You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PWY83342.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PWY83342.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
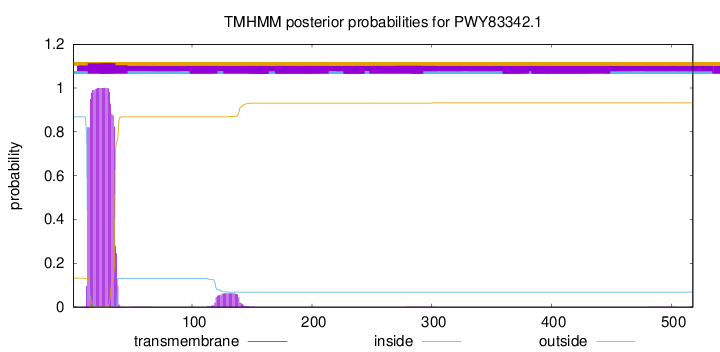
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus heteromorphus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus heteromorphus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PWY83342.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH36 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH135 | 48 | 279 | 2.5e-83 | 0.9662447257383966 |
| GH135 | 287 | 507 | 7.7e-67 | 0.919831223628692 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 403383 | Spherulin4 | 1.81e-103 | 53 | 287 | 1 | 238 | Spherulation-specific family 4. This protein is found in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Proteins in this family are typically between 250 and 398 amino acids in length. There is a conserved NPG sequence motif and there are two completely conserved G residues that may be functionally important. Starvation will often induce spherulation - the production of spores - and this process may involve DNA-methylation. Changes in the methylation of spherulin4 are associated with the formation of spherules, but these changes are probably transient. Methylation of the gene accompanies its transcriptional activation, and spherulin4 mRNA is only detectable in late spherulating cultures and mature spherules. It is a spherulation-specific protein. |
| 403383 | Spherulin4 | 1.47e-79 | 289 | 509 | 15 | 238 | Spherulation-specific family 4. This protein is found in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Proteins in this family are typically between 250 and 398 amino acids in length. There is a conserved NPG sequence motif and there are two completely conserved G residues that may be functionally important. Starvation will often induce spherulation - the production of spores - and this process may involve DNA-methylation. Changes in the methylation of spherulin4 are associated with the formation of spherules, but these changes are probably transient. Methylation of the gene accompanies its transcriptional activation, and spherulin4 mRNA is only detectable in late spherulating cultures and mature spherules. It is a spherulation-specific protein. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.02e-278 | 36 | 510 | 1 | 476 | |
| 2.90e-164 | 1 | 289 | 1 | 289 | |
| 2.90e-164 | 1 | 289 | 1 | 289 | |
| 2.90e-164 | 1 | 289 | 1 | 289 | |
| 2.89e-156 | 1 | 278 | 66 | 343 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.21e-63 | 36 | 287 | 14 | 270 | Crystal Structure of Aspergillus clavatus Sph3 in complex with GalNAc [Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1] |
|
| 2.70e-62 | 43 | 276 | 5 | 241 | Crystal Structure of Aspergillus clavatus Sph3 [Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
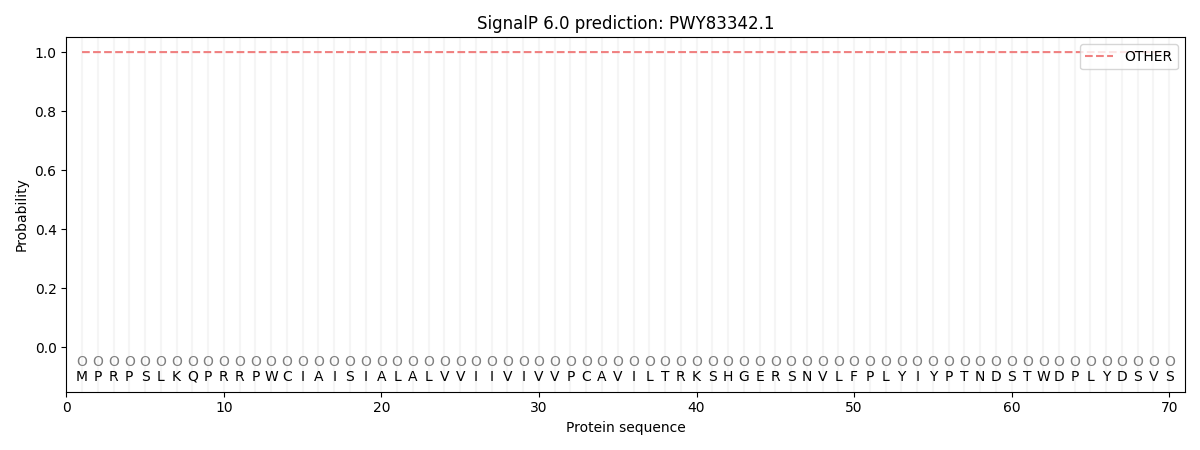
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000019 | 0.000023 |