You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: TPX39680.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: TPX39680.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Synchytrium endobioticum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Chytridiomycota; Chytridiomycetes; ; Synchytriaceae; Synchytrium; Synchytrium endobioticum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | TPX39680.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE5 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | beta-glucuronidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2961; End:7411 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKYRPNRYVC ILLLSIASMV HTSQPQRLHV FDFTTPRPRP YRTNTISANY MGFSIEWNDM | 60 |
| QSLFTPTAQQ IVFQLFSNLQ SLSTKPLLIR VGGISEDEVW LVDSKFERNE KVFKFLIDAP | 120 |
| LLEGMTSLAS QLSIEYLIGL PTMHSMRNVK ATVEFAQALV DHGVINHTTG VELGNEPRNS | 180 |
| RISAADYARD YWIVMLEALY SSIPELQNLT FAGLSSYTPD EDIESHLDTI TKGLSSFQNN | 240 |
| QVKTMLTAHT YGTYGHVSIQ ELLNTPTPQE FDYMHKVGKY GETHDVILGE TNSVIGVGGG | 300 |
| VTAASNVFGS ALWALDFYAY AAWKGLGSAR LHGVMALENF TNIENDFHYS PFLINQDAET | 360 |
| AAKRPVNIRP LYYAMIAFTR ALSFVSAAHD IIPIMPTNKT APVTFIKVYG FSTAKGAKAS | 420 |
| FLIINKSNVL DMVSFNLPPN VHGEAVHIER LTAPSVSSTN GIAYAGQTFD GSVNGMPSGM | 480 |
| RVFEQVQVGP DGMYEIAVEA YSACVVLAGE GMELCGKDCS DNECIVSIHR QQEHGPVCDY | 540 |
| YSFITVERHL ASPRSVSISQ SISRRSRYYH LRTPQVMNPL TQLYARVRPI VPVAVLLLLL | 600 |
| ARYIGPGLYK FLRIYYHVSR LPGEISIGGF VRRGPAKGYR AFQEMHRKHR KKVVKIWPTT | 660 |
| ISVSDPKIVR ELLMVRDIPK ADMYQAFRFE FLPDHIFATS DRDFHKDIRR VLSPAFGIAY | 720 |
| LKSQETHILH AVDDLLAKWD GIIADTIDGP GLVNIWMDMH RVGTEVIGEI AFGTTFGTLR | 780 |
| NDSTAAALVE NIEQGFRVGA RMAFFPQALR KYPLIPIVKH SHQVSRNFIE MMTPVIYARR | 840 |
| NGTARKDILQ CLIDGKWKDG TPLSDLHITV SALIMMFAGS DTSSNTMAFT IIHLLKNPHV | 900 |
| LERVVAEVLS VPLPAGQKLF TSNDVKTMMP YLEACIKESM RLTPVAIAVV RQADQDMVLH | 960 |
| GTEDTYFVPK GTTIILSSET LHNDPDTWKD PEVYQPERFL DAAAENEAST FSNISGNYMP | 1020 |
| FSHGSRNCIG QHLALAEMRI VLANILKRYE LYDVDPSQSR EVSFQITLQL DSSSYIIGVQ | 1080 |
| KRDA | 1084 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.166:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH79 | 48 | 333 | 1.8e-24 | 0.6725274725274726 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 410684 | CYP67-like | 2.80e-77 | 652 | 1051 | 2 | 391 | cytochrome P450 family 67 and similar cytochrome P450s. This subfamily includes Uromyces viciae-fabae cytochrome P450 67 (CYP67), also called planta-induced rust protein 16, Cystobasidium minutum (Rhodotorula minuta) cytochrome P450rm, and other fungal cytochrome P450s. P450rm catalyzes the formation of isobutene and 4-hydroxylation of benzoate. The gene encoding CYP67 is a planta-induced gene that is expressed in haustoria and rust-infected leaves. The CYP67-like subfamily belongs to the large cytochrome P450 (P450, CYP) superfamily of heme-containing proteins that catalyze a variety of oxidative reactions of a large number of structurally different endogenous and exogenous compounds in organisms from all major domains of life. CYPs bind their diverse ligands in a buried, hydrophobic active site, which is accessed through a substrate access channel formed by two flexible helices and their connecting loop. |
| 410651 | cytochrome_P450 | 4.24e-74 | 653 | 1072 | 3 | 389 | cytochrome P450 (CYP) superfamily. Cytochrome P450 (P450, CYP) is a large superfamily of heme-containing proteins that catalyze a variety of oxidative reactions of a large number of structurally different endogenous and exogenous compounds in organisms from all major domains of life. CYPs with > 40% sequence identity are members of the same family. There are approximately 2250 CYP families: mammals, insects, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea have around 18, 208, 277, 805, 591, and 14 families, respectively. CYPs bind their diverse ligands in a buried, hydrophobic active site, which is accessed through a substrate access channel formed by two flexible helices and their connecting loop. Their monooxygenase activity relies on the reductive scission of molecular oxygen bound to the P450 heme iron, and the delivery of two electrons to the heme iron during the catalytic cycle. CYPs use a variety of redox partners, such as the eukaryotic diflavin enzyme NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase and the bacterial/mitochondrial NAD(P)H-ferredoxin reductase and ferredoxin partners. Some CYPs are naturally linked to their redox partners and others have evolved to bypass requirements for redox partners, and instead react directly with hydrogen peroxide or NAD(P)H to facilitate oxidative or reductive catalysis. |
