You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PHPALM_7512-t46_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PHPALM_7512-t46_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
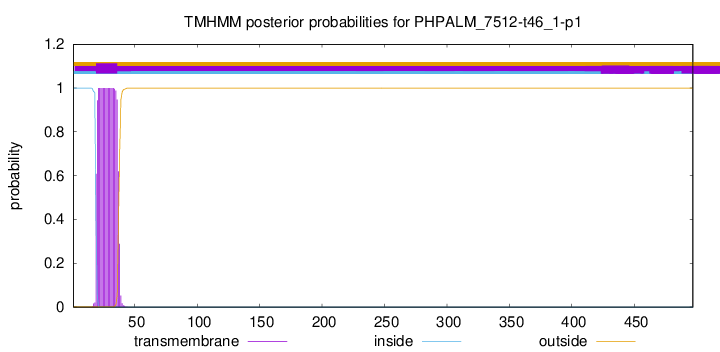
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora palmivora | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora palmivora | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PHPALM_7512-t46_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT71 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT62 | 139 | 308 | 1.2e-29 | 0.664179104477612 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397491 | Anp1 | 1.69e-36 | 127 | 366 | 3 | 262 | Anp1. The members of this family (Anp1, Van1 and Mnn9) are membrane proteins required for proper Golgi function. These proteins co-localize within the cis Golgi, and that they are physically associated in two distinct complexes. |
| 260004 | RNase_HI_RT_Ty1 | 9.48e-22 | 412 | 484 | 68 | 140 | Ty1/Copia family of RNase HI in long-term repeat retroelements. Ribonuclease H (RNase H) enzymes are divided into two major families, Type 1 and Type 2, based on amino acid sequence similarities and biochemical properties. RNase H is an endonuclease that cleaves the RNA strand of an RNA/DNA hybrid in a sequence non-specific manner in the presence of divalent cations. RNase H is widely present in various organisms including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. RNase HI has also been observed as adjunct domains to the reverse transcriptase gene in retroviruses, in long-term repeat (LTR)-bearing and non-LTR retrotransposons. RNase HI in LTR retrotransposons perform degradation of the original RNA template, generation of a polypurine tract (the primer for plus-strand DNA synthesis), and final removal of RNA primers from newly synthesized minus and plus strands. The catalytic residues for RNase H enzymatic activity, three aspartatic acids and one glutamic acid residue (DEDD) are unvaried across all RNase H domains. Phylogenetic patterns of RNase HI of LTR retroelements is classified into five major families, Ty3/Gypsy, Ty1/Copia, Bel/Pao, DIRS1, and the vertebrate retroviruses. The Ty1/Copia family is widely distributed among the genomes of plants, fungi, and animals. RNase H inhibitors have been explored as an anti-HIV drug target because RNase H inactivation inhibits reverse transcription. |
| 224137 | GT2 | 1.44e-05 | 255 | 409 | 81 | 219 | Glycosyltransferase, GT2 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.77e-48 | 146 | 410 | 85 | 376 | |
| 1.77e-48 | 146 | 410 | 85 | 376 | |
| 5.94e-47 | 144 | 413 | 184 | 472 | |
| 1.20e-46 | 148 | 409 | 69 | 367 | |
| 6.38e-44 | 138 | 412 | 84 | 399 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.12e-12 | 208 | 412 | 88 | 302 | Crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mnn9 in complex with GDP and Mn. [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.64e-19 | 169 | 412 | 81 | 337 | Mannan polymerase complex subunit mnn9 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=mnn9 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.80e-12 | 165 | 412 | 173 | 421 | Vanadate resistance protein OS=Candida albicans OX=5476 GN=VAN1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.60e-12 | 208 | 412 | 178 | 392 | Mannan polymerase complexes subunit MNN9 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=MNN9 PE=1 SV=3 |
|
| 2.97e-12 | 209 | 412 | 155 | 368 | Mannan polymerase complex subunit MNN9 OS=Candida albicans (strain SC5314 / ATCC MYA-2876) OX=237561 GN=MNN9 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.20e-11 | 202 | 412 | 296 | 514 | Mannan polymerase I complex VAN1 subunit OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=VAN1 PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000011 | 0.000010 |