You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PPTG_11320-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PPTG_11320-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora parasitica | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora parasitica | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PPTG_11320-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA1 | 38 | 347 | 1.5e-44 | 0.9834983498349835 |
| AA1 | 251 | 510 | 3.6e-25 | 0.39385474860335196 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 274555 | ascorbase | 5.98e-47 | 27 | 537 | 4 | 539 | L-ascorbate oxidase, plant type. Members of this protein family are the copper-containing enzyme L-ascorbate oxidase (EC 1.10.3.3), also called ascorbase. This family is found in flowering plants, and shows greater sequence similarity to a family of laccases (EC 1.10.3.2) from plants than to other known ascorbate oxidases. |
| 177843 | PLN02191 | 4.54e-43 | 10 | 516 | 9 | 547 | L-ascorbate oxidase |
| 259869 | CuRO_1_LCC_like | 3.04e-41 | 25 | 143 | 1 | 120 | Cupredoxin domain 1 of laccase-like multicopper oxidases; including laccase, CueO, spore coat protein A, ascorbate oxidase and similar proteins. Laccase-like multicopper oxidases (MCOs) in this family contain three cupredoxin domains. They are able to couple oxidation of substrates with reduction of dioxygen to water. MCOs are capable of oxidizing a vast range of substrates, varying from aromatic to inorganic compounds such as metals. Although the members of this family have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats. The copper ions are bound in several sites; Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. Also included in this family are cupredoxin domains 1, 3, and 5 of the 6-domain MCO ceruloplasmin and similar proteins. |
| 259926 | CuRO_1_Diphenol_Ox | 6.17e-41 | 27 | 143 | 3 | 119 | The first cupredoxin domain of fungal laccase, diphenol oxidase. Diphenol oxidase belongs to the laccase family. It catalyzes the initial steps in melanin biosynthesis from diphenols. Melanin is one of the virulence factors of infectious fungi. In the pathogenesis of C. neoformans, melanin pigments have been shown to protect the fungal cells from oxidative and microbicidal activities of host defense systems. Laccase is a blue multicopper oxidase (MCO) which catalyzes the oxidation of a variety aromatic - notably phenolic and inorganic substances coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. It has been implicated in a wide spectrum of biological activities and, in particular, plays a key role in morphogenesis, development and lignin metabolism. Although MCOs have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats that include one mononuclear and one trinuclear copper center. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. |
| 225043 | SufI | 6.23e-41 | 3 | 518 | 7 | 451 | Multicopper oxidase with three cupredoxin domains (includes cell division protein FtsP and spore coat protein CotA) [Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.11e-227 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 545 | |
| 9.88e-205 | 8 | 537 | 2 | 537 | |
| 1.50e-167 | 8 | 541 | 7 | 570 | |
| 6.73e-163 | 13 | 536 | 12 | 561 | |
| 8.99e-78 | 18 | 525 | 34 | 545 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.06e-53 | 57 | 515 | 35 | 472 | Crystal structure of LacB from Trametes sp. AH28-2 [Trametes sp. AH28-2],3KW7_B Crystal structure of LacB from Trametes sp. AH28-2 [Trametes sp. AH28-2] |
|
| 1.85e-53 | 28 | 523 | 7 | 475 | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A FULLY FUNCTIONAL LACCASE FROM THE LIGNINOLYTIC FUNGUS PYCNOPORUS CINNABARINUS [Trametes cinnabarina] |
|
| 7.48e-53 | 4 | 523 | 2 | 496 | Crystal structure of laccases from Pycnoporus sanguineus, izoform II [Trametes coccinea],5NQ9_A Crystal structure of laccases from Pycnoporus sanguineus, izoform II, monoclinic [Trametes sanguinea],5NQ9_C Crystal structure of laccases from Pycnoporus sanguineus, izoform II, monoclinic [Trametes sanguinea] |
|
| 4.99e-52 | 28 | 515 | 7 | 468 | Chain A, Laccase [Lentinus tigrinus],2QT6_B Chain B, Laccase [Lentinus tigrinus] |
|
| 1.88e-51 | 39 | 523 | 18 | 477 | Chain A, LACCASE 2 [Trametes versicolor] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.38e-54 | 28 | 523 | 30 | 505 | Laccase-5 OS=Trametes versicolor OX=5325 GN=LCC5 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 2.41e-53 | 28 | 523 | 30 | 505 | Laccase-5 OS=Trametes villosa OX=47662 GN=LCC5 PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 1.42e-51 | 7 | 515 | 4 | 488 | Laccase OS=Pycnoporus cinnabarinus OX=5643 GN=LCC3-1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 5.34e-51 | 39 | 523 | 38 | 497 | Laccase-2 OS=Trametes versicolor OX=5325 GN=LCC2 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.00e-50 | 7 | 523 | 4 | 498 | Laccase OS=Trametes hirsuta OX=5327 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
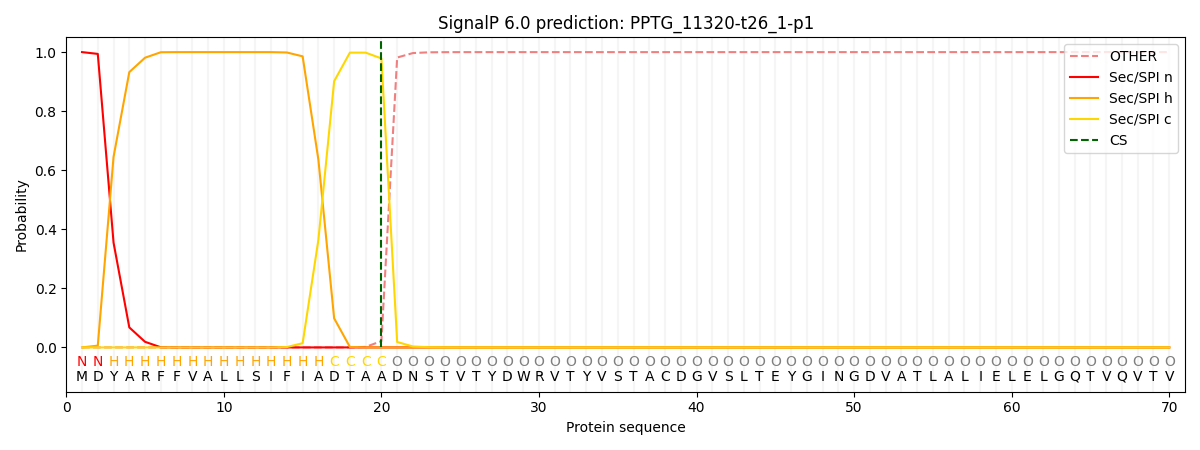
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000254 | 0.999709 | CS pos: 20-21. Pr: 0.9786 |
