You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PTTG_09691-t43_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PTTG_09691-t43_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Puccinia triticina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Pucciniomycetes; ; Pucciniaceae; Puccinia; Puccinia triticina | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PTTG_09691-t43_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT15 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.1:5 | 3.2.1.116:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 96 | 369 | 1.9e-84 | 0.9925650557620818 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200456 | AmyAc_bac_euk_AmyA | 1.15e-129 | 72 | 415 | 3 | 324 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial and eukaryotic Alpha amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes AmyA proteins from bacteria, fungi, mammals, insects, mollusks, and nematodes. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 200454 | AmyAc_bac1_AmyA | 1.94e-45 | 72 | 320 | 3 | 263 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 214758 | Aamy | 2.87e-23 | 72 | 161 | 2 | 98 | Alpha-amylase domain. |
| 200458 | AmyAc_euk_AmyA | 8.10e-19 | 100 | 255 | 60 | 212 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in eukaryotic Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes eukaryotic alpha-amylases including proteins from fungi, sponges, and protozoans. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 200459 | AmyAc_AmyMalt_CGTase_like | 7.45e-17 | 96 | 255 | 60 | 219 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in maltogenic amylases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, and related proteins. Enzymes such as amylases, cyclomaltodextrinase (CDase), and cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase) degrade starch to smaller oligosaccharides by hydrolyzing the alpha-D-(1,4) linkages between glucose residues. In the case of CGTases, an additional cyclization reaction is catalyzed yielding mixtures of cyclic oligosaccharides which are referred to as alpha-, beta-, or gamma-cyclodextrins (CDs), consisting of six, seven, or eight glucose residues, respectively. CGTases are characterized depending on the major product of the cyclization reaction. Besides having similar catalytic site residues, amylases and CGTases contain carbohydrate binding domains that are distant from the active site and are implicated in attaching the enzyme to raw starch granules and in guiding the amylose chain into the active site. The maltogenic alpha-amylase from Bacillus is a five-domain structure, unlike most alpha-amylases, but similar to that of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. In addition to the A, B, and C domains, they have a domain D and a starch-binding domain E. Maltogenic amylase is an endo-acting amylase that has activity on cyclodextrins, terminally modified linear maltodextrins, and amylose. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.55e-118 | 67 | 465 | 33 | 433 | |
| 1.60e-118 | 67 | 465 | 33 | 433 | |
| 2.12e-118 | 66 | 465 | 34 | 432 | |
| 9.61e-118 | 66 | 451 | 31 | 409 | |
| 1.02e-117 | 66 | 451 | 31 | 409 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.51e-86 | 74 | 453 | 6 | 386 | Chain A, ALPHA-AMYLASE [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis] |
|
| 6.73e-86 | 74 | 453 | 6 | 386 | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE TERNARY COMPLEX BETWEEN PSYCHROPHILIC ALPHA AMYLASE FROM PSEUDOALTEROMONAS HALOPLANCTIS IN COMPLEX WITH A HEPTA-SACCHARIDE AND A TRIS MOLECULE [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis],1G9H_A TERNARY COMPLEX BETWEEN PSYCHROPHILIC ALPHA-AMYLASE, COMII (PSEUDO TRI-SACCHARIDE FROM BAYER) AND TRIS (2-AMINO-2-HYDROXYMETHYL-PROPANE-1,3-DIOL) [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis],1L0P_A Crystal Structure Analysis Of The Complex Between Psychrophilic Alpha Amylase From Pseudoalteromonas Haloplanctis And Nitrate [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis] |
|
| 7.76e-86 | 74 | 453 | 6 | 386 | ALPHA-AMYLASE FROM ALTEROMONAS HALOPLANCTIS [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis],1AQM_A ALPHA-AMYLASE FROM ALTEROMONAS HALOPLANCTIS COMPLEXED WITH TRIS [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis],1B0I_A ALPHA-AMYLASE FROM ALTEROMONAS HALOPLANCTIS [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis] |
|
| 1.09e-85 | 74 | 453 | 6 | 386 | Chain A, ALPHA-AMYLASE [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis] |
|
| 3.72e-85 | 74 | 453 | 6 | 386 | Chain A, alpha-amylase [Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.57e-114 | 66 | 468 | 31 | 423 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces thermoviolaceus OX=1952 GN=amy PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 2.94e-107 | 67 | 476 | 29 | 425 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces limosus OX=1947 GN=aml PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.63e-106 | 67 | 476 | 29 | 425 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces griseus OX=1911 GN=amy PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 3.51e-99 | 72 | 465 | 36 | 419 | Alpha-amylase OS=Streptomyces violaceus OX=1936 GN=aml PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 2.07e-88 | 67 | 455 | 34 | 430 | Alpha-amylase OS=Thermomonospora curvata OX=2020 GN=tam PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
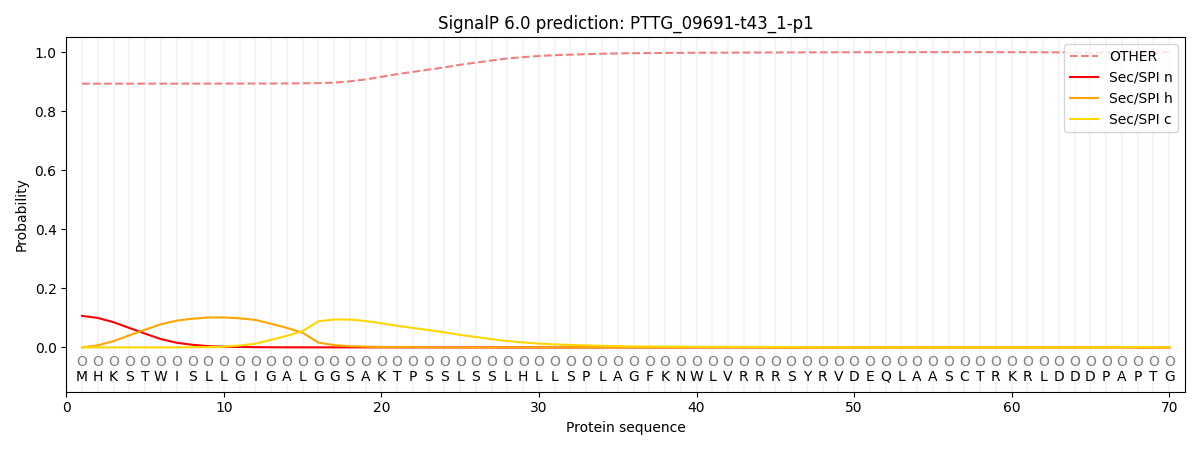
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.901136 | 0.098863 |
