You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SPRG_11439-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SPRG_11439-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Saprolegnia parasitica | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Saprolegniaceae; Saprolegnia; Saprolegnia parasitica | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SPRG_11439-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH5 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 172856; End:174652 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MLRVVFLLAA LATCCIADTD DRAALRARVK AWKESGPGQE AQARGLASGL EATDIDAELD | 60 |
| AFQETLDMVA TLNAQYPQAR FSEQNPFALM TQAAFEKWVR GNKPARNETW SRTSTEDATV | 120 |
| LPASTATTSI DWSTSGCMAP VRNQGVCGSC FAYAAVAAAE SAYCLVNNRQ LTLFSDQQAL | 180 |
| SCGPGNGCYG GWSDLSLGWM AANGMCTLDA YPNTNEWTMT TAACEKNCAP TKMPFTTVAS | 240 |
| TVGEVELEQA LNLQPVAVDI GSSSPVFKNY AGGVITGGCD TWFDHVLLGV GYGNDDAGLP | 300 |
| YFKMKNSWGT WWGENGYVRL QRGVGGVGTC GLARHAAYPV VFTPQFNLVT SSGHVLSEYY | 360 |
| SNLFAGPSRG PSPNEQWNYD SRTHHIKVNS NHECLDAYYD GSAFKVHTYT CDASNGNQRW | 420 |
| RIDSANHRIA HRTHPNLCLD VDPSQNNKVQ VWACGNPAPN QWLAVSEERV KLYSFNNRFL | 480 |
| SSNGEMIQFP PEGSYPYEWV VSNADNTWRA RSNTGDPQRC LDAYQPWNGG VVHLYACDAT | 540 |
| NANQKWRYDP STKQLRHLTH LGFCLDMRTA DGSQAHLWRC NAPTNDLQRF TYASQSFP | 598 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBM13 | 370 | 473 | 4.8e-17 | 0.5691489361702128 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 239068 | Peptidase_C1A | 2.47e-46 | 128 | 339 | 2 | 210 | Peptidase C1A subfamily (MEROPS database nomenclature); composed of cysteine peptidases (CPs) similar to papain, including the mammalian CPs (cathepsins B, C, F, H, L, K, O, S, V, X and W). Papain is an endopeptidase with specific substrate preferences, primarily for bulky hydrophobic or aromatic residues at the S2 subsite, a hydrophobic pocket in papain that accommodates the P2 sidechain of the substrate (the second residue away from the scissile bond). Most members of the papain subfamily are endopeptidases. Some exceptions to this rule can be explained by specific details of the catalytic domains like the occluding loop in cathepsin B which confers an additional carboxydipeptidyl activity and the mini-chain of cathepsin H resulting in an N-terminal exopeptidase activity. Papain-like CPs have different functions in various organisms. Plant CPs are used to mobilize storage proteins in seeds. Parasitic CPs act extracellularly to help invade tissues and cells, to hatch or to evade the host immune system. Mammalian CPs are primarily lysosomal enzymes with the exception of cathepsin W, which is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum. They are responsible for protein degradation in the lysosome. Papain-like CPs are synthesized as inactive proenzymes with N-terminal propeptide regions, which are removed upon activation. In addition to its inhibitory role, the propeptide is required for proper folding of the newly synthesized enzyme and its stabilization in denaturing pH conditions. Residues within the propeptide region also play a role in the transport of the proenzyme to lysosomes or acidified vesicles. Also included in this subfamily are proteins classified as non-peptidase homologs, which lack peptidase activity or have missing active site residues. |
| 395062 | Peptidase_C1 | 8.71e-42 | 128 | 340 | 3 | 212 | Papain family cysteine protease. |
| 214761 | Pept_C1 | 1.62e-32 | 128 | 339 | 3 | 175 | Papain family cysteine protease. |
| 240310 | PTZ00200 | 1.45e-26 | 130 | 332 | 238 | 436 | cysteine proteinase; Provisional |
