You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SDRG_13038-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SDRG_13038-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Saprolegnia diclina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Saprolegniaceae; Saprolegnia; Saprolegnia diclina | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SDRG_13038-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT8 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 173807 | Peptidases_S8_BacillopeptidaseF-like | 1.70e-93 | 158 | 419 | 1 | 264 | Peptidase S8 family domain in BacillopeptidaseF-like proteins. Bacillus subtilis produces and secretes proteases and other types of exoenzymes at the end of the exponential phase of growth. The ones that make up this group is known as bacillopeptidase F, encoded by bpr, a serine protease with high esterolytic activity which is inhibited by PMSF. Like other members of the peptidases S8 family these have a Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. The stability of these enzymes may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. |
| 173800 | Peptidases_S8_subtilisin_Vpr-like | 8.95e-43 | 158 | 431 | 1 | 282 | Peptidase S8 family domain in Vpr-like proteins. The maturation of the peptide antibiotic (lantibiotic) subtilin in Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 includes posttranslational modifications of the propeptide and proteolytic cleavage of the leader peptide. Vpr was identified as one of the proteases, along with WprA, that are capable of processing subtilin. Asp, Ser, His triadPeptidases S8 or Subtilases are a serine endo- and exo-peptidase clan. They have an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. The stability of subtilases may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. Some members of this clan contain disulfide bonds. These enzymes can be intra- and extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures and pH values. |
| 173803 | Peptidases_S8_Subtilisin_subset | 4.26e-42 | 160 | 417 | 1 | 229 | Peptidase S8 family domain in Subtilisin proteins. This group is composed of many different subtilisins: Pro-TK-subtilisin, subtilisin Carlsberg, serine protease Pb92 subtilisin, and BPN subtilisins just to name a few. Pro-TK-subtilisin is a serine protease from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis and consists of a signal peptide, a propeptide, and a mature domain. TK-subtilisin is matured from pro-TK-subtilisin upon autoprocessing and degradation of the propeptide. Unlike other subtilisins though, the folding of the unprocessed form of pro-TK-subtilisin is induced by Ca2+ binding which is almost completed prior to autoprocessing. Ca2+ is required for activity unlike the bacterial subtilisins. The propeptide is not required for folding of the mature domain unlike the bacterial subtilases because of the stability produced from Ca2+ binding. Subtilisin Carlsberg is extremely similar in structure to subtilisin BPN'/Novo thought it has a 30% difference in amino acid sequence. The substrate binding regions are also similar and 2 possible Ca2+ binding sites have been identified recently. Subtilisin Carlsberg possesses the highest commercial importance as a proteolytic additive for detergents. Serine protease Pb92, the serine protease from the alkalophilic Bacillus strain PB92, also contains two calcium ions and the overall folding of the polypeptide chain closely resembles that of the subtilisins. Members of the peptidases S8 and S35 clan include endopeptidases, exopeptidases and also a tripeptidyl-peptidase. The S8 family has an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. The S53 family contains a catalytic triad Glu/Asp/Ser. The stability of these enzymes may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. Some members of this clan contain disulfide bonds. These enzymes can be intra- and extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures and pH values. |
