You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SPRG_20212-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SPRG_20212-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Saprolegnia parasitica | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Saprolegniaceae; Saprolegnia; Saprolegnia parasitica | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SPRG_20212-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT57 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.34:28 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT48 | 790 | 1495 | 1.3e-247 | 0.9309878213802436 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396784 | Glucan_synthase | 1.30e-163 | 791 | 1474 | 3 | 712 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component. This family consists of various 1,3-beta-glucan synthase components including Gls1, Gls2 and Gls3 from yeast. 1,3-beta-glucan synthase EC:2.4.1.34 also known as callose synthase catalyzes the formation of a beta-1,3-glucan polymer that is a major component of the fungal cell wall. The reaction catalyzed is:- UDP-glucose + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N+1). |
| 405046 | FKS1_dom1 | 2.93e-37 | 99 | 203 | 5 | 106 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase subunit FKS1, domain-1. The FKS1_dom1 domain is likely to be the 'Class I' region just N-terminal to the first set of transmembrane helices that is involved in 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis itself. This family is found on proteins with family Glucan_synthase, pfam02364. |
| 395036 | Sugar_tr | 1.13e-09 | 1675 | 2101 | 2 | 436 | Sugar (and other) transporter. |
| 340917 | MFS_XylE_like | 5.69e-08 | 1740 | 2051 | 47 | 324 | D-xylose-proton symporter and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This subfamily includes bacterial transporters such as D-xylose-proton symporter (XylE or XylT), arabinose-proton symporter (AraE), galactose-proton symporter (GalP), major myo-inositol transporter IolT, glucose transport protein, putative metabolite transport proteins YfiG, YncC, and YwtG, and similar proteins. The symporters XylE, AraE, and GalP facilitate the uptake of D-xylose, arabinose, and galactose, respectively, across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell. IolT is involved in polyol metabolism and myo-inositol degradation into acetyl-CoA. The XylE-like subfamily belongs to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 340916 | MFS_GLUT6_8_Class3_like | 1.79e-06 | 1868 | 2103 | 176 | 413 | Glucose transporter (GLUT) types 6 and 8, Class 3 GLUTs, and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This subfamily is composed of glucose transporter type 6 (GLUT6), GLUT8, plant early dehydration-induced gene ERD6-like proteins, and similar insect proteins including facilitated trehalose transporter Tret1-1. GLUTs, also called Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporters (SLC2A), are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). Insect Tret1-1 is a low-capacity facilitative transporter for trehalose that mediates the transport of trehalose synthesized in the fat body and the incorporation of trehalose into other tissues that require a carbon source. GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. They belong to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 20 | 2172 | 96 | 2295 | |
| 0.0 | 21 | 2166 | 55 | 2270 | |
| 0.0 | 9 | 2176 | 36 | 2325 | |
| 0.0 | 9 | 2131 | 27 | 2239 | |
| 0.0 | 30 | 2170 | 76 | 2222 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.34e-217 | 21 | 1663 | 256 | 1915 | Callose synthase 7 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS7 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 3.26e-216 | 4 | 1663 | 229 | 1910 | Callose synthase 5 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS5 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 6.55e-210 | 21 | 1663 | 251 | 1875 | Callose synthase 9 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS9 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 1.19e-209 | 21 | 1663 | 263 | 1889 | Callose synthase 10 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS10 PE=2 SV=5 |
|
| 2.27e-209 | 5 | 1663 | 236 | 1903 | Putative callose synthase 6 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS6 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000094 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
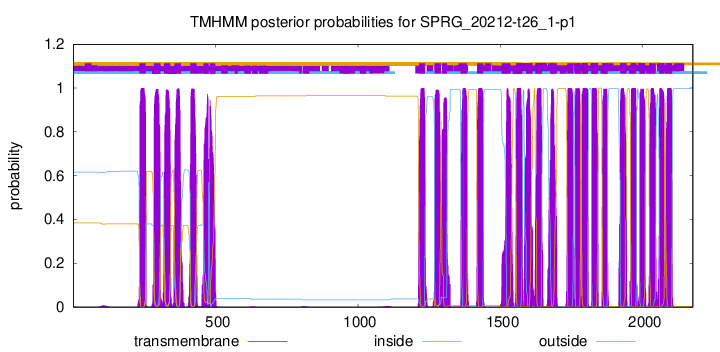
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 232 | 254 |
| 284 | 306 |
| 319 | 341 |
| 356 | 378 |
| 411 | 433 |
| 458 | 475 |
| 480 | 499 |
| 1214 | 1236 |
| 1269 | 1291 |
| 1295 | 1312 |
| 1361 | 1383 |
| 1418 | 1440 |
| 1505 | 1536 |
| 1556 | 1578 |
| 1591 | 1613 |
| 1623 | 1645 |
| 1676 | 1698 |
| 1735 | 1757 |
| 1762 | 1781 |
| 1785 | 1807 |
| 1820 | 1842 |
| 1857 | 1876 |
| 1921 | 1943 |
| 1958 | 1977 |
| 1989 | 2008 |
| 2023 | 2045 |
| 2058 | 2076 |
| 2081 | 2103 |
