You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PMAA_002400-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PMAA_002400-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
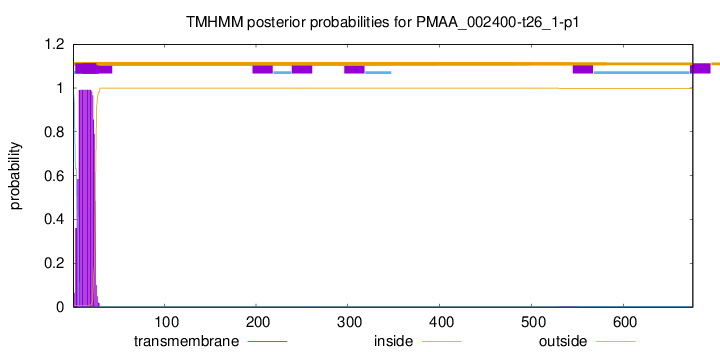
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Talaromyces marneffei | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Trichocomaceae; Talaromyces; Talaromyces marneffei | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PMAA_002400-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | polysaccharide deacetylase, putative | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE4 | 207 | 323 | 2.9e-21 | 0.8461538461538461 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396800 | MoaE | 2.10e-41 | 523 | 636 | 1 | 113 | MoaE protein. This family contains the MoaE protein that is involved in biosynthesis of molybdopterin. Molybdopterin, the universal component of the pterin molybdenum cofactors, contains a dithiolene group serving to bind Mo. Addition of the dithiolene sulfurs to a molybdopterin precursor requires the activity of the converting factor. Converting factor contains the MoaE and MoaD proteins. |
| 238385 | MoaE | 2.97e-41 | 528 | 656 | 1 | 124 | MoaE family. Members of this family are involved in biosynthesis of the molybdenum cofactor (Moco), an essential cofactor for a diverse group of redox enzymes. Moco biosynthesis is an evolutionarily conserved pathway present in eubacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Moco contains a tricyclic pyranopterin, termed molybdopterin (MPT), which carries the cis-dithiolene group responsible for molybdenum ligation. This dithiolene group is generated by MPT synthase in the second major step in Moco biosynthesis. MPT synthase is a heterotetramer consisting of two large (MoaE) and two small (MoaD) subunits. |
| 213022 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 1.14e-40 | 209 | 389 | 1 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| 200578 | CE4_CtAXE_like | 1.52e-31 | 212 | 395 | 4 | 174 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase and its bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase (CtAXE, EC 3.1.1.72), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. CtAXE deacetylates O-acetylated xylan, a key component of plant cell walls. It shows no detectable activity on generic esterase substrates including para-nitrophenyl acetate. It is specific for sugar-based substrates and will precipitate acetylxylan, as a consequence of deacetylation. CtAXE is a monomeric protein containing a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold as other CE4 esterases. However, due to differences in the topography of the substrate-binding groove, the chemistry of the active center, and metal ion coordination, CtAXE has different metal ion preference and lacks activity on N-acetyl substrates. It is significantly activated by Co2+. Moreover, CtAXE displays distinctly different ligand coordination to the metal ion, utilizing an aspartate, a histidine, and four water molecules, as opposed to the conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad of other CE4 esterases. |
| 178014 | PLN02390 | 3.80e-31 | 539 | 654 | 1 | 110 | molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.67e-51 | 504 | 666 | 597 | 755 | |
| 1.75e-22 | 199 | 402 | 31 | 236 | |
| 2.19e-20 | 196 | 404 | 59 | 266 | |
| 2.19e-20 | 196 | 404 | 59 | 266 | |
| 1.29e-18 | 183 | 406 | 270 | 476 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.14e-22 | 521 | 658 | 22 | 154 | Crystal structure of human molybdopterin synthase complex [Homo sapiens],5MPO_D Crystal structure of human molybdopterin synthase complex [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.38e-21 | 521 | 643 | 10 | 131 | Crystal structure of human Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit (MOCS2B) [Homo sapiens],4AP8_B Crystal structure of human Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit (MOCS2B) [Homo sapiens],4AP8_C Crystal structure of human Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit (MOCS2B) [Homo sapiens],4AP8_D Crystal structure of human Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit (MOCS2B) [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 6.88e-19 | 520 | 650 | 12 | 147 | Chain A, MOLYBDOPTERIN-CONVERTING FACTOR SUBUNIT 2 1 [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],2WP4_B Chain B, MOLYBDOPTERIN-CONVERTING FACTOR SUBUNIT 2 1 [Mycobacterium tuberculosis] |
|
| 1.12e-18 | 516 | 646 | 3 | 132 | Structural analysis of molybdopterin synthases from two mycobacteria pathogens [Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155],6JC0_D Structural analysis of molybdopterin synthases from two mycobacteria pathogens [Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155] |
|
| 3.12e-18 | 194 | 407 | 25 | 232 | Chain A, Aspergillus niger contig An12c0130, genomic contig [Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.52e-61 | 504 | 666 | 32 | 193 | Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit OS=Coccidioides immitis (strain RS) OX=246410 GN=cnxH PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 3.09e-58 | 504 | 668 | 14 | 174 | Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=cnxH PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.61e-55 | 504 | 666 | 21 | 179 | Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=cnxH PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.61e-55 | 504 | 666 | 21 | 179 | Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163) OX=451804 GN=cnxH PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 4.28e-55 | 504 | 668 | 30 | 190 | Molybdopterin synthase catalytic subunit OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=cnxH PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000236 | 0.999719 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.9801 |