You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: TSTA_056250-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: TSTA_056250-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
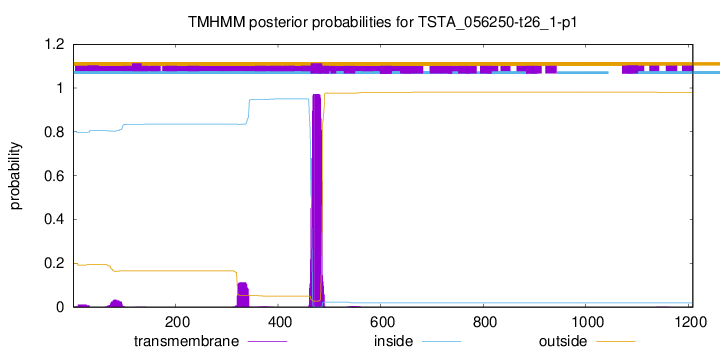
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Talaromyces stipitatus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Trichocomaceae; Talaromyces; Talaromyces stipitatus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | TSTA_056250-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | alpha-1,2-mannosyltransferase (Alg2), putative | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1146029; End:1149954 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKTSPRLNII IIHPDLGIGG AERLIIDVAL ALQNRGHQVT IYTSHCDKSH CFEEARDGTL | 60 |
| DIRVRGNTIF PPLLLGRFHL LMAVLRQLHL TISVLSEMGR TGKTQTKAGE KREESEEYKD | 120 |
| DIFIIDQLPA CVPVLKTWGR RFAQIRGGKQ RILFYCHFPD QLLARRNEGY IIVRLLKEAY | 180 |
| RYPLDWFEGW AMSASDKVVA NSNFTRGVVK RVFGSDRLGD VKIVYPCVDT KESAPTETEV | 240 |
| VKGELWGEKK ILLSINRFER KKGIDLAIRA YNGLSKEERI GTRLVIAGGY DNRVQENVQY | 300 |
| HKELNDLALR LGLQTATSKT VISALSIPDA VDVLFLLSVP SAFRDTLLHN SKLLLYTPVN | 360 |
| EHFGIVPVEA MHAGLPVLAS NTGGPLESVV ENETGWLRDT TQIEEWTSIM RNVLLDLTDQ | 420 |
| DLAKMAASGK KRVKDVFSLH ALEDKLEEEL RDMLESNRRP FMNLQYLLLA FLFSGVVGAV | 480 |
| MVALILRRVW QILEERDIGY TSQDKMPEVI DLLDSSPLEP SHLQPPPSTQ ARHSSVRFPS | 540 |
| PSNATTASAA AIPASSPNFL SDDFDSSLFT FDTPGRSAKK RKLTPQAERT ASLQPRVEAQ | 600 |
| PRAVAKSSTQ NVIHSDYSIF TFSDDIESPG LPHVNRANTG TPTAITKKTT VSTTSTTFSG | 660 |
| LSTTKVKAYK RNGEESDPIV FTSSAPEHTT AKERQQSRQN KLLDDSGTKS WPSVITIDDD | 720 |
| DYDEIQDWGD PFNVSPQNAL DKLLGDPRPS LKPAYSDRTA ALLASLRTQD STEKKLTTTS | 780 |
| KGKNSTTSFD DVDFDFGEDS LSDVPQRPTD IPKTKRKLKV DAEEKVAKAQ EREAAREQRK | 840 |
| REKEAEKERK RLEKEKKAKE KQLAADIAEV NKSKIHKKES IPEMIVDLAS TFEGTSVGNQ | 900 |
| VVEYLKNLSA EHTFFESSMP NIVKWRRKKR SNYNEDAARW EPCQPYIASE DHVLCMLSAQ | 960 |
| EFVDMVICEG DMQTLDGHVQ RLKGSYRDCK PIYLIEGLTT WMRRNQNSRN RAYQAEVLRQ | 1020 |
| INDVDDTPED TNAQGKQRGR KTKKAKKPED TPPVADDTIE DALLELQVTH NCLIYHTNAP | 1080 |
| GETAEWIKNF SEHISTIPYR HVQMGNYDGA AFCMETGQVK TGEDKVDTFV KMLQEINRVT | 1140 |
| APMAYGIVSQ YPSAVDLLHA MKKHGPTLLE NVRKSANKNG ALTDSRIGLA VSKRLYKVFM | 1200 |
| GLDETSADI | 1209 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.257:6 | 2.4.1.132:6 |
|---|
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 340834 | GT4_ALG2-like | 0.0 | 7 | 446 | 1 | 392 | alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 and similar proteins. This family is most closely related to the GT4 family of glycosyltransferases. ALG2, a 1,3-mannosyltransferase, in yeast catalyzes the mannosylation of Man(2)GlcNAc(2)-dolichol diphosphate and Man(1)GlcNAc(2)-dolichol diphosphate to form Man(3)GlcNAc(2)-dolichol diphosphate. A deficiency of this enzyme causes an abnormal accumulation of Man1GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol and Man2GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol, which is associated with a type of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG), designated CDG-Ii, in humans. |
| 410860 | XPF_nuclease_Mms4 | 3.30e-87 | 867 | 1100 | 1 | 220 | XPF-like nuclease domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae crossover junction endonuclease Mms4 and similar proteins. Budding yeast Mms4, also known as Eme1 in other organisms, is a putative transcriptional (co)activator that protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells from endogenous and environmental DNA damage. It interacts with MUS81 to form a DNA structure-specific endonuclease with substrate preference for branched DNA structures with a 5'-end at the branch nick. Typical substrates include 3'-flap structures, D-loops, replication forks with regressed leading strands and nicked Holliday junctions. The nuclease domain of Mms4 lacks the catalytic motif. |
| 340831 | GT4_PimA-like | 3.25e-42 | 8 | 451 | 1 | 366 | phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosyltransferase. This family is most closely related to the GT4 family of glycosyltransferases and named after PimA in Propionibacterium freudenreichii, which is involved in the biosynthesis of phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides (PIM) which are early precursors in the biosynthesis of lipomannans (LM) and lipoarabinomannans (LAM), and catalyzes the addition of a mannosyl residue from GDP-D-mannose (GDP-Man) to the position 2 of the carrier lipid phosphatidyl-myo-inositol (PI) to generate a phosphatidyl-myo-inositol bearing an alpha-1,2-linked mannose residue (PIM1). Glycosyltransferases catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. The acceptor molecule can be a lipid, a protein, a heterocyclic compound, or another carbohydrate residue. This group of glycosyltransferases is most