You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PHYCI_71361T0-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PHYCI_71361T0-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
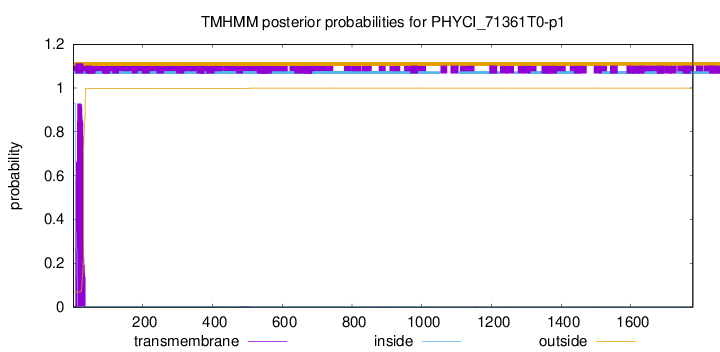
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora cinnamomi | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora cinnamomi | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PHYCI_71361T0-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Cdc2-related protein kinase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 75922; End:82659 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MTFSRRVRNV CAIATLFAAV IIPQVDAWLP PIIAKGNKFF DSDTGLEFRM KGMAYYPRPN | 60 |
| SGELASVSNY DWAADEHEAV WKPHLEIMKD LGVNTIRLYS VDPSVSHDKF MCACSEAGIY | 120 |
| VLVGISAPCE NCSIQDLEPP NCYPDELFTR GQMVYNAFSV YDNTLGFSVG NENNLQVKYG | 180 |
| ASGTTTAPCV KAFLRDMRSY AASCSGSVRQ VPMGLDIADI PPRWQWISYY DCAVNDDENT | 240 |
| RAEWMGFNPY VECDPATHTK YSQSSGLVTL MAEYANVKYA RPLMFGEFGC NKGANTIDGY | 300 |
| ENQREFYDAK WMNEEKDMTT EIVGGNVFEF STELANLVDK TALTKTADAG KYGVGYFQPD | 360 |
| DCDHDKVACE FTPYPEYDNL KKAYTTTANS TVTHDSFNPS RTKILTCPTT MSINLPPTPT | 420 |
| NVTLLACTAL QPVCNGSSAN SYKHTDSSTS MGEKRTPSNG EGASALASSS SSGSSKKSAA | 480 |
| TTATPAASVA ALLFSAAIAV LLDIVRSVGA STFVIPCCSH GEELLALSQP QPQPQPLGRA | 540 |
| RGAGRQQHEL RPAAGAAPRA AHRAQRVPAA APGARQGYET DENDAEEDQE VGEKQYVQLK | 600 |
| ENGWQLYCPP EEREGDTVFA IPKKRLLPTS SGRSSAAGSR EPSPKREVMS QSPVDTPSPV | 660 |
| AMAKLESSFT TAKKNQYGEP LDRDGKIVSK TLLVKFLPKE YDARGLRSLF VSRKHPNALV | 720 |
| DADVFHFLDG TGWALVELES NELAASFRRT LDRRNLLDKM LRVYQAGAKE LENYRYQKGK | 780 |
| VQVMRQQAST DKNNTSPSEE KENVQVVERQ DPYCFGRKLN WLVTEEELKN LSVQQVLSAS | 840 |
| LEETLRVKYV KSIFHIAKGL RLDREDATSA IIALNRFFTF HAMPMEVDIY AATMLHLFLK | 900 |
| AHARNVPWTA FVKEVYKAKH GAAAAERLTA ASPELGVLKR HLVKAEGELL EGLHYDVTGE | 960 |
| DPYALLDLLT TRKSSKKLVT MSQDGFTQQV TPFLSSLPPP EVQKEAKHLV AEALPLPIWT | 1020 |
| RTPVECVMLS VVYVSAAVTE ALSPSSATPM TRIPDFLPQL DLQANTSEAR MLLDCSLSIC | 1080 |
| TQLKDRWLRL EKQSKASQQQ KQKQKQNQTK NADSSEFDLE QFAVSKDKKD VEISERITRL | 1140 |
| LKHWINLPTP TVPSVLSVAS AVSSVPMGMR NFGVTAPTQS GVKNFITFKA MGSSVPVPSS | 1200 |
| STGQINEAEA VISALSIFPQ KSAASDTIVG DTRLHTDEIT KVESIRKRAF LGIISSEVNL | 1260 |
| DLAGQSVYLQ SWPYLEQEVF FTEERGINEA CLRELSAATT LSSLLPDRFM KLYGIIFPAD | 1320 |
| RKDRQANESG ATSNKPSSTA TTVDELDLLA ATIDDDGNPL PEGIDRLTRQ KHYLAFEQPL | 1380 |
| HMFSGIFEAH VSLTPELRKK AIFDMLQSLS AVHDQGYVHR FVAPSHLLVF KNGIKLGGFH | 1440 |
| AMRKIANIKP KDGEGSSMAA YEMTDGERKE HCYGAWLYVT APEVLLGETK YSWRADVWSA | 1500 |
| GCVALAILLE KVPFLQGPDI KVQLDLIYRL CGTPSSSWEG AHKLPLYSTF RPKHEYKMRL | 1560 |
| RKTLLEQRSK FPEFPEDAVE VLEAMLQLDP SRRCTVKKLL EMRYFDSVRS NGRTFDFSGL | 1620 |
| PSTFPVQKKK LVQHLLKSKA KKHRSAGSSS RSSGSARPSH HHSSHRHSNS DHHRHKRSAS | 1680 |
| SAHDGSSSGG DKSSHHDRHR PRTDKRKSRS LSTSRREVKH AMEDVEMQDA SEYVPLPASF | 1740 |
| TASAGYSPSQ PMVDTDDSLP RREKRVKLGW GMGLNSES | 1778 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH72 | 29 | 336 | 4.6e-72 | 0.8942307692307693 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397351 | Glyco_hydro_72 | 5.33e-57 | 26 | 388 | 6 | 315 | Glucanosyltransferase. This is a family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored beta(1-3)glucanosyltransferases. The active site residues in the Aspergillus fumigatus example are the two glutamate residues at 160 and 261. |