| 395020 | p450 | 2.73e-73 | 634 | 1051 | 11 | 433 | Cytochrome P450. Cytochrome P450s are haem-thiolate proteins involved in the oxidative degradation of various compounds. They are particularly well known for their role in the degradation of environmental toxins and mutagens. They can be divided into 4 classes, according to the method by which electrons from NAD(P)H are delivered to the catalytic site. Sequence conservation is relatively low within the family - there are only 3 absolutely conserved residues - but their general topography and structural fold are highly conserved. The conserved core is composed of a coil termed the 'meander', a four-helix bundle, helices J and K, and two sets of beta-sheets. These constitute the haem-binding loop (with an absolutely conserved cysteine that serves as the 5th ligand for the haem iron), the proton-transfer groove and the absolutely conserved EXXR motif in helix K. While prokaryotic P450s are soluble proteins, most eukaryotic P450s are associated with microsomal membranes. their general enzymatic function is to catalyze regiospecific and stereospecific oxidation of non-activated hydrocarbons at physiological temperatures. |
| 410683 | CYP57A1-like | 8.66e-70 | 652 | 1058 | 2 | 408 | cytochrome P450 family 57, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 and similar cytochrome P450s. This family is composed of fungal cytochrome P450s including: Nectria haematococca cytochrome P450 57A1 (CYP57A1), also called pisatin demethylase, which detoxifies the phytoalexin pisatin; Penicillium aethiopicum P450 monooxygenase gsfF, also called griseofulvin synthesis protein F, which catalyzes the coupling of orcinol and phloroglucinol rings in griseophenone B to form desmethyl-dehydrogriseofulvin A during the biosynthesis of griseofulvin, a spirocyclic fungal natural product used to treat dermatophyte infections; and Penicillium aethiopicum P450 monooxygenase vrtE, also called viridicatumtoxin synthesis protein E, which catalyzes hydroxylation at C5 of the polyketide backbone during the biosynthesis of viridicatumtoxin, a tetracycline-like fungal meroterpenoid. The CYP57A1-like family belongs to the large cytochrome P450 (P450, CYP) superfamily of heme-containing proteins that catalyze a variety of oxidative reactions of a large number of structurally different endogenous and exogenous compounds in organisms from all major domains of life. CYPs bind their diverse ligands in a buried, hydrophobic active site, which is accessed through a substrate access channel formed by two flexible helices and their connecting loop. |
| 410677 | CYP24A1-like | 6.77e-67 | 649 | 1051 | 1 | 404 | cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A, polypeptide 1 and similar cytochrome P450s. This family is composed of vertebrate cytochrome P450 24A1 (CYP24A1) and similar proteins including several Drosophila proteins such as CYP315A1 (also called protein shadow) and CYP314A1 (also called ecdysone 20-monooxygenase), and vertebrate CYP11 and CYP27 subfamilies. Both CYP314A1 and CYP315A1, which has ecdysteroid C2-hydroxylase activity, are involved in the metabolism of insect hormones. CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 have roles in calcium homeostasis and metabolism, and the regulation of vitamin D. CYP24A1 catabolizes calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D), the physiologically active vitamin D hormone, by catalyzing its hydroxylation, while CYP27B1 is a calcidiol 1-monooxygenase that coverts 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 to calcitriol. The CYP24A1-like family belongs to the large cytochrome P450 (P450, CYP) superfamily of heme-containing proteins that catalyze a variety of oxidative reactions of a large number of structurally different endogenous and exogenous compounds in organisms from all major domains of life. CYPs bind their diverse ligands in a buried, hydrophobic active site, which is accessed through a substrate access channel formed by two flexible helices and their connecting loop. