You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: QRD81209.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: QRD81209.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
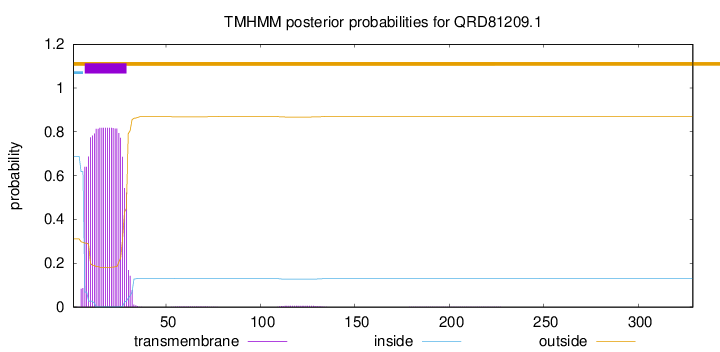
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus flavus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus flavus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | QRD81209.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | putative extracellular arabinanase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 150975; End:152133 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MSTRSPFPLS FTMLSFLAAL SLPLALVNAY ANPGTCNGNC WAHDPGLWKH DDGRYFLFST | 60 |
| GNGIHISSAP SLQGPWTEVG YALPDGSSIN HDGNKNLWAP DVHKGDDGKY YMYYSVSTLG | 120 |
| SQNSVIGVAS STTMEPGSWT DHGSTGLSSD GSQGYNTIDA NWIKIGDQQV LNFGSYWQGL | 180 |
| YQIDLAGPLK IGTAAPVNIA YNATGQHAIE ASFLYQQNGF YYLFFSSGKA NGYDTSFPAQ | 240 |
| GEEYRINVCR SSTGRGDFVD KNGVSCLQSG GTTVLASHDN VYGPGGQGVL EDNGAVLYYH | 300 |
| YAPRNGDLSV SSYQFGWNRL NWVDGWPTV | 329 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.99:2 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 39 | 327 | 3.5e-128 | 0.9965753424657534 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350152 | GH43_AnAbnA-like | 6.27e-157 | 42 | 323 | 1 | 286 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Aspergillus niger endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (AbnA). This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes characterized enzymes with endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities such as Aspergillus niger AbnA, Aspergillus niveus AbnA, and Chrysosporium lucknowense Abn1. It belongs to the GH43_Arb43a subgroup of the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43_Arb43a subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. The GH43_Arb43a subgroup includes many enzymes such as Bacillus subtilis arabinanase Abn2, that hydrolyzes sugar beet arabinan (branched), linear alpha-1,5-L-arabinan and pectin, and are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350112 | GH43_Arb43a-like | 9.21e-83 | 42 | 322 | 1 | 277 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase Arb43A. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. Many of these enzymes such as the Bacillus subtilis arabinanase Abn2, that hydrolyzes sugar beet arabinan (branched), linear alpha-1,5-L-arabinan and pectin, are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350150 | GH43_BsArb43A-like | 6.82e-48 | 42 | 300 | 1 | 253 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase Arb43A. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes annotated as having endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities, and includes Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase (AbnA;BSU28810) (Arb43A). It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. Many of these enzymes such as the Bacillus subtilis arabinanase Abn2, that hydrolyzes sugar beet arabinan (branched), linear alpha-1,5-L-arabinan and pectin, are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350151 | GH43_CjArb43A-like | 1.70e-43 | 42 | 294 | 1 | 264 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Cellvibrio japonicus Ueda107 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase / exo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase 43A (ArbA;CJA_0805) (Arb43A). This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes annotated with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities, and includes the bifunctional Cellvibrio japonicus Ueda107 endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase / exo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase 43A (ArbA;CJA_0805) (Arb43A). It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. Many of these enzymes such as the Bacillus subtilis arabinanase Abn2, that hydrolyzes sugar beet arabinan (branched), linear alpha-1,5-L-arabinan and pectin, are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350128 | GH43_ABN-like | 3.54e-38 | 44 | 306 | 10 | 272 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 such as arabinan endo-1 5-alpha-L-arabinosidase. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activity. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QMW38972.1|GH43_6 | 9.74e-255 | 1 | 329 | 1 | 329 |
| QMW26892.1|GH43_6 | 9.74e-255 | 1 | 329 | 1 | 329 |
| QRD81209.1|GH43_6 | 9.74e-255 | 1 | 329 | 1 | 329 |
| UDD54689.1|GH43_6 | 9.74e-255 | 1 | 329 | 1 | 329 |
| BAE64437.1|GH43_6 | 6.14e-246 | 13 | 329 | 1 | 317 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1WL7_A | 4.34e-42 | 23 | 327 | 5 | 310 | Structure of the thermostable arabinanase [Geobacillus thermodenitrificans] |
| 3CU9_A | 8.95e-42 | 23 | 327 | 5 | 310 | High resolution crystal structure of 1,5-alpha-L-arabinanase from Geobacillus Stearothermophilus [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 6A8I_A | 2.91e-41 | 23 | 327 | 6 | 311 | Crystal structure of endo-arabinanase ABN-TS D147N mutant in complex with arabinohexaose [Geobacillus thermodenitrificans],6A8I_B Crystal structure of endo-arabinanase ABN-TS D147N mutant in complex with arabinohexaose [Geobacillus thermodenitrificans] |
| 6A8H_A | 8.00e-41 | 23 | 327 | 6 | 311 | Crystal structure of endo-arabinanase ABN-TS D27A mutant in complex with arabinotriose [Geobacillus thermodenitrificans] |
| 3D5Y_A | 9.51e-41 | 23 | 327 | 5 | 310 | Chain A, Intracellular arabinanase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],3D5Z_A Chain A, Intracellular arabinanase [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q2U1X8|ABNC_ASPOR | 1.09e-246 | 13 | 329 | 1 | 317 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase C OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=abnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|B8NMD3|ABNC_ASPFN | 1.09e-246 | 13 | 329 | 1 | 317 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase C OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=abnC PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|A5AAG2|ABNC_ASPNC | 7.92e-148 | 13 | 329 | 1 | 317 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase C OS=Aspergillus niger (strain CBS 513.88 / FGSC A1513) OX=425011 GN=abnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q0CRJ6|ABNC_ASPTN | 4.00e-146 | 20 | 329 | 7 | 320 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase C OS=Aspergillus terreus (strain NIH 2624 / FGSC A1156) OX=341663 GN=abnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|A1CN18|ABNC_ASPCL | 4.23e-143 | 24 | 329 | 11 | 319 | Probable arabinan endo-1,5-alpha-L-arabinosidase C OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=abnC PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000287 | 0.999695 | CS pos: 29-30. Pr: 0.9737 |