You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SAPIO_CDS6902-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SAPIO_CDS6902-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Microascaceae; Scedosporium; Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SAPIO_CDS6902-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH5 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA7 | 126 | 307 | 1e-43 | 0.3799126637554585 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 270622 | PKc | 5.71e-43 | 857 | 1142 | 3 | 215 | Catalytic domain of Protein Kinases. PKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine or tyrosine residues on protein substrates. PKs make up a large family of serine/threonine kinases (STKs), protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs), and dual-specificity PKs that phosphorylate both serine/threonine and tyrosine residues of target proteins. Majority of protein phosphorylation occurs on serine residues while only 1% occurs on tyrosine residues. Protein phosphorylation is a mechanism by which a wide variety of cellular proteins, such as enzymes and membrane channels, are reversibly regulated in response to certain stimuli. PKs often function as components of signal transduction pathways in which one kinase activates a second kinase, which in turn, may act on other kinases; this sequential action transmits a signal from the cell surface to target proteins, which results in cellular responses. The PK family is one of the largest known protein families with more than 100 homologous yeast enzymes and more than 500 human proteins. A fraction of PK family members are pseudokinases that lack crucial residues for catalytic activity. The mutiplicity of kinases allows for specific regulation according to substrate, tissue distribution, and cellular localization. PKs regulate many cellular processes including proliferation, division, differentiation, motility, survival, metabolism, cell-cycle progression, cytoskeletal rearrangement, immunity, and neuronal functions. Many kinases are implicated in the development of various human diseases including different types of cancer. The PK family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and actin-fragmin kinase. |
| 214567 | S_TKc | 2.93e-37 | 849 | 1140 | 1 | 250 | Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain. Phosphotransferases. Serine or threonine-specific kinase subfamily. |
| 270687 | STKc_CAMK | 1.14e-29 | 848 | 1140 | 1 | 255 | The catalytic domain of CAMK family Serine/Threonine Kinases. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CaMKs are multifunctional calcium and calmodulin (CaM) stimulated STKs involved in cell cycle regulation. There are several types of CaMKs including CaMKI, CaMKII, and CaMKIV. CaMKI proteins are monomeric and they play pivotal roles in the nervous system, including long-term potentiation, dendritic arborization, neurite outgrowth, and the formation of spines, synapses, and axons. CaMKII is a signaling molecule that translates upstream calcium and reactive oxygen species (ROS) signals into downstream responses that play important roles in synaptic function and cardiovascular physiology. CAMKIV is implicated in regulating several transcription factors like CREB, MEF2, and retinoid orphan receptors, as well as in T-cell development and signaling. The CAMK family also consists of other related kinases including the Phosphorylase kinase Gamma subunit (PhKG), the C-terminal kinase domains of Ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) and Mitogen and stress-activated kinase (MSK), Doublecortin-like kinase (DCKL), and the MAPK-activated protein kinases MK2, MK3, and MK5, among others. The CAMK family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
| 223589 | SPS1 | 1.53e-24 | 848 | 1141 | 1 | 275 | Serine/threonine protein kinase [Signal transduction mechanisms]. |