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UQC88515.1|GT1 | 2.52e-42 | 653 | 1082 | 432 | 820 |
| QKD56596.1|GH3 | 2.44e-34 | 653 | 1071 | 9 | 408 |
| QHN99607.1|GT1 | 5.37e-17 | 839 | 1051 | 274 | 477 |
| QHO55764.1|GT1 | 1.96e-16 | 875 | 1051 | 1 | 168 |
| QKD46448.1|GH36 | 2.76e-15 | 641 | 1050 | 62 | 478 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7MK8_A | 2.34e-33 | 637 | 1083 | 35 | 477 | Chain A, Isoform 2 of Cytochrome P450 3A7 [Homo sapiens],7MK8_B Chain B, Isoform 2 of Cytochrome P450 3A7 [Homo sapiens] |
| 5VCD_A | 2.73e-33 | 637 | 1068 | 35 | 459 | Crystal structure of the cysteine depleted CYP3A4 bound to glycerol [Homo sapiens],5VCE_A Crystal structure of the cysteine depleted CYP3A4 bound to ritonavir [Homo sapiens],5VCG_A Crystal structure of the cysteine depleted CYP3A4 bound to bromoergocryptine [Homo sapiens] |
| 5VEU_A | 1.54e-31 | 651 | 1076 | 45 | 461 | Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_B Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_C Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_D Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_E Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_F Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_G Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_H Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_I Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_J Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_K Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],5VEU_L Human Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],6MJM_A Substrate Free Cytochrome P450 3A5 (CYP3A5) [Homo sapiens],7SV2_A Chain A, Cytochrome P450 3A5 [Homo sapiens],7SV2_B Chain B, Cytochrome P450 3A5 [Homo sapiens],7SV2_C Chain C, Cytochrome P450 3A5 [Homo sapiens],7SV2_D Chain D, Cytochrome P450 3A5 [Homo sapiens] |
| 7LAD_A | 1.56e-31 | 651 | 1076 | 46 | 462 | Chain A, Cytochrome P450 3A5 [Homo sapiens] |
| 7KVK_A | 1.69e-31 | 637 | 1068 | 35 | 459 | Chain A, Cytochrome P450 3A4 [Homo sapiens],7KVK_B Chain B, Cytochrome P450 3A4 [Homo sapiens],7KVS_A Chain A, Cytochrome P450 3A4 [Homo sapiens],7KVS_B Chain B, Cytochrome P450 3A4 [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|A0A1L9WQP6|ACRD_ASPA1 | 1.91e-51 | 598 | 1082 | 24 | 500 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase acrD OS=Aspergillus aculeatus (strain ATCC 16872 / CBS 172.66 / WB 5094) OX=690307 GN=acrD PE=2 SV=1 |
| sp|W7MLD1|FUS8_GIBM7 | 1.29e-49 | 606 | 1082 | 45 | 513 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase FUS8 OS=Gibberella moniliformis (strain M3125 / FGSC 7600) OX=334819 GN=FUS8 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|S0EE84|FUS8_GIBF5 | 2.64e-48 | 604 | 1082 | 43 | 513 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase FUS8 OS=Gibberella fujikuroi (strain CBS 195.34 / IMI 58289 / NRRL A-6831) OX=1279085 GN=FUS8 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|A0A6J4BC30|LUC2_FUSSX | 5.93e-45 | 643 | 1082 | 87 | 509 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase LUC2 OS=Fusarium sp. OX=29916 GN=LUC2 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|A0A0D1DT62|CYP2_USTMA | 2.01e-42 | 639 | 1084 | 75 | 532 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase cayp2 OS=Ustilago maydis (strain 521 / FGSC 9021) OX=237631 GN=cyp2 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
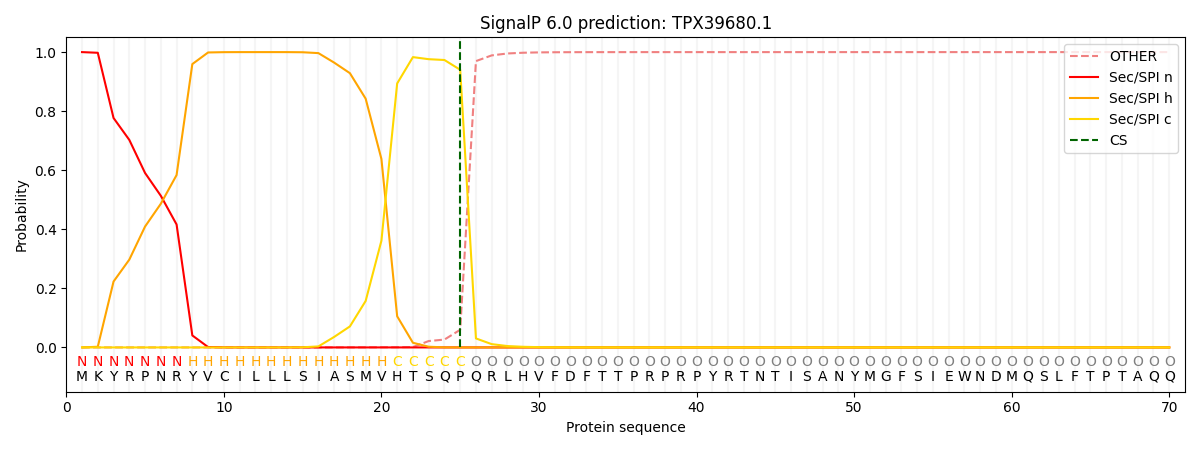
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000212 | 0.999758 | CS pos: 25-26. Pr: 0.9402 |
