You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: PGTG_00963-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: PGTG_00963-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
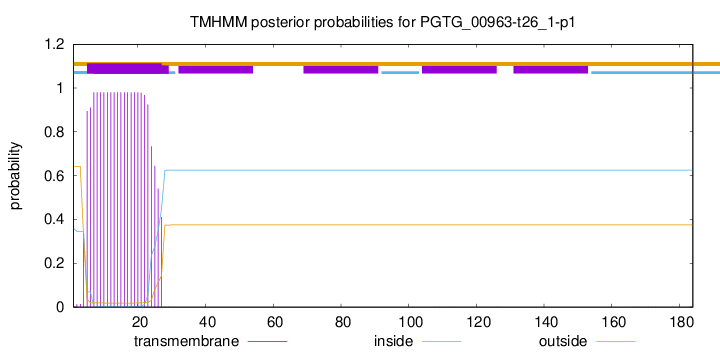
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Puccinia graminis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Pucciniomycetes; ; Pucciniaceae; Puccinia; Puccinia graminis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | PGTG_00963-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH152 | 29 | 169 | 1.3e-20 | 0.6435185185185185 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 185754 | Thaumatin-like | 5.70e-22 | 25 | 183 | 1 | 157 | the sweet-tasting protein, thaumatin, and thaumatin-like proteins involved in host defense. This family is represented by the sweet-tasting protein thaumatin from the African berry Thaumatococcus daniellii and thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs) involved in host defense and a wide range of developmental processes in fungi, plants, and animals. Plant TLPs are classified as pathogenesis-related (PR) protein family 5 (PR5), their expression is induced by environmental stresses such as pathogen/pest attack, drought and cold. TLPs included in this family are such proteins as zeamatin, found in high concentrations in cereal seeds; osmotin, a salt-induced protein in osmotically stressed plants; and PpAZ44, a propylene-induced TLP in abscission of young fruit. Several members of the plant TLP family have been reported as food allergens from fruits (i.e., cherry, Pru av 2; bell pepper, Cap a1; tomatoes, Lyc e NP24) and pollen allergens from conifers (i.e., mountain cedar, Jun a 3; Arizona cypress, Cup a3; Japanese cedar, Cry j3). Thaumatin and TLPs are three-domain, crescent-fold structures with either an electronegative, electropositive, or neutral cleft occurring between domains I and II. It has been proposed that the antifungal activity of plant PR5 proteins relies on the strong electronegative character of this cleft. Some TLPs hydrolyze the beta-1,3-glucans of the type commonly found in fungal walls. Most TLPs contain 16 conserved Cys residues. A deletion within the third domain (domain II) of the Triticum aestivum thaumatin-like xylanase inhibitor is observed, thus, only 10 conserved Cys residues are present within this smaller TLP and similar homologs. |
| 185756 | TLP-P | 8.81e-21 | 28 | 183 | 4 | 150 | thaumatin and allergenic/antifungal thaumatin-like proteins: plant homologs. This subfamily is represented by the sweet-tasting protein thaumatin from the African berry Thaumatococcus daniellii, allergenic/antifungal Thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs), and related plant proteins. TLPs are involved in host defense and a wide range of developmental processes in fungi, plants, and animals. Plant TLPs are classified as pathogenesis-related (PR) protein family 5 (PR5), their expression is induced by environmental stresses such as pathogen/pest attack, drought and cold. TLPs in this subfamily include such proteins as zeamatin, found in high concentrations in cereal seeds, and osmotin, a salt-induced protein in osmotically stressed plants. Several members of the plant TLP family have been reported as food allergens from fruits (i.e., cherry, Pru av 2; bell pepper, Cap a1; tomatoes, Lyc e NP24) and pollen allergens from conifers (i.e., mountain cedar, Jun a 3; Arizona cypress, Cup a3; Japanese cedar, Cry j3). Thaumatin and TLPs are three-domain, crescent-fold structures with either an electronegative, electropositive, or neutral cleft occurring between domains I and II. It has been proposed that the antifungal activity of plant PR5 proteins relies on the strong electronegative character of this cleft. IgE-binding epitopes of mountain Cedar (Juniperus ashei) allergen Jun a 3, which interact with pooled IgE from patients