You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: RVD87920.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: RVD87920.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Arthrobotrys flagrans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Orbiliomycetes; ; Orbiliaceae; Arthrobotrys; Arthrobotrys flagrans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | RVD87920.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH76 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2569855; End:2572271 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKFTSIALTS TLTATSFGNP IPEDDNMIQK RATSCTVSAY SSVSSAKSSC TSITLSNIAV | 60 |
| PAGKTLDLTG LKSGQVVTFA GRTTFGYKEW EGPLVSVSGT DVKIIGASGS VLDGEGSRWW | 120 |
| DGKGGNGGKT KTKFFAAHSL KSSSIASVTI KDSPVQVFSF SSATSVTVTK PTINNKNGDT | 180 |
| NSLGHNTDAF DIGNSDHITI DGATVYNQDD CLAINSGTNI IFTNGYCSGG HGLSIGSVGG | 240 |
| RSNSVVDTVT ISNSQIVNSD NGIRVKTVSG ATGSVKGVTY SNITLNGIKK YGIVIQQDYE | 300 |
| NGSPTGTPTN GVKIDKLKLS GVTGTVTSSA TNVYILCRIY LEVDLVTARP YSQGFPILQI | 360 |
| RNASIANVTT TTNSDADPQG WNTKTLSDLP KIDSARAQLS ILNSAYSYHG IFIVHDELRE | 420 |
| VPTSNVLFSR KINALDPELE GTAEDVFKVF QDFLTAHPTE TVLCSIKWDY DRSGQPSDFE | 480 |
| SLLESLFNDG SHGSWYTSST FPKLDDARGK IVLIRRYNEN LGFYMDVSNN TPDHTDSTGQ | 540 |
| FRVQDIYNPS TLPDGTPNYD TKWNAVKNFL NTRQPFNSSQ LNLNCLSAVK IEGINVLYKP | 600 |
| AFWANEINAR MRTWLGTIET QTANLGIVAM DFPDVPGSDW SFSVK | 645 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.15:80 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH28 | 45 | 337 | 3.2e-62 | 0.8738461538461538 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395231 | Glyco_hydro_28 | 4.36e-121 | 50 | 337 | 1 | 288 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 28. Glycosyl hydrolase family 28 includes polygalacturonase EC:3.2.1.15 as well as rhamnogalacturonase A(RGase A), EC:3.2.1.-. These enzymes are important in cell wall metabolism. |
| 176528 | PI-PLCc_BcPLC_like | 2.86e-37 | 444 | 634 | 76 | 266 | Catalytic domain of Bacillus cereus phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C and similar proteins. This subfamily corresponds to the catalytic domain present in Bacillus cereus phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 4.6.1.13) and its sequence homologs found in bacteria and eukaryota. Bacterial PI-PLCs participate in Ca2+-independent PI metabolism, hydrolyzing the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol (PI) to produce phosphorylated myo-inositol and diacylglycerol (DAG). Although their precise physiological function remains unclear, bacterial PI-PLCs may function as virulence factors in some pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial PI-PLCs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain. Their catalytic mechanism is based on general base and acid catalysis utilizing two well conserved histidines, and consists of two steps, a phosphotransfer and a phosphodiesterase reaction. This family also includes some uncharacterized eukaryotic homologs, which contains a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain, X domain. They are similar to bacterial PI-PLCs, and distinct from typical eukaryotic PI-PLCs, which have a multidomain organization that consists of a PLC catalytic core domain, and various regulatory domains, and strictly require Ca2+ for their catalytic activities. The prototype of this family is Bacillus cereus PI-PLC, which has a moderate thermal stability and is active as a monomer. |
| 176500 | PI-PLCc_bacteria_like | 3.67e-23 | 442 | 637 | 80 | 262 | Catalytic domain of bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and similar proteins. This subfamily corresponds to the catalytic domain present in bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 4.6.1.13) and their sequence homologs found in eukaryota. Bacterial PI-PLCs participate in Ca2+-independent PI metabolism, hydrolyzing the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol (PI) to produce phosphorylated myo-inositol and diacylglycerol (DAG). Although their precise physiological function remains unclear, bacterial PI-PLCs may function as virulence factors in some pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial PI-PLCs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain. Its