You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: QEL63077.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: QEL63077.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
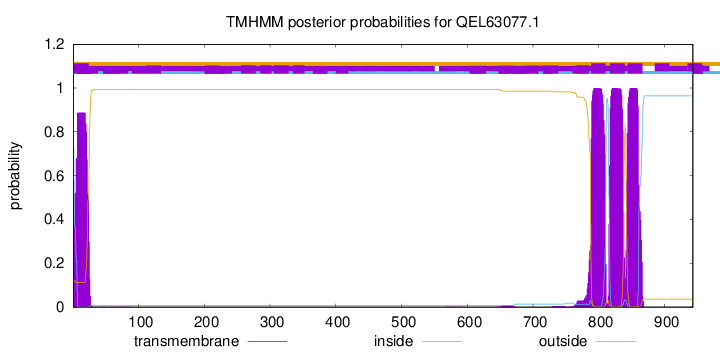
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | [Candida] auris | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Saccharomycetes; ; Debaryomycetaceae; Candida; [Candida] auris | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | QEL63077.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT71 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.16:11 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 389 | 911 | 1.4e-281 | 0.9905123339658444 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 367353 | Chitin_synth_2 | 0.0 | 390 | 911 | 4 | 525 | Chitin synthase. Members of this family are fungal chitin synthase EC:2.4.1.16 enzymes. They catalyze chitin synthesis as follows: UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N+1). |
| 133033 | Chitin_synth_C | 2.09e-101 | 416 | 762 | 2 | 244 | C-terminal domain of Chitin Synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin. Chitin synthase, also called UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:chitin 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of GlcNAc residues formed by covalent beta-1,4 linkages. Chitin is an important component of the cell wall of fungi and bacteria and it is synthesized on the cytoplasmic surface of the cell membrane by membrane bound chitin synthases. Studies with fungi have revealed that most of them contain more than one chitin synthase gene. At least five subclasses of chitin synthases have been identified. |
| 133045 | CESA_like | 1.37e-20 | 416 | 673 | 2 | 165 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| 224136 | BcsA | 6.11e-17 | 581 | 871 | 132 | 400 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| 133056 | GT2_HAS | 2.41e-08 | 588 | 759 | 79 | 232 | Hyaluronan synthases catalyze polymerization of hyaluronan. Hyaluronan synthases (HASs) are bi-functional glycosyltransferases that catalyze polymerization of hyaluronan. HASs transfer both GlcUA and GlcNAc in beta-(1,3) and beta-(1,4) linkages, respectively to the hyaluronan chain using UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-GlcUA as substrates. HA is made as a free glycan, not attached to a protein or lipid. HASs do not need a primer for HA synthesis; they initiate HA biosynthesis de novo with only UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-GlcUA, and Mg2+. Hyaluronan (HA) is a linear heteropolysaccharide composed of (1-3)-linked beta-D-GlcUA-beta-D-GlcNAc disaccharide repeats. It can be found in vertebrates and a few microbes and is typically on the cell surface or in the extracellular space, but is also found inside mammalian cells. Hyaluronan has several physiochemical and biological functions such as space filling, lubrication, and providing a hydrated matrix through which cells can migrate. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 943 | 1 | 943 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 943 | 1743 | 2723 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 943 | 177 | 1157 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 943 | 177 | 1157 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 943 | 171 | 1152 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 915 | 245 | 1191 | Chitin synthase 4 OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=chs-4 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 930 | 221 | 1193 | Chitin synthase D OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=chsD PE=1 SV=4 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 915 | 241 | 1186 | Chitin synthase 4 OS=Magnaporthe oryzae (strain 70-15 / ATCC MYA-4617 / FGSC 8958) OX=242507 GN=CHS4 PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 911 | 203 | 1149 | Chitin synthase 3 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=CHS3 PE=1 SV=3 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 928 | 201 | 1194 | Chitin synthase 3 OS=Candida albicans OX=5476 GN=CHS3 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
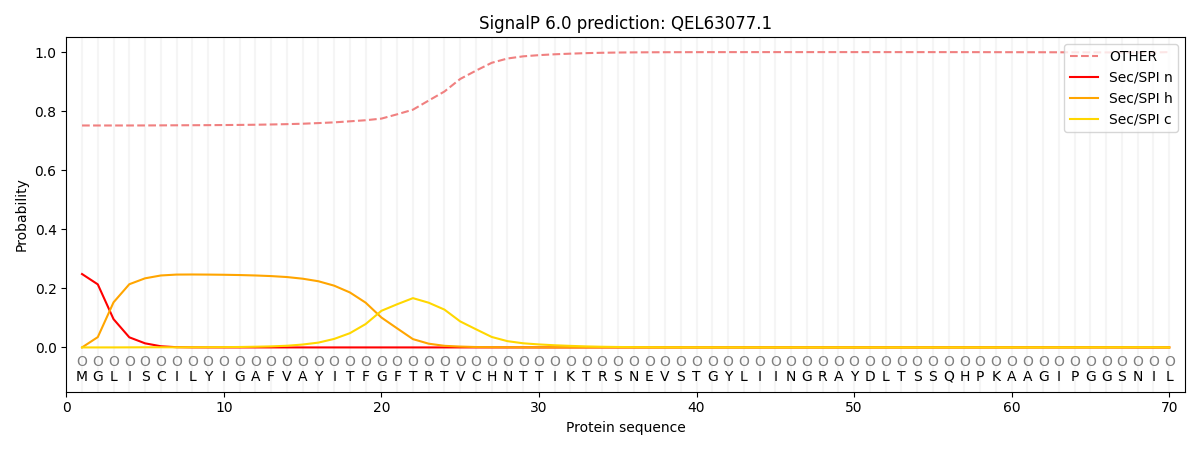
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.763912 | 0.236102 |