You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: THC93458.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: THC93458.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
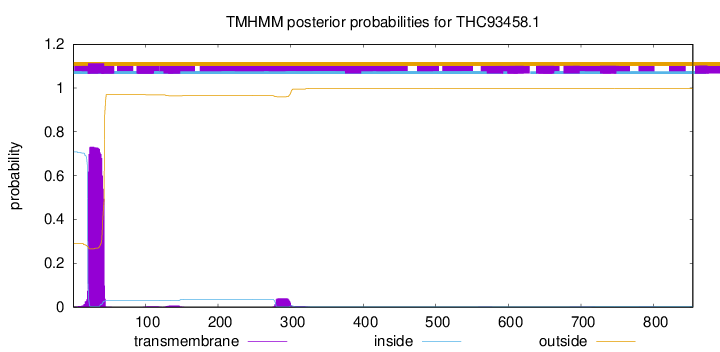
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus tanneri | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus tanneri | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | THC93458.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 1.1.3.16:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA3 | 306 | 846 | 1e-127 | 0.9894366197183099 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 235000 | PRK02106 | 3.30e-86 | 307 | 847 | 8 | 532 | choline dehydrogenase; Validated |
| 225186 | BetA | 7.92e-79 | 307 | 852 | 10 | 539 | Choline dehydrogenase or related flavoprotein [Lipid transport and metabolism, General function prediction only]. |
| 274888 | Rv0697 | 1.28e-50 | 308 | 842 | 4 | 483 | dehydrogenase, Rv0697 family. This model describes a set of dehydrogenases belonging to the glucose-methanol-choline oxidoreductase (GMC oxidoreductase) family. Members of the present family are restricted to Actinobacterial genome contexts containing also members of families TIGR03962 and TIGR03969 (the mycofactocin system), and are proposed to be uniform in function. |
| 187585 | carb_red_PTCR-like_SDR_c | 7.28e-49 | 23 | 235 | 3 | 200 | Porcine testicular carbonyl reductase (PTCR)-like, classical (c) SDRs. PTCR is a classical SDR which catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of ketones on steroids and prostaglandins. Unlike most SDRs, PTCR functions as a monomer. This subgroup also includes human carbonyl reductase 1 (CBR1) and CBR3. CBR1 is an NADPH-dependent SDR with broad substrate specificity and may be responsible for the in vivo reduction of quinones, prostaglandins, and other carbonyl-containing compounds. In addition it includes poppy NADPH-dependent salutaridine reductase which catalyzes the stereospecific reduction of salutaridine to 7(S)-salutaridinol in the biosynthesis of morphine, and Arabidopsis SDR1,a menthone reductase, which catalyzes the reduction of menthone to neomenthol, a compound with antimicrobial activity; SDR1 can also carry out neomenthol oxidation. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet), an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Classical SDRs are typically about 250 residues long, while extended SDRs are approximately 350 residues. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes are typically in the 15-30% range, but the enzymes share the Rossmann fold NAD-binding motif and characteristic NAD-binding and catalytic sequence patterns. These enzymes catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser (Ser-138, 15-PGDH numbering) and/or an Asn (Asn-107, 15-PGDH numbering) contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Extended SDRs have additional elements in the C-terminal region, and typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. Some atypical SDRs have lost catalytic activity and/or have an unusual NAD(P)-binding motif and missing or unusual active site residues. Reactions catalyzed within the SDR family include isomerization, decarboxylation, epimerization, C=N bond reduction, dehydratase activity, dehalogenation, Enoyl-CoA reduction, and carbonyl-alcohol oxidoreduction. |
| 187586 | carb_red_sniffer_like_SDR_c | 4.16e-43 | 23 | 259 | 1 | 225 | carbonyl reductase sniffer-like, classical (c) SDRs. Sniffer is an NADPH-dependent carbonyl reductase of the classical SDR family. Studies in Drosophila melanogaster implicate Sniffer in the prevention of neurodegeneration due to aging and oxidative-stress. This subgroup also includes Rhodococcus sp. AD45 IsoH, which is an NAD-dependent 1-hydroxy-2-glutathionyl-2-methyl-3-butene dehydrogenase involved in isoprene metabolism, Aspergillus nidulans StcE encoded by a gene which is part of a proposed sterigmatocystin biosynthesis gene cluster, Bacillus circulans SANK 72073 BtrF encoded by a gene found in the butirosin biosynthesis gene cluster, and Aspergillus parasiticus nor-1 involved in the biosynthesis of aflatoxins. