN=AAO PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 3.59e-21 | 40 | 332 | 36 | 333 | L-ascorbate oxidase OS=Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis OX=51351 GN=AO PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
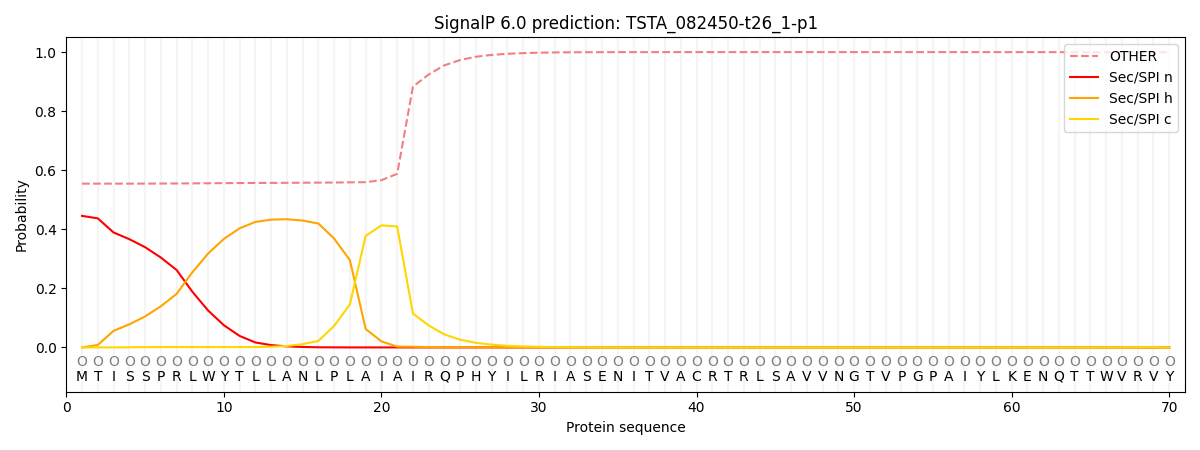
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.563870 | 0.436123 |
