You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SAPIO_CDS9159-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SAPIO_CDS9159-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Microascaceae; Scedosporium; Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SAPIO_CDS9159-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT76 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1555181; End:1559172 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MDLKEEPQGS HNDSIREESE GTSSIDPALE ASIRKKLDMR LMPILTLVYL FAFIDRSNAG | 60 |
| NARVLGMGED LKLDGYRFNI ALSAFYVPYI LFEVPANVMC KIAGPKIWIP TLAILFGLVV | 120 |
| TCMSTLKSYE GFIVARVFLG FAEAGIMPGI SYTLACFYRR RELVTRVGLY ASVASLSGAF | 180 |
| GGLLATAFTK IPSWGIIHTW RNIFFFEGII SIILGIVAFF ILPSSPATAS FLTPEECKVA | 240 |
| VSRIADDLKT EQIETIKKEY FKRAIWNPNT ILLAVAMLCS LTSMNSMALF VPSILNAMGY | 300 |
| SGIHSQLLSV PPYAWATIVC ISVSTLSDRT CKRGKWILTV MPFTVAGFIV LLTPAKVAVH | 360 |
| YFALFLCLTG VFTASPMLVA WSIDNSAGHL TRAIVSGFSP ESGSAVPATS TFSPAPSHFN | 420 |
| SHHFLASAFD SFDDQRRLIA LCLTMMFSKQ IITAQTIHST TTERHRSQLP VMAPHLQRHA | 480 |
| NLNQPGPRRF YFSSLRRHRR RIVAVVIVVA IYYFFRFTPA PPRSIANSNG GRPTRTTPDR | 540 |
| DLDPQPHFIY RSSFRMNPNS AYEADVDAAL VSLEHRVTRG EVDDGQNVSQ KRPRKLWQIL | 600 |
| LGPAERGPDS WAFEEKNRAW EYTVVRDEWA NSFVNDTFGA IPGLVDLYKS YPYDVLRADL | 660 |
| LRYLILWFYG GYYADTDINP ARAIDSCPPL APVLPTNQDI HNANISLVIG IEIDEPWASA | 720 |
| KLMREWHWIR TYGFVQYNLY APQRFSPLLR RAIVRVLAHT KRHKDASWLT GPIYNEKTIL | 780 |
| EITGPGVFTD AVLDVLSETL PITHPLVQAS VAADAEVGDL AVPVGAESKR ERVTWAPFHR | 840 |
| LREPLWIDAT EAAAGKSMGG LGVLPISVWG NGQRHSGSES FRSPHACINH RFKGTWKKGW | 900 |
| WQRWFGKQNR | 910 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 340885 | MFS_FEN2_like | 7.70e-102 | 36 | 397 | 1 | 362 | Pantothenate transporter FEN2 and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This family is composed of Saccharomyces cerevisiae pantothenate transporter FEN2 (or fenpropimorph resistance protein 2) and similar proteins from fungi and bacteria including fungal vitamin H transporter, allantoate permease, and high-affinity nicotinic acid transporter, as well as Pseudomonas putida phthalate transporter and nicotinate degradation protein T (nicT). These proteins are involved in the uptake into the cell of specific substrates such as pathothenate, biotin, allantoate, and nicotinic acid, among others. The FEN2-like family belongs to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 340877 | MFS_ExuT_GudP_like | 9.67e-40 | 40 | 383 | 3 | 295 | Hexuronate transporter, Glucarate transporter, and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This family is composed of predominantly bacterial transporters for hexuronate (ExuT), glucarate (GudP), galactarate (GarP), and galactonate (DgoT). They mediate the uptake of these compounds into the cell. They belong to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 369468 | MFS_1 | 1.26e-31 | 45 | 398 | 1 | 333 | Major Facilitator Superfamily. |
| 349949 | MFS | 2.73e-20 | 45 | 398 | 1 | 333 | Major Facilitator Superfamily. The Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) is a large and diverse group of secondary transporters that includes uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. MFS proteins facilitate the transport across cytoplasmic or internal membranes of a variety of substrates including ions, sugar phosphates, drugs, neurotransmitters, nucleosides, amino acids, and peptides. They do so using the electrochemical potential of the transported substrates. Uniporters transport a single substrate, while symporters and antiporters transport two substrates in the same or in opposite directions, respectively, across membranes. MFS proteins are typically 400 to 600 amino acids in length, and the majority contain 12 transmembrane alpha helices (TMs) connected by hydrophilic loops. The N- and C-terminal halves of these proteins display weak similarity and may be the result of a gene duplication/fusion event. Based on kinetic studies and the structures of a few bacterial superfamily members, GlpT (glycerol-3-phosphate transporter), LacY (lactose permease), and EmrD (multidrug transporter), MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. Bacterial members function primarily for nutrient uptake, and as drug-efflux pumps to confer antibiotic resistance. Some MFS proteins have medical significance in humans such as the glucose transporter Glut4, which is impaired in type II diabetes, and glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT), which causes glycogen storage disease when mutated. |
| 225180 | UhpC | 2.21e-14 | 35 | 276 | 24 | 260 | Sugar phosphate permease [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCS21634.1|GT32 | 2.39e-142 | 538 | 906 | 49 | 414 |
| CAP98643.1|GT32 | 4.94e-137 | 519 | 906 | 37 | 421 |
| BCR86108.1|GT32 | 6.29e-137 | 533 | 906 | 54 | 418 |
| QMW37982.1|GT32 | 1.05e-136 | 535 | 906 | 48 | 413 |
| UCK58385.1|GT32 | 1.05e-136 | 535 | 906 | 48 | 413 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q9P6J0|YHDC_SCHPO | 5.51e-59 | 19 | 397 | 19 | 401 | Uncharacterized transporter C1683.12 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPBC1683.12 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|A0A2Z4HQ22|EFUF_HORCR | 3.12e-57 | 26 | 398 | 36 | 410 | MFS-type transporter efuF OS=Hormonema carpetanum OX=284138 GN=efuF PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9US37|YFZ4_SCHPO | 2.49e-55 | 25 | 394 | 45 | 416 | Uncharacterized transporter C1039.04 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPAC1039.04 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9US44|YIZG_SCHPO | 2.87e-55 | 32 | 393 | 50 | 412 | Uncharacterized transporter C1002.16c OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPAC1002.16c PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|A0A0A2IBP6|CNSO_PENEN | 8.50e-53 | 28 | 397 | 47 | 428 | MFS-type transporter cnsO OS=Penicillium expansum OX=27334 GN=cnsO PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999983 | 0.000019 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
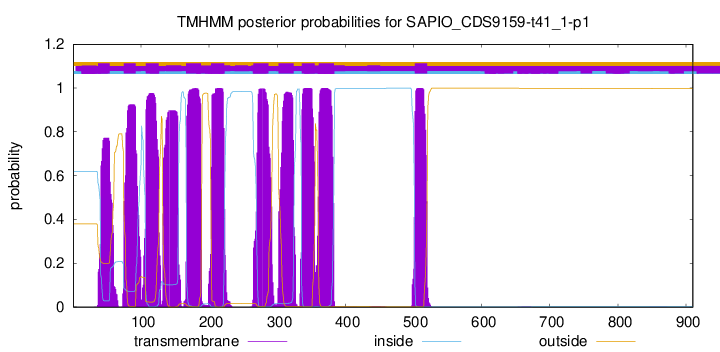
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 37 | 54 |
| 75 | 92 |
| 107 | 126 |
| 166 | 188 |
| 203 | 222 |
| 265 | 287 |
| 302 | 324 |
| 336 | 355 |
| 361 | 383 |
| 502 | 520 |