catalytic mechanism is based on general base and acid catalysis utilizing two well conserved histidines, and consists of two steps, a phosphotransfer and a phosphodiesterase reaction. Eukaryotic homologs in this family are named as phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain containing proteins (PI-PLCXD). They are distinct from the typical eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C (PI-PLC, EC 3.1.4.11), which have a multidomain organization that consists of a PLC catalytic core domain, and various regulatory domains. The catalytic core domain is assembled from two highly conserved X- and Y-regions split by a divergent linker sequence. In contrast, eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain, X domain, which is closely related to that of bacterial PI-PLCs. Although the biological function of eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs still remains unclear, it may be distinct from that of typical eukaryotic PI-PLCs. This family also includes a distinctly different type of eukaryotic PLC, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (GPI-PLC), an integral membrane protein characterized in the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei. T. brucei GPI-PLC hydrolyzes the GPI-anchor on the variant specific glycoprotein (VSG), releasing dimyristyl glycerol (DMG), which may facilitate the evasion of the protozoan to the host's immune system. It does not require Ca2+ for its activity and is more closely related to bacterial PI-PLCs, but not mammalian PI-PLCs. |
| 215540 | PLN03010 | 3.76e-22 | 88 | 325 | 122 | 347 | polygalacturonase |
| 177865 | PLN02218 | 4.19e-22 | 50 | 335 | 95 | 388 | polygalacturonase ADPG |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGX52986.1|GH28 | 1.44e-209 | 1 | 337 | 1 | 338 |
| AUT30987.1|GH28 | 1.55e-131 | 5 | 337 | 4 | 330 |
| BAG72102.1|GH28 | 1.68e-130 | 25 | 337 | 25 | 337 |
| BAG72132.1|GH28 | 1.68e-130 | 25 | 337 | 25 | 337 |
| BAG72131.1|GH28 | 2.38e-130 | 25 | 337 | 25 | 337 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2IQ7_A | 4.23e-131 | 34 | 337 | 2 | 304 | Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_B Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_C Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_D Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_E Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_F Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini],2IQ7_G Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins [Colletotrichum lupini] |
| 6KVE_A | 3.20e-129 | 28 | 337 | 5 | 311 | Chain A, Endo-polygalacturonase [Evansstolkia leycettana] |
| 6KVH_A | 3.20e-129 | 28 | 337 | 5 | 311 | Chain A, endo-polygalacturonase [Evansstolkia leycettana] |
| 7E56_A | 3.87e-128 | 34 | 337 | 2 | 303 | Chain A, Endo-polygalacturonase [Evansstolkia leycettana] |
| 1IA5_A | 1.08e-113 | 32 | 337 | 1 | 306 | Polygalacturonase From Aspergillus Aculeatus [Aspergillus aculeatus],1IB4_A Crystal Structure of Polygalacturonase from Aspergillus Aculeatus at Ph4.5 [Aspergillus aculeatus],1IB4_B Crystal Structure of Polygalacturonase from Aspergillus Aculeatus at Ph4.5 [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|P35335|PGLRB_ASPOR | 8.89e-128 | 30 | 337 | 26 | 330 | Endopolygalacturonase B OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=pgaB PE=2 SV=2 |
| sp|B8N7Z8|PGLRB_ASPFN | 1.26e-127 | 34 | 337 | 30 | 330 | Probable endopolygalacturonase B OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=pgaB PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P49575|PGLRA_ASPPA | 2.51e-127 | 34 | 337 | 30 | 330 | Probable endopolygalacturonase A OS=Aspergillus parasiticus OX=5067 GN=pgaA PE=2 SV=1 |
| sp|P41749|PGLRA_ASPFA | 7.97e-126 | 34 | 337 | 30 | 330 | Endopolygalacturonase A OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC MYA-384 / AF70) OX=1392242 GN=pgaA PE=2 SV=1 |
| sp|Q4WBE1|PGLRB_ASPFU | 4.65e-125 | 34 | 337 | 31 | 331 | Probable endopolygalacturonase B OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=pgaB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
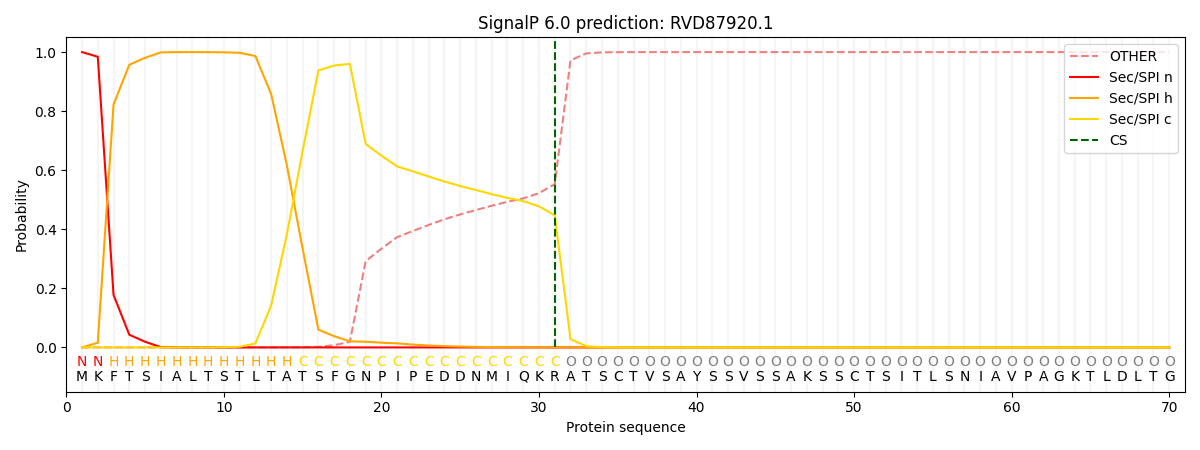
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000680 | 0.999322 | CS pos: 31-32. Pr: 0.4475 |
