You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: SAPIO_CDS1199-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: SAPIO_CDS1199-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Microascaceae; Scedosporium; Scedosporium apiospermum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | SAPIO_CDS1199-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA7 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Carboxypeptidase B | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1315078; End:1319219 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKSLAWSAVF LPFALASAVP RADAGAKVDY TGFKGLRVKI PHGHSHFDVE KDLAGLLTHV | 60 |
| VNFGHGDYLD IVVSPEKVAS VEQRVDAEVV VHDVGAALAE EGEPIRTYAV PSESWFTGYH | 120 |
| TYADHLQFLK DLQGGFPQQS ELINIGNSVQ NRAISGIHIW GSGGKGSKPA VLFHGTVHAR | 180 |
| EWISTMTAEY MAWQLLTLYS NTPAVRALVD NYDFYILPIV NPDGFVYTQT NDRYWRKNRQ | 240 |
| TVSSSSCVGR DINRNWSYKW EIPGGASTSP CSETYKGQAP GDSPEARALM RHVDSLRDGK | 300 |
| GIKFYIDFHS YGQYILWPFG YDCSFVAPDD AAHNSLASKG RTAISNVYGT SYTIGNSCRA | 360 |
| LYATTGDSVD YVHGVGNSTY SYTIELRDTG RSGFALPASQ IQPTVKETWA GVIAMLANIY | 420 |
| HKVEPGRPPP GESDDGDSSG HGLQLVVKAN TVDGMVPVGE IATKRGDIYH GTFRASIKLT | 480 |
| RSLGTCTAFY WYFNDSQEID MEFLSKEFNF ETNTFPVNLV LHSKESVAAG FDAVKAGTWA | 540 |
| RVNLPFDPTE DYHEYRFDFI PGSVNFYAEG VNIATMDGPA VPTSSGHILL SHWSSGNPKW | 600 |
| SGGPPEQDAT VAIRYFKAYF NSSDADRQTE WERRCRDAND PDTLCHVPSV LDDPDAAAHF | 660 |
| FTATTPTDEK TGDGNAGSTI SRPLGFLSWM AVVWAGYWHS SWMDLYI | 707 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 349433 | M14_CP_A-B_like | 2.01e-179 | 119 | 419 | 1 | 300 | Peptidase M14 carboxypeptidase subfamily A/B-like. The Peptidase M14 Carboxypeptidase (CP) A/B subfamily is one of two main M14 CP subfamilies defined by sequence and structural homology, the other being the N/E subfamily. CPs hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains. They have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. Enzymes belonging to the A/B subfamily are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by a globular N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The A/B enzymes can be further divided based on their substrate specificity; Carboxypeptidase A-like (CPA-like) enzymes favor hydrophobic residues while carboxypeptidase B-like (CPB-like) enzymes only cleave the basic residues lysine or arginine. There are nine members in the A/B family: CPA1, CPA2, CPA3, CPA4, CPA5, CPA6, CPB, CPO and CPU. CPA1, CPA2 and CPB are produced by the pancreas. The A forms have slightly different specificities, with CPA1 preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulkier aromatic side chains. CPA3 is found in secretory granules of mast cells and functions in inflammatory processes. CPA4 is detected in hormone-regulated tissues, and is thought to play a role in prostate cancer. CPA5 is present in discrete regions of pituitary and other tissues, and cleaves aliphatic C-terminal residues. CPA6 is highly expressed in embryonic brain and optic muscle, suggesting that it may play a specific role in cell migration and axonal guidance. CPU (also called CPB2) is produced and secreted by the liver as the inactive precursor, PCPU, commonly referred to as thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI). Little is known about CPO but it has been suggested to have specificity for acidic residues. |
| 214748 | Zn_pept | 1.34e-110 | 119 | 404 | 1 | 276 | Zn_pept domain. |
| 395189 | Peptidase_M14 | 3.31e-110 | 126 | 411 | 2 | 287 | Zinc carboxypeptidase. |
