You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PSURA_96418T0-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PSURA_96418T0-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora ramorum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora ramorum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PSURA_96418T0-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 1.1.99.18:3 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA3 | 245 | 773 | 7.5e-109 | 0.9671532846715328 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395236 | His_Phos_1 | 7.03e-55 | 41 | 237 | 1 | 194 | Histidine phosphatase superfamily (branch 1). The histidine phosphatase superfamily is so named because catalysis centers on a conserved His residue that is transiently phosphorylated during the catalytic cycle. Other conserved residues contribute to a 'phosphate pocket' and interact with the phospho group of substrate before, during and after its transfer to the His residue. Structure and sequence analyses show that different families contribute different additional residues to the 'phosphate pocket' and, more surprisingly, differ in the position, in sequence and in three dimensions, of a catalytically essential acidic residue. The superfamily may be divided into two main branches. The larger branch 1 contains a wide variety of catalytic functions, the best known being fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase (found in a bifunctional protein with 2-phosphofructokinase) and cofactor-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase. The latter is an unusual example of a mutase activity in the superfamily: the vast majority of members appear to be phosphatases. The bacterial regulatory protein phosphatase SixA is also in branch 1 and has a minimal, and possible ancestral-like structure, lacking the large domain insertions that contribute to binding of small molecules in branch 1 members. |
| 225186 | BetA | 1.95e-42 | 243 | 780 | 1 | 538 | Choline dehydrogenase or related flavoprotein [Lipid transport and metabolism, General function prediction only]. |
| 223483 | PhoE | 1.74e-41 | 40 | 246 | 4 | 206 | Broad specificity phosphatase PhoE [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 214859 | PGAM | 3.85e-28 | 40 | 191 | 1 | 152 | Phosphoglycerate mutase family. Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGAM) and bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM) are structurally related enzymes that catalyse reactions involving the transfer of phospho groups between the three carbon atoms of phosphoglycerate... Both enzymes can catalyse three different reactions with different specificities, the isomerization of 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PGA) to 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) with 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) as the primer of the reaction, the synthesis of 2,3-DPG from 1,3-DPG with 3-PGA as a primer and the degradation of 2,3-DPG to 3-PGA (phosphatase activity). In mammals, PGAM is a dimeric protein with two isoforms, the M (muscle) and B (brain) forms. In yeast, PGAM is a tetrameric protein. |
| 132718 | HP_PGM_like | 5.01e-23 | 40 | 226 | 1 | 143 | Histidine phosphatase domain found in phosphoglycerate mutases and related proteins, mostly phosphatases; contains a His residue which is phosphorylated during the reaction. Subgroup of the catalytic domain of a functionally diverse set of proteins, most of which are phosphatases. The conserved catalytic core of this domain contains a His residue which is phosphorylated in the reaction. This subgroup contains cofactor-dependent and cofactor-independent phosphoglycerate mutases (dPGM, and BPGM respectively), fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (F26BP)ase, Sts-1, SixA, and related proteins. Functions include roles in metabolism, signaling, or regulation, for example, F26BPase affects glycolysis and gluconeogenesis through controlling the concentration of F26BP; BPGM controls the concentration of 2,3-BPG (the main allosteric effector of hemoglobin in human blood cells); human Sts-1 is a T-cell regulator; Escherichia coli Six A participates in the ArcB-dependent His-to-Asp phosphorelay signaling system. Deficiency and mutation in many of the human members result in disease, for example erythrocyte BPGM deficiency is a disease associated with a decrease in the concentration of 2,3-BPG. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.83e-232 | 250 | 844 | 29 | 637 | |
| 1.80e-166 | 249 | 896 | 23 | 697 | |
| 8.57e-155 | 249 | 896 | 23 | 701 | |
| 9.75e-141 | 247 | 768 | 21 | 542 | |
| 2.59e-135 | 247 | 757 | 19 | 526 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.50e-49 | 243 | 784 | 1 | 544 | Chain A, cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1KDG_B Chain B, cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
|
| 8.55e-49 | 250 | 784 | 3 | 539 | Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1NAA_B Chain B, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
|
| 2.16e-37 | 134 | 774 | 118 | 763 | Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Thermothelomyces myriococcoides] |
|
| 4.23e-37 | 243 | 774 | 1 | 541 | Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Thermothelomyces myriococcoides],4QI5_A Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Thermothelomyces myriococcoides] |
|
| 3.46e-35 | 228 | 772 | 208 | 760 | Cellobiose dehydrogenase from Neurospora crassa, NcCDH [Neurospora crassa OR74A],4QI7_B Cellobiose dehydrogenase from Neurospora crassa, NcCDH [Neurospora crassa OR74A] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.56e-47 | 243 | 784 | 228 | 771 | Cellobiose dehydrogenase OS=Phanerodontia chrysosporium OX=2822231 GN=CDH-1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.55e-20 | 245 | 773 | 2 | 531 | 4-pyridoxate dehydrogenase OS=Mesorhizobium japonicum (strain LMG 29417 / CECT 9101 / MAFF 303099) OX=266835 GN=padh1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.03e-17 | 234 | 777 | 1 | 528 | Choline oxidase OS=Arthrobacter globiformis OX=1665 GN=codA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.40e-17 | 250 | 753 | 2 | 504 | Alcohol dehydrogenase [acceptor] OS=Pseudomonas putida OX=303 GN=alkJ PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 3.11e-16 | 250 | 753 | 2 | 504 | Alcohol dehydrogenase [acceptor] OS=Pseudomonas oleovorans OX=301 GN=alkJ PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
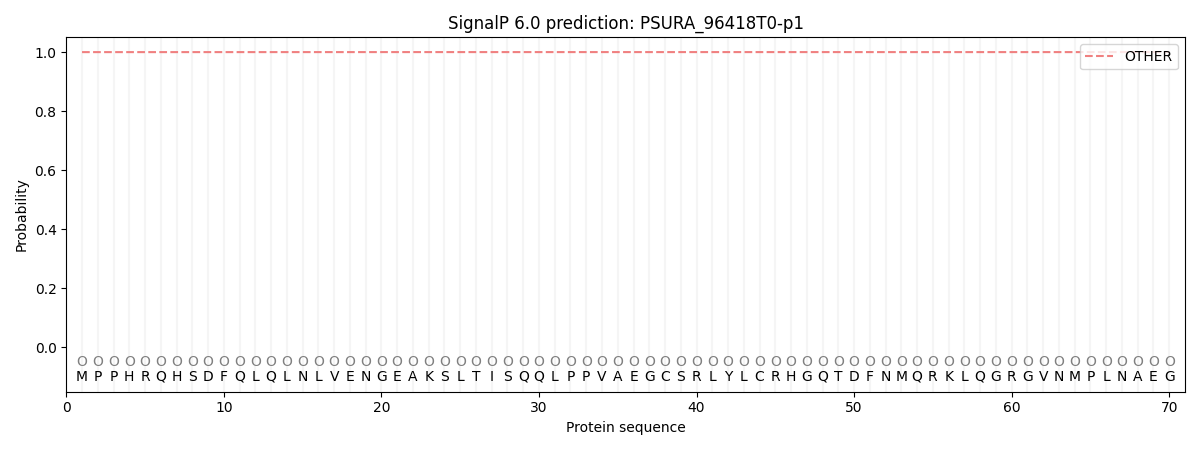
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000015 | 0.000000 |