| 270832 | STKc_CDK9_like | 2.46e-35 | 1373 | 1605 | 80 | 291 | Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 9-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. This subfamily is composed of CDK9 and CDK12 from higher eukaryotes, yeast BUR1, C-type plant CDKs (CdkC), and similar proteins. CDK9, BUR1, and CdkC are functionally equivalent. They act as a kinase for the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II and participate in regulating mutliple steps of gene expression including transcription elongation and RNA processing. CDK9 and CdkC associate with T-type cyclins while BUR1 associates with the cyclin BUR2. CDK12 is a unique CDK that contains an arginine/serine-rich (RS) domain, which is predominantly found in splicing factors. CDK12 interacts with cyclins L1 and L2, and participates in regulating transcription and alternative splicing. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDK9-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
| 270823 | STKc_CDK_like | 8.15e-34 | 1367 | 1605 | 68 | 282 | Catalytic domain of Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. CDKs are partly regulated by their subcellular localization, which defines substrate phosphorylation and the resulting specific function. CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, and CDK6 have well-defined functions in the cell cycle, such as the regulation of the early G1 phase by CDK4 or CDK6, the G1/S phase transition by CDK2, or the entry of mitosis by CDK1. They also exhibit overlapping cyclin specificity and functions in certain conditions. Knockout mice with a single CDK deleted remain viable with specific phenotypes, showing that some CDKs can compensate for each other. For example, CDK4 can compensate for the loss of CDK6, however, double knockout mice with both CDK4 and CDK6 deleted die in utero. CDK8 and CDK9 are mainly involved in transcription while CDK5 is implicated in neuronal function. CDK7 plays essential roles in both the cell cycle as a CDK-Activating Kinase (CAK) and in transcription as a component of the general transcription factor TFIIH. The CDK-like subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
| 270833 | STKc_CDK7 | 5.88e-31 | 1405 | 1605 | 111 | 285 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 7. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDK7 plays essential roles in the cell cycle and in transcription. It associates with cyclin H and MAT1 and acts as a CDK-Activating Kinase (CAK) by phosphorylating and activating cell cycle CDKs (CDK1/2/4/6). In the brain, it activates CDK5. CDK7 is also a component of the general transcription factor TFIIH, which phosphorylates the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II when it is bound with unphosphorylated DNA, as present in the pre-initiation complex. Following phosphorylation, the CTD dissociates from the DNA which allows transcription initiation. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDK7 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
| 270847 | STKc_CDK12 | 3.26e-30 | 1373 | 1600 | 92 | 297 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 12. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. CDK12 is also called Cdc2-related protein kinase 7 (CRK7) or Cdc2-related kinase arginine/serine-rich (CrkRS). It is a unique CDK that contains an RS domain, which is predominantly found in splicing factors. CDK12 is widely expressed in tissues. It interacts with cyclins L1 and L2, and plays roles in regulating transcription and alternative splicing. CDKs belong to a large family of STKs that are regulated by their cognate cyclins. Together, they are involved in the control of cell-cycle progression, transcription, and neuronal function. The CDK12 subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIZ24052.1|GH72 | 0.0 | 1 | 1778 | 494 | 2516 |