closely related to the previously defined glycosyltransferase family 1 (GT1). The members of this family may transfer UDP, ADP, GDP, or CMP linked sugars. The diverse enzymatic activities among members of this family reflect a wide range of biological functions. The protein structure available for this family has the GTB topology, one of the two protein topologies observed for nucleotide-sugar-dependent glycosyltransferases. GTB proteins have distinct N- and C- terminal domains each containing a typical Rossmann fold. The two domains have high structural homology despite minimal sequence homology. The large cleft that separates the two domains includes the catalytic center and permits a high degree of flexibility. The members of this family are found mainly in certain bacteria and archaea. |
| 223515 | RfaB | 1.27e-35 | 6 | 457 | 2 | 381 | Glycosyltransferase involved in cell wall bisynthesis [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 395425 | Glycos_transf_1 | 1.66e-30 | 248 | 432 | 1 | 158 | Glycosyl transferases group 1. Mutations in this domain of PIGA lead to disease (Paroxysmal Nocturnal haemoglobinuria). Members of this family transfer activated sugars to a variety of substrates, including glycogen, Fructose-6-phosphate and lipopolysaccharides. Members of this family transfer UDP, ADP, GDP or CMP linked sugars. The eukaryotic glycogen synthases may be distant members of this family. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QGA14416.1|GT4 | 7.09e-298 | 1 | 490 | 1 | 488 |
| QKX58089.1|GT4 | 3.46e-255 | 1 | 487 | 1 | 493 |
| QMW45313.1|GT4 | 1.40e-216 | 1 | 489 | 1 | 480 |
| UDD61243.1|GT4 | 5.29e-216 | 1 | 489 | 38 | 517 |
| BAE63034.1|GT4 | 7.85e-216 | 1 | 489 | 1 | 480 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2ZIV_B | 3.32e-12 | 876 | 1196 | 15 | 335 | Crystal structure of the Mus81-Eme1 complex [Homo sapiens] |
| 2ZIU_B | 2.28e-09 | 876 | 1196 | 15 | 325 | Crystal structure of the Mus81-Eme1 complex [Homo sapiens],2ZIX_B Crystal structure of the Mus81-Eme1 complex [Homo sapiens] |
| 4P0P_B | 3.97e-09 | 878 | 1196 | 69 | 377 | Crystal structure of Human Mus81-Eme1 in complex with 5'-flap DNA, and Mg2+ [Homo sapiens],4P0Q_B Crystal structure of Human Mus81-Eme1 in complex with 5'-flap DNA [Homo sapiens],4P0R_B human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens],4P0R_D human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens],4P0S_B human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens],4P0S_D human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens],4P0S_F human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens],4P0S_H human Mus81-Eme1-3'flap DNA complex [Homo sapiens] |
| 2F9F_A | 6.86e-08 | 235 | 397 | 11 | 144 | Crystal Structure of the Putative Mannosyl Transferase (wbaZ-1)from Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Northeast Structural Genomics Target GR29A. [Archaeoglobus fulgidus DSM 4304] |
| 5D00_A | 7.79e-07 | 156 | 455 | 104 | 377 | Crystal structure of BshA from B. subtilis complexed with N-acetylglucosaminyl-malate and UMP [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168],5D00_B Crystal structure of BshA from B. subtilis complexed with N-acetylglucosaminyl-malate and UMP [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168],5D01_A Crystal structure of BshA from B. subtilis complexed with N-acetylglucosaminyl-malate [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168],5D01_B Crystal structure of BshA from B. subtilis complexed with N-acetylglucosaminyl-malate [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q8X0H8|ALG2_NEUCR | 1.05e-125 | 1 | 453 | 5 | 437 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase alg-2 OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=alg-2 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q6CWQ0|ALG2_KLULA | 2.80e-100 | 1 | 458 | 1 | 440 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 OS=Kluyveromyces lactis (strain ATCC 8585 / CBS 2359 / DSM 70799 / NBRC 1267 / NRRL Y-1140 / WM37) OX=284590 GN=ALG2 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q6BVA4|ALG2_DEBHA | 2.27e-97 | 8 | 459 | 11 | 444 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 OS=Debaryomyces hansenii (strain ATCC 36239 / CBS 767 / BCRC 21394 / JCM 1990 / NBRC 0083 / IGC 2968) OX=284592 GN=ALG2 PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|O94738|ALG2_RHIPU | 4.42e-97 | 3 | 447 | 2 | 417 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 OS=Rhizomucor pusillus OX=4840 GN=ALG2 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q96WW6|ALG2_SCHPO | 4.84e-93 | 2 | 456 | 13 | 429 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase alg2 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=alg2 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000064 | 0.000001 |