| 239111 | Peptidase_C1A_CathepsinB | 3.99e-24 | 132 | 324 | 10 | 224 | Cathepsin B group; composed of cathepsin B and similar proteins, including tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen (TIN-Ag). Cathepsin B is a lysosomal papain-like cysteine peptidase which is expressed in all tissues and functions primarily as an exopeptidase through its carboxydipeptidyl activity. Together with other cathepsins, it is involved in the degradation of proteins, proenzyme activation, Ag processing, metabolism and apoptosis. Cathepsin B has been implicated in a number of human diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis and Alzheimer's disease. The unique carboxydipeptidyl activity of cathepsin B is attributed to the presence of an occluding loop in its active site which favors the binding of the C-termini of substrate proteins. Some members of this group do not possess the occluding loop. TIN-Ag is an extracellular matrix basement protein which was originally identified as a target Ag involved in anti-tubular basement membrane antibody-mediated interstitial nephritis. It plays a role in renal tubulogenesis and is defective in hereditary tubulointerstitial disorders. TIN-Ag is exclusively expressed in kidney tissues. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIG55540.1|CBM13 | 7.08e-280 | 10 | 598 | 12 | 599 |
| AIG56318.1|CBM13 | 3.54e-185 | 25 | 575 | 19 | 558 |
| AIG56282.1|CBM13 | 6.04e-182 | 17 | 594 | 20 | 580 |
| AIG55595.1|CBM13|GH17 | 3.49e-54 | 348 | 592 | 305 | 558 |
| AIG56230.1|CBM13|GH17 | 1.64e-51 | 315 | 592 | 221 | 506 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6MIS_A | 9.92e-36 | 129 | 341 | 4 | 214 | Native ananain in complex with E-64 [Ananas comosus],6MIS_B Native ananain in complex with E-64 [Ananas comosus],6OKJ_A Native ananain from Ananas comosus [Ananas comosus],6OKJ_B Native ananain from Ananas comosus [Ananas comosus] |
| 6YCC_A | 1.02e-35 | 129 | 341 | 4 | 214 | Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to the E64 inhibitor [Ananas comosus],6YCC_B Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to the E64 inhibitor [Ananas comosus],6YCD_A Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to the TLCK inhibitor [Ananas comosus],6YCD_B Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to the TLCK inhibitor [Ananas comosus] |
| 3P5W_A | 1.14e-35 | 130 | 342 | 5 | 218 | Actinidin from Actinidia arguta planch (Sarusashi) [Actinidia arguta] |
| 6Y6L_A | 2.49e-34 | 129 | 341 | 4 | 214 | Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus with a thiomethylated catalytic cysteine [Ananas comosus],6Y6L_B Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus with a thiomethylated catalytic cysteine [Ananas comosus],6YCB_A Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to with the E64 inhibitor [Ananas comosus],6YCB_B Structure the ananain protease from Ananas comosus covalently bound to with the E64 inhibitor [Ananas comosus] |
| 3P5U_A | 2.77e-34 | 130 | 342 | 5 | 218 | Actinidin from Actinidia arguta planch (Sarusashi) [Actinidia arguta],3P5V_A Actinidin from Actinidia arguta planch (Sarusashi) [Actinidia arguta],3P5X_A Actinidin from Actinidia arguta planch (Sarusashi) [Actinidia arguta] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q7XWK5|SAG39_ORYSJ | 6.08e-35 | 85 | 339 | 83 | 337 | Senescence-specific cysteine protease SAG39 OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=SAG39 PE=2 SV=2 |
| sp|A5HII1|ACTN_ACTDE | 7.45e-35 | 56 | 345 | 60 | 347 | Actinidain OS=Actinidia deliciosa OX=3627 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|A2XQE8|SAG39_ORYSI | 8.35e-35 | 85 | 339 | 83 | 337 | Senescence-specific cysteine protease SAG39 OS=Oryza sativa subsp. indica OX=39946 GN=OsI_14861 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P80884|ANAN_ANACO | 8.59e-34 | 62 | 341 | 61 | 336 | Ananain OS=Ananas comosus OX=4615 GN=AN1 PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|P43156|CYSP_HEMSP | 7.61e-33 | 52 | 340 | 50 | 345 | Thiol protease SEN102 OS=Hemerocallis sp. OX=29711 GN=SEN102 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
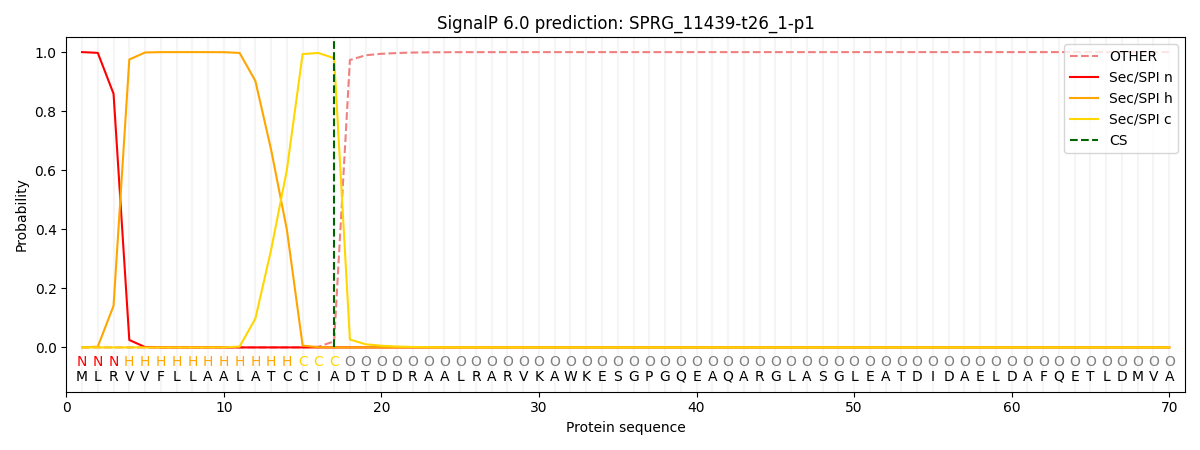
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000264 | 0.999692 | CS pos: 17-18. Pr: 0.9793 |
