You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SMR57718.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SMR57718.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Zymoseptoria tritici | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Dothideomycetes; ; Mycosphaerellaceae; Zymoseptoria; Zymoseptoria tritici | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SMR57718.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH62 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 1.14.99.55:4 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBM20 | 696 | 785 | 2.6e-19 | 0.9555555555555556 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99886 | CBM20_glucoamylase | 2.00e-31 | 688 | 793 | 1 | 105 | Glucoamylase (glucan1,4-alpha-glucosidase), C-terminal CBM20 (carbohydrate-binding module, family 20) domain. Glucoamylases are inverting, exo-acting starch hydrolases that hydrolyze starch and related polysaccharides by releasing the nonreducing end glucose. They are mainly active on alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds but also have some activity towards 1,6-glycosidic bonds occurring in natural oligosaccharides. The ability of glucoamylases to cleave 1-6-glycosidic binds is called "debranching activity" and is of importance in industrial applications, where complete degradation of starch to glucose is needed. Most glucoamylases are multidomain proteins containing an N-terminal catalytic domain, a C-terminal CBM20 domain, and a highly O-glycosylated linker region that connects the two. The CBM20 domain is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 395557 | CBM_20 | 1.54e-28 | 695 | 790 | 1 | 95 | Starch binding domain. |
| 99883 | CBM20_alpha_amylase | 8.19e-22 | 695 | 795 | 1 | 95 | Alpha-amylase, C-terminal CBM20 (carbohydrate-binding module, family 20) domain. This domain is found in several bacterial and fungal alpha-amylases including the maltopentaose-forming amylases (G5-amylases). Most alpha-amylases have, in addition to the C-terminal CBM20 domain, an N-terminal catalytic domain belonging to glycosyl hydrolase family 13, which hydrolyzes internal alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds in starch and related saccharides, yielding maltotriose and maltose. Two types of soluble substrates are used by alpha-amylases including long substrates (e.g. amylose) and short substrates (e.g. maltodextrins or maltooligosaccharides). The CBM20 domain is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 119437 | CBM20 | 2.20e-21 | 696 | 794 | 1 | 96 | The family 20 carbohydrate-binding module (CBM20), also known as the starch-binding domain, is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 215006 | CBM_2 | 8.28e-20 | 695 | 781 | 1 | 87 | Starch binding domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 809 | 1 | 809 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 809 | 1 | 809 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 809 | 1 | 809 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 809 | 1 | 809 | |
| 3.40e-33 | 683 | 795 | 27 | 139 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.86e-23 | 691 | 795 | 3 | 108 | GLUCOAMYLASE, GRANULAR STARCH-BINDING DOMAIN COMPLEX WITH CYCLODEXTRIN, NMR, MINIMIZED AVERAGE STRUCTURE [Aspergillus niger],1ACZ_A GLUCOAMYLASE, GRANULAR STARCH-BINDING DOMAIN COMPLEX WITH CYCLODEXTRIN, NMR, 5 STRUCTURES [Aspergillus niger],1KUL_A Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Aspergillus niger],1KUM_A Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Aspergillus niger],5GHL_A Crystal structure Analysis of the starch-binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger [Aspergillus niger],5GHL_B Crystal structure Analysis of the starch-binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger [Aspergillus niger],5GHL_C Crystal structure Analysis of the starch-binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger [Aspergillus niger],5GHL_D Crystal structure Analysis of the starch-binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger [Aspergillus niger] |
|
| 4.82e-18 | 698 | 795 | 518 | 616 | Structure of the catalytic domain of Aspergillus niger Glucoamylase [Aspergillus niger] |
|
| 2.56e-14 | 688 | 795 | 491 | 598 | Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei],2VN7_A Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei] |
|
| 2.34e-10 | 688 | 795 | 485 | 593 | Crystal structure of Penicillium oxalicum Glucoamylase [Penicillium oxalicum 114-2] |
|
| 2.47e-07 | 705 | 790 | 594 | 682 | FIVE-DOMAIN ALPHA-AMYLASE FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS, MALTOSE/ACARBOSE COMPLEX [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],1QHP_A Five-Domain Alpha-Amylase From Bacillus Stearothermophilus, Maltose Complex [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.20e-20 | 686 | 795 | 503 | 612 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=glaA PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 2.83e-18 | 691 | 795 | 534 | 639 | Glucoamylase I OS=Aspergillus kawachii OX=1069201 GN=gaI PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.14e-17 | 691 | 795 | 534 | 639 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus usamii OX=186680 GN=glaA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.62e-17 | 698 | 795 | 542 | 640 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus awamori OX=105351 GN=GLAA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.62e-17 | 698 | 795 | 542 | 640 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus niger OX=5061 GN=GLAA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
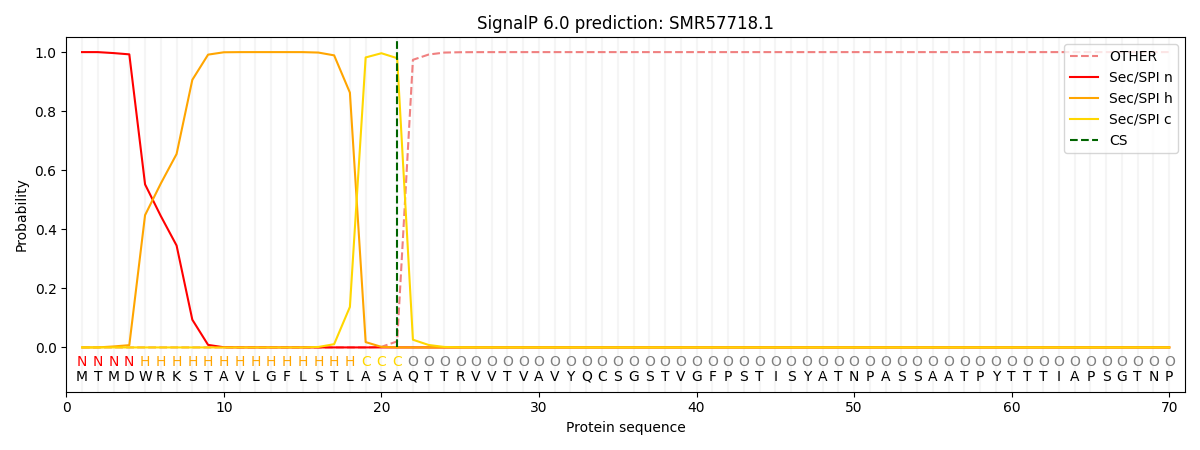
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000244 | 0.999738 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.9794 |