| AIG55825.1|GH72 | 1.76e-161 | 26 | 444 | 24 | 444 |
| AIG56180.1|GH72 | 1.16e-159 | 28 | 464 | 42 | 482 |
| CCA15748.1|GH72 | 2.87e-139 | 27 | 459 | 2186 | 2612 |
| AIG55538.1|GH72 | 7.36e-137 | 17 | 419 | 15 | 432 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6B3E_A | 1.77e-26 | 1373 | 1608 | 94 | 307 | Crystal structure of human CDK12/CyclinK in complex with an inhibitor [Homo sapiens],6B3E_C Crystal structure of human CDK12/CyclinK in complex with an inhibitor [Homo sapiens] |
| 4UN0_C | 2.00e-26 | 1373 | 1608 | 98 | 311 | Crystal structure of the human CDK12-cyclinK complex [Homo sapiens],4UN0_D Crystal structure of the human CDK12-cyclinK complex [Homo sapiens] |
| 5FIH_A | 2.42e-26 | 30 | 291 | 34 | 279 | SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE GAS2P (E176Q MUTANT) IN COMPLEX WITH LAMINARITETRAOSE AND LAMINARIPENTAOSE [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
| 2W62_A | 2.42e-26 | 30 | 291 | 34 | 279 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gas2p in complex with laminaripentaose [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],2W63_A Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Gas2p In Complex With Laminaritriose And Laminaritetraose [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],5O9O_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 7. [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9P_A Crystal structure of Gas2 in complex with compound 10 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9Q_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 6 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9R_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 9 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9Y_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 11 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_B Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_C Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA6_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 12 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C] |
| 2W61_A | 2.42e-26 | 30 | 291 | 34 | 279 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gas2p apostructure (E176Q mutant) [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q9Y7Y7|GAS4_SCHPO | 3.34e-35 | 7 | 333 | 3 | 301 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gas4 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=gas4 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|B0XT72|GEL1_ASPFC | 1.50e-33 | 14 | 336 | 15 | 300 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gel1 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163) OX=451804 GN=gel1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|B0Y8H9|GEL2_ASPFC | 2.18e-33 | 2 | 348 | 4 | 319 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gel2 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163) OX=451804 GN=gel2 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P0C954|GEL2_ASPFU | 2.18e-33 | 2 | 348 | 4 | 319 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gel2 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=gel2 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P0C7S9|GEL1_ASPFU | 1.61e-32 | 14 | 336 | 15 | 300 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gel1 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=gel1 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
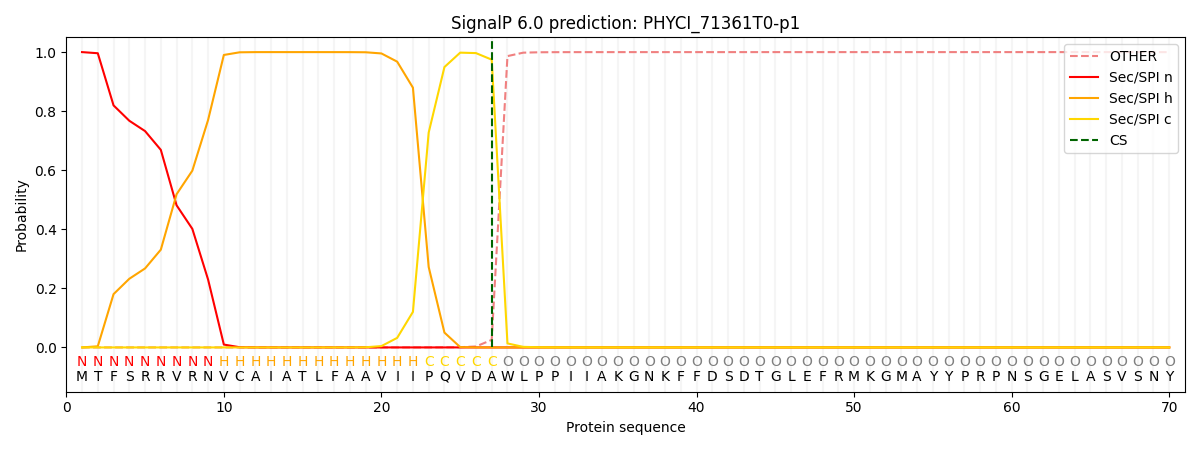
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000458 | 0.999519 | CS pos: 27-28. Pr: 0.9745 |