You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PHYBL_185781T0-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PHYBL_185781T0-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phycomyces blakesleeanus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Mucoromycota; Mucoromycetes; ; Phycomycetaceae; Phycomyces; Phycomyces blakesleeanus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PHYBL_185781T0-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT15 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT5 | 145 | 758 | 1.3e-33 | 0.9936440677966102 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 340822 | GT5_Glycogen_synthase_DULL1-like | 1.76e-07 | 145 | 758 | 2 | 473 | Glycogen synthase GlgA and similar proteins. This family is most closely related to the GT5 family of glycosyltransferases. Glycogen synthase (EC:2.4.1.21) catalyzes the formation and elongation of the alpha-1,4-glucose backbone using ADP-glucose, the second and key step of glycogen biosynthesis. This family includes starch synthases of plants, such as DULL1 in Zea mays and glycogen synthases of various organisms. |
| 223374 | GlgA | 1.28e-06 | 145 | 660 | 3 | 413 | Glycogen synthase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 223515 | RfaB | 1.61e-05 | 536 | 682 | 195 | 345 | Glycosyltransferase involved in cell wall bisynthesis [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 340816 | Glycosyltransferase_GTB-type | 4.41e-05 | 544 | 659 | 114 | 231 | glycosyltransferase family 1 and related proteins with GTB topology. Glycosyltransferases catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. The acceptor molecule can be a lipid, a protein, a heterocyclic compound, or another carbohydrate residue. The structures of the formed glycoconjugates are extremely diverse, reflecting a wide range of biological functions. The members of this family share a common GTB topology, one of the two protein topologies observed for nucleotide-sugar-dependent glycosyltransferases. GTB proteins have distinct N- and C- terminal domains each containing a typical Rossmann fold. The two domains have high structural homology despite minimal sequence homology. The large cleft that separates the two domains includes the catalytic center and permits a high degree of flexibility. |
| 400563 | Glyco_transf_5 | 6.31e-05 | 145 | 355 | 1 | 172 | Starch synthase catalytic domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.11e-202 | 1 | 784 | 1 | 825 | |
| 3.20e-153 | 1 | 764 | 2 | 723 | |
| 2.71e-81 | 96 | 765 | 90 | 809 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
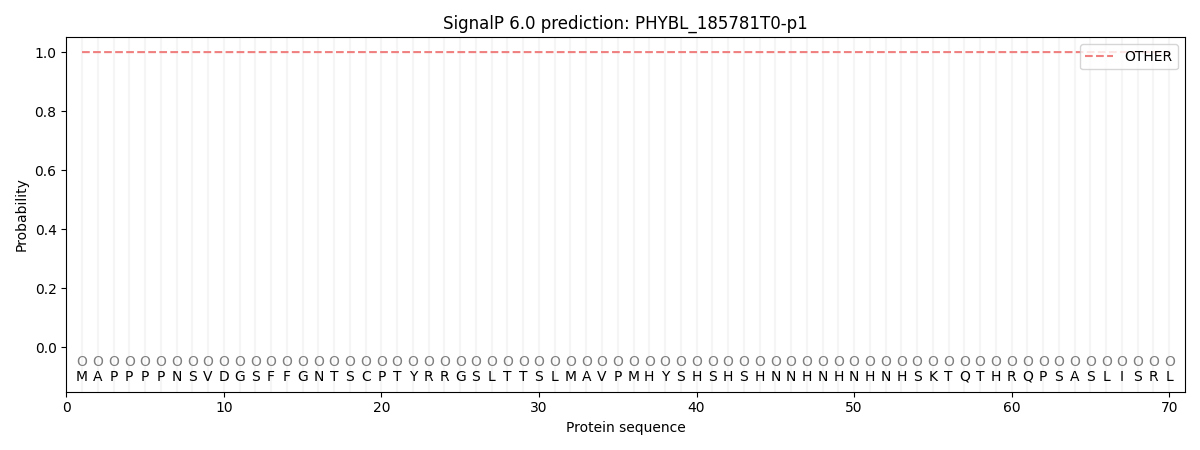
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000027 | 0.000000 |