| 349432 | M14_CPT | 1.36e-77 | 116 | 412 | 1 | 292 | Peptidase M14 Carboxypeptidase T subfamily. Peptidase M14-like domain of carboxypeptidase (CP) T (CPT), CPT belongs to the M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs). The M14 family are zinc-binding CPs which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. CPT has moderate similarity to CPA and CPB, and exhibits dual-substrate specificity by cleaving C-terminal hydrophobic amino acid residues like CPA and C-terminal positively charged residues like CPB. CPA and CPB are M14 family peptidases but do not belong to this CPT group. The substrate specificity difference between CPT and CPA and CPB is ascribed to a few amino acid substitutions at the substrate-binding pocket while the spatial organization of the binding site remains the same as in all Zn-CPs. CPT has increased thermal stability in presence of Ca2+ ions, and two disulfide bridges which give an additional stabilization factor. |
| 349442 | M14_CPA | 7.12e-77 | 116 | 411 | 3 | 290 | Peptidase M14 carboxypeptidase subfamily A/B-like; Carboxypeptidase A subgroup. Peptidase M14 Carboxypeptidase (CP) A (CPA) belongs to the A/B subfamily of the M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs). The M14 family are zinc-binding CPs which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. CPA enzymes generally favor hydrophobic residues. A/B subfamily enzymes are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by a globular N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The procarboxypeptidase A (PCPA) is produced by the exocrine pancreas and stored as a stable zymogen in the pancreatic granules until secretion into the digestive tract occurs. This subfamily includes CPA1, CPA2 and CPA4 forms. Within these A forms, there are slightly different specificities, with CPA1 preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulkier aromatic side chains. CPA4, detected in hormone-regulated tissues, is thought to play a role in prostate cancer. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBB86764.1|GH16_23 | 4.14e-81 | 442 | 694 | 135 | 392 |
| CDP32289.1|GH16_23 | 5.80e-81 | 442 | 694 | 135 | 392 |
| AEO58087.1|GH16_23 | 2.32e-80 | 442 | 689 | 157 | 410 |
| QBZ62950.1|GH16_23 | 8.86e-80 | 442 | 693 | 130 | 383 |
| UKZ96476.1|GH16_23 | 4.77e-77 | 416 | 679 | 95 | 364 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1AYE_A | 2.30e-65 | 77 | 419 | 60 | 396 | Human Procarboxypeptidase A2 [Homo sapiens] |
| 1DTD_A | 3.89e-65 | 116 | 419 | 3 | 298 | Crystal Structure Of The Complex Between The Leech Carboxypeptidase Inhibitor And The Human Carboxypeptidase A2 (Lci-Cpa2) [Homo sapiens] |
| 2PCU_A | 8.21e-64 | 116 | 419 | 5 | 301 | Human carboxypeptidase A4 in complex with a cleaved hexapeptide. [Homo sapiens] |
| 2BO9_A | 8.97e-64 | 116 | 419 | 7 | 303 | Human carboxypeptidase A4 in complex with human latexin. [Homo sapiens],2BO9_C Human carboxypeptidase A4 in complex with human latexin. [Homo sapiens] |
| 4A94_A | 9.52e-64 | 116 | 419 | 9 | 305 | Structure of the carboxypeptidase inhibitor from Nerita versicolor in complex with human CPA4 [Homo sapiens],4A94_B Structure of the carboxypeptidase inhibitor from Nerita versicolor in complex with human CPA4 [Homo sapiens],4BD9_A Structure of the complex between SmCI and human carboxypeptidase A4 [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|D4AS12|MCPA_ARTBC | 7.63e-113 | 15 | 419 | 10 | 419 | Probable metallocarboxypeptidase A OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=MCPA PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|D4DL57|MCPA_TRIVH | 2.14e-112 | 15 | 419 | 10 | 419 | Probable metallocarboxypeptidase A OS=Trichophyton verrucosum (strain HKI 0517) OX=663202 GN=MCPA PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|A6XGK3|MCPA_TRIRU | 2.14e-112 | 15 | 419 | 10 | 419 | Metallocarboxypeptidase A OS=Trichophyton rubrum OX=5551 GN=MCPA PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|B6V865|MCPA_TRITO | 4.67e-111 | 15 | 419 | 10 | 419 | Metallocarboxypeptidase A OS=Trichophyton tonsurans OX=34387 GN=MCPA PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|B8XGR3|MCPA_TRIEQ | 6.58e-111 | 15 | 419 | 10 | 419 | Metallocarboxypeptidase A OS=Trichophyton equinum OX=63418 GN=MCPA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
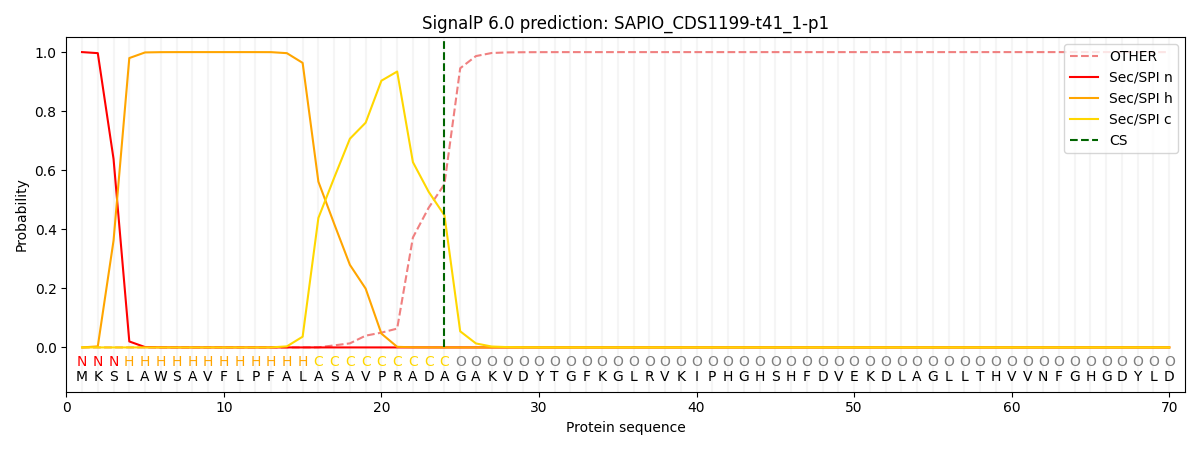
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000215 | 0.999770 | CS pos: 24-25. Pr: 0.4474 |