| 270855 | STKc_Nek | 3.40e-23 | 848 | 1141 | 1 | 255 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Never In Mitosis gene A (NIMA)-related kinase. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The Nek family is composed of 11 different mammalian members (Nek1-11) with similarity to the catalytic domain of Aspergillus nidulans NIMA kinase, the founding member of the Nek family, which was identified in a screen for cell cycle mutants that were prevented from entering mitosis. Neks contain a conserved N-terminal catalytic domain and a more divergent C-terminal regulatory region of various sizes and structures. They are involved in the regulation of downstream processes following the activation of Cdc2, and many of their functions are cell cycle-related. They play critical roles in microtubule dynamics during ciliogenesis and mitosis. The Nek family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.80e-61 | 16 | 558 | 491 | 1052 | |
| 2.80e-61 | 16 | 558 | 491 | 1052 | |
| 2.56e-18 | 576 | 768 | 470 | 645 | |
| 1.23e-17 | 124 | 557 | 72 | 497 | |
| 1.23e-17 | 124 | 557 | 72 | 497 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.15e-180 | 25 | 559 | 28 | 562 | Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO615 at pH 7.5 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464],6F73_A Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO615 at pH 5.0 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464],6F73_B Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO615 at pH 5.0 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464] |
|
| 7.08e-54 | 7 | 563 | 12 | 590 | Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO713 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464],6F74_B Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO713 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464],6F74_C Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO713 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464],6F74_D Crystal structure of VAO-type flavoprotein MtVAO713 from Myceliophthora thermophila C1 [Thermothelomyces thermophilus ATCC 42464] |
|
| 2.52e-23 | 127 | 549 | 52 | 453 | The crystal structure of EncM H138T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYE_B The crystal structure of EncM H138T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus] |
|
| 4.50e-23 | 127 | 549 | 52 | 453 | The crystal structure of EncM V135T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYG_B The crystal structure of EncM V135T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYG_C The crystal structure of EncM V135T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYG_D The crystal structure of EncM V135T mutant [Streptomyces maritimus] |
|
| 6.01e-23 | 127 | 549 | 52 | 453 | The crystal structure of EncM T139V mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYD_B The crystal structure of EncM T139V mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYD_C The crystal structure of EncM T139V mutant [Streptomyces maritimus],6FYD_D The crystal structure of EncM T139V mutant [Streptomyces maritimus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.11e-179 | 25 | 559 | 28 | 562 | VAO-type flavoprotein oxidase VAO615 OS=Myceliophthora thermophila (strain ATCC 42464 / BCRC 31852 / DSM 1799) OX=573729 GN=MYCTH_2305637 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.84e-166 | 7 | 558 | 9 | 562 | Bifunctional decalin synthase calF OS=Penicillium decumbens OX=69771 GN=calF PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.44e-154 | 7 | 558 | 12 | 573 | FAD-linked oxidoreductase orf1 OS=Neocamarosporium betae OX=1979465 GN=orf1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.55e-146 | 19 | 559 | 21 | 551 | FAD-linked oxidoreductase ZEB1 OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=ZEB1 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 3.88e-127 | 22 | 557 | 26 | 554 | FAD-linked oxidoreductase patO OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=patO PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
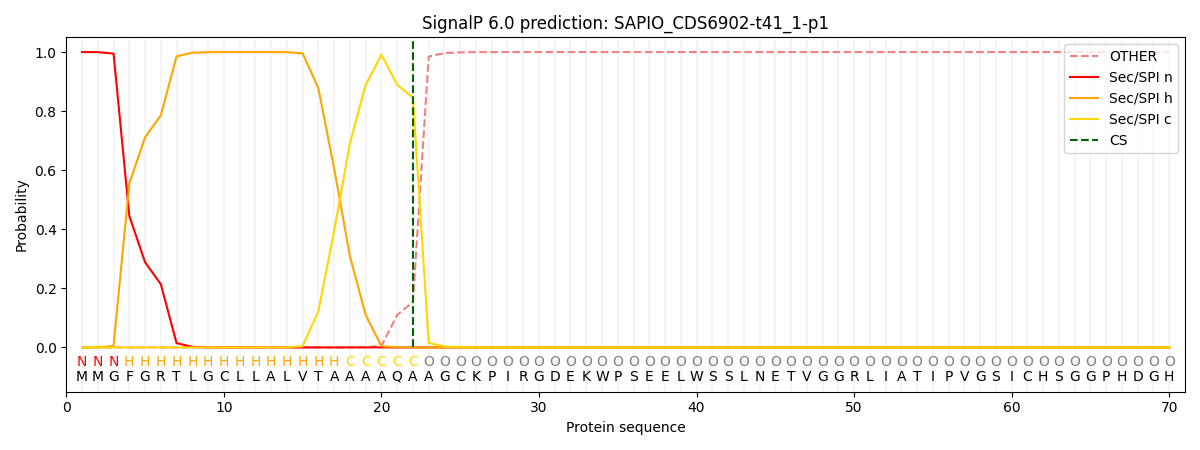
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000276 | 0.999714 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.8458 |
