You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PSURA_77376T0-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PSURA_77376T0-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora ramorum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora ramorum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PSURA_77376T0-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.14:41 | 3.2.1.-:2 | 3.2.1.17:2 | 3.2.1.132:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH18 | 119 | 302 | 2.6e-21 | 0.49324324324324326 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119349 | GH18_chitinase-like | 1.82e-22 | 126 | 365 | 21 | 210 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of beta-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) which is a major component of the cell wall of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitinases have been identified in viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoan parasites, insects, and plants. The structure of the GH18 domain is an eight-stranded beta/alpha barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The GH18 family includes chitotriosidase, chitobiase, hevamine, zymocin-alpha, narbonin, SI-CLP (stabilin-1 interacting chitinase-like protein), IDGF (imaginal disc growth factor), CFLE (cortical fragment-lytic enzyme) spore hydrolase, the type III and type V plant chitinases, the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases, and the chitolectins. The GH85 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 85) ENGases (endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases) are closely related to the GH18 chitinases and are included in this alignment model. |
| 214753 | Glyco_18 | 2.97e-18 | 126 | 286 | 23 | 184 | Glyco_18 domain. |
| 395573 | Glyco_hydro_18 | 2.55e-15 | 126 | 287 | 20 | 176 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 18. |
| 119365 | GH18_chitinase | 4.24e-15 | 123 | 286 | 20 | 209 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolases, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of N-acetylglucosamine and have been identified in bacteria, fungi, insects, plants, viruses, and protozoan parasites. The structure of this domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. |
| 119351 | GH18_chitolectin_chitotriosidase | 3.45e-11 | 130 | 286 | 29 | 188 | This conserved domain family includes a large number of catalytically inactive chitinase-like lectins (chitolectins) including YKL-39, YKL-40 (HCGP39), YM1, oviductin, and AMCase (acidic mammalian chitinase), as well as catalytically active chitotriosidases. The conserved domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel fold belonging to the family 18 glycosyl hydrolases. The fold has a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The chitolectins lack a key active site glutamate (the proton donor required for hydrolytic activity) but retain highly conserved residues involved in oligosaccharide binding. Chitotriosidase is a chitinolytic enzyme expressed in maturing macrophages, which suggests that it plays a part in antimicrobial defense. Chitotriosidase hydrolyzes chitotriose, as well as colloidal chitin to yield chitobiose and is therefore considered an exochitinase. Chitotriosidase occurs in two major forms, the large form being converted to the small form by either RNA or post-translational processing. Although the small form, containing the chitinase domain alone, is sufficient for the chitinolytic activity, the additional C-terminal chitin-binding domain of the large form plays a role in processing colloidal chitin. The chitotriosidase gene is nonessential in humans, as about 35% of the population are heterozygous and 6% homozygous for an inactivated form of the gene. HCGP39 is a 39-kDa human cartilage glycoprotein thought to play a role in connective tissue remodeling and defense against pathogens. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.59e-10 | 123 | 320 | 42 | 259 | |
| 4.79e-10 | 123 | 320 | 42 | 259 | |
| 5.22e-10 | 123 | 320 | 74 | 291 | |
| 1.39e-09 | 123 | 297 | 138 | 330 | |
| 3.37e-09 | 129 | 313 | 33 | 240 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.13e-08 | 127 | 297 | 40 | 228 | Crystal structure of Aspergillus niger chitinase B [Aspergillus niger] |
|
| 2.66e-06 | 147 | 297 | 80 | 233 | The crystal structure of a chitinase CrChi1 from the nematophagous fungus Clonostachys rosea [Clonostachys rosea],3G6M_A crystal structure of a chitinase CrChi1 from the nematophagous fungus Clonostachys rosea in complex with a potent inhibitor caffeine [Clonostachys rosea] |
|
| 4.57e-06 | 123 | 297 | 23 | 215 | Chain A, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_A Chain A, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_B Chain B, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_C Chain C, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_D Chain D, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.37e-08 | 147 | 287 | 98 | 241 | Endochitinase 1 OS=Metarhizium anisopliae OX=5530 GN=chit1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.53e-07 | 154 | 287 | 105 | 241 | Endochitinase 1 OS=Metarhizium robertsii (strain ARSEF 23 / ATCC MYA-3075) OX=655844 GN=chit1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.45e-06 | 123 | 320 | 24 | 240 | Endochitinase B OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=chiB PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.45e-06 | 123 | 320 | 24 | 240 | Endochitinase B OS=Emericella nidulans OX=162425 GN=chiB PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
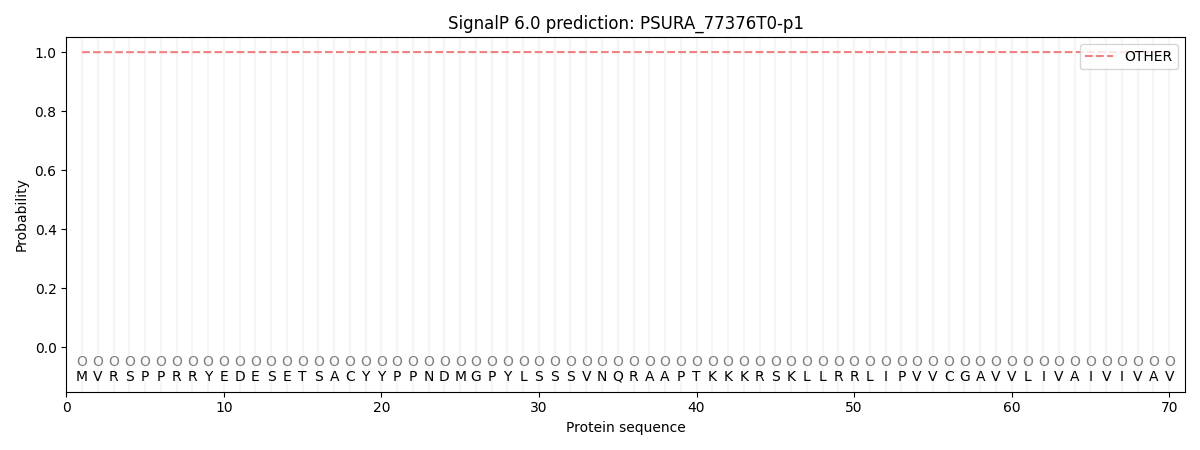
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999825 | 0.000205 |