| 395035 | Peptidase_S8 | 3.14e-40 | 158 | 419 | 1 | 273 | Subtilase family. Subtilases are a family of serine proteases. They appear to have independently and convergently evolved an Asp/Ser/His catalytic triad, like that found in the trypsin serine proteases (see pfam00089). Structure is an alpha/beta fold containing a 7-stranded parallel beta sheet, order 2314567. |
| 173790 | Peptidases_S8_PCSK9_ProteinaseK_like | 3.36e-40 | 158 | 418 | 24 | 253 | Peptidase S8 family domain in ProteinaseK-like proteins. The peptidase S8 or Subtilase clan of proteases have a Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad that is not homologous to trypsin. This CD contains several members of this clan including: PCSK9 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9), Proteinase_K, Proteinase_T, and other subtilisin-like serine proteases. PCSK9 posttranslationally regulates hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLRs) by binding to LDLRs on the cell surface, leading to their degradation. The binding site of PCSK9 has been localized to the epidermal growth factor-like repeat A (EGF-A) domain of the LDLR. Characterized Proteinases K are secreted endopeptidases with a high degree of sequence conservation. Proteinases K are not substrate-specific and function in a wide variety of species in different pathways. It can hydrolyze keratin and other proteins with subtilisin-like specificity. The number of calcium-binding motifs found in these differ. Proteinase T is a novel proteinase from the fungus Tritirachium album Limber. The amino acid sequence of proteinase T as deduced from the nucleotide sequence is about 56% identical to that of proteinase K. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 748 | 1 | 745 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 748 | 1 | 748 | |
| 4.89e-301 | 1 | 748 | 1 | 751 | |
| 2.90e-299 | 9 | 748 | 8 | 748 | |
| 6.36e-83 | 493 | 748 | 441 | 691 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.02e-24 | 59 | 419 | 53 | 393 | Chain A, Subtilisin-like serine protease [Thermococcus kodakarensis],3AFG_B Chain B, Subtilisin-like serine protease [Thermococcus kodakarensis] |
|
| 1.26e-20 | 58 | 401 | 3 | 340 | Crystal structure of Pro-F17H/S324A [Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1] |
|
| 1.02e-19 | 158 | 399 | 21 | 269 | Crystal Structure of alkaline serine protease KP-43 from Bacillus sp. KSM-KP43 (1.30 angstrom, 100 K) [Bacillus sp. KSM-KP43],1WME_A Crystal Structure of alkaline serine protease KP-43 from Bacillus sp. KSM-KP43 (1.50 angstrom, 293 K) [Bacillus sp. KSM-KP43] |
|
| 1.30e-19 | 58 | 401 | 3 | 340 | Chain A, Tk-subtilisin [Thermococcus kodakarensis],2ZWP_B Chain B, Tk-subtilisin [Thermococcus kodakarensis] |
|
| 1.35e-19 | 139 | 401 | 16 | 271 | Chain A, Tk-subtilisin [Thermococcus kodakarensis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.78e-38 | 11 | 419 | 46 | 486 | Bacillopeptidase F OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=bpr PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 2.69e-23 | 59 | 419 | 76 | 416 | Subtilisin-like serine protease OS=Thermococcus kodakarensis (strain ATCC BAA-918 / JCM 12380 / KOD1) OX=69014 GN=TK1689 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.72e-19 | 58 | 401 | 27 | 364 | Tk-subtilisin OS=Thermococcus kodakarensis (strain ATCC BAA-918 / JCM 12380 / KOD1) OX=69014 GN=TK1675 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 7.31e-19 | 38 | 418 | 23 | 358 | Subtilisin Carlsberg OS=Bacillus licheniformis OX=1402 GN=subC PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 1.98e-18 | 52 | 396 | 30 | 371 | Subtilisin OS=Bacillus sp. (strain TA39) OX=29336 GN=sub1 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
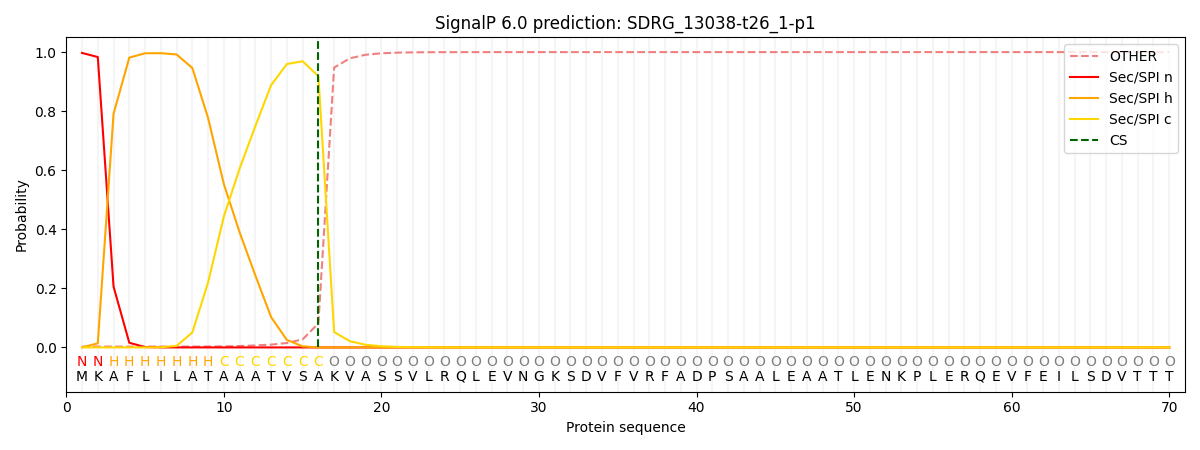
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.005859 | 0.994116 | CS pos: 16-17. Pr: 0.9184 |