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet), an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Classical SDRs are typically about 250 residues long, while extended SDRs are approximately 350 residues. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes are typically in the 15-30% range, but the enzymes share the Rossmann fold NAD-binding motif and characteristic NAD-binding and catalytic sequence patterns. These enzymes catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser (Ser-138, 15-PGDH numbering) and/or an Asn (Asn-107, 15-PGDH numbering) contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Extended SDRs have additional elements in the C-terminal region, and typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. Some atypical SDRs have lost catalytic activity and/or have an unusual NAD(P)-binding motif and missing or unusual active site residues. Reactions catalyzed within the SDR family include isomerization, decarboxylation, epimerization, C=N bond reduction, dehydratase activity, dehalogenation, Enoyl-CoA reduction, and carbonyl-alcohol oxidoreduction. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.63e-191 | 292 | 849 | 13 | 572 | |
| 4.21e-190 | 288 | 849 | 7 | 573 | |
| 8.15e-178 | 290 | 849 | 20 | 581 | |
| 2.46e-148 | 301 | 850 | 39 | 541 | |
| 2.90e-127 | 279 | 842 | 1 | 570 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.56e-46 | 307 | 842 | 43 | 594 | Crystal structure of pyranose dehydrogenase from Agaricus meleagris, wildtype [Leucoagaricus meleagris] |
|
| 5.39e-41 | 307 | 849 | 4 | 564 | Crystal structure of aryl-alcohol oxidase from Pleurotus eryngii in complex with p-anisic acid [Pleurotus eryngii] |
|
| 2.42e-40 | 307 | 849 | 5 | 565 | Crystal structure of aryl-alcohol-oxidase from Pleurotus eryingii [Pleurotus eryngii] |
|
| 1.14e-39 | 307 | 847 | 8 | 583 | Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE2_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE3_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE4_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE4_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE5_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE5_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE6_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE6_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE7_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],6ZE7_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],7AA2_A Chain A, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495],7AA2_B Chain B, FAD-dependent oxidoreductase [Thermochaetoides thermophila DSM 1495] |
|
| 7.94e-36 | 301 | 847 | 10 | 527 | Crystal structure of choline oxidase reveals insights into the catalytic mechanism [Arthrobacter globiformis],2JBV_B Crystal structure of choline oxidase reveals insights into the catalytic mechanism [Arthrobacter globiformis],4MJW_A Crystal Structure of Choline Oxidase in Complex with the Reaction Product Glycine Betaine [Arthrobacter globiformis],4MJW_B Crystal Structure of Choline Oxidase in Complex with the Reaction Product Glycine Betaine [Arthrobacter globiformis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.25e-54 | 307 | 847 | 39 | 592 | Pyranose dehydrogenase OS=Agaricus campestris OX=56157 GN=pdh1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.16e-53 | 307 | 847 | 43 | 597 | Pyranose dehydrogenase 3 OS=Leucoagaricus meleagris OX=201219 GN=pdh3 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.02e-52 | 301 | 843 | 37 | 593 | Pyranose dehydrogenase OS=Agaricus xanthodermus OX=83518 GN=pdh1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.15e-52 | 307 | 842 | 8 | 529 | Oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase OS=Paraburkholderia phymatum (strain DSM 17167 / CIP 108236 / LMG 21445 / STM815) OX=391038 GN=betA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.66e-51 | 302 | 823 | 2 | 511 | Oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase OS=Pseudomonas putida (strain ATCC 47054 / DSM 6125 / CFBP 8728 / NCIMB 11950 / KT2440) OX=160488 GN=betA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
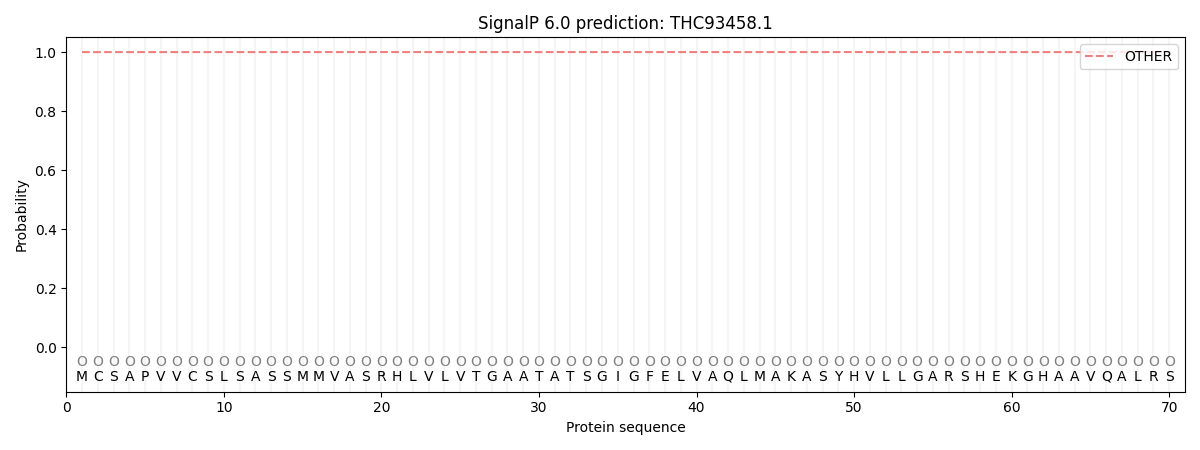
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000056 | 0.000000 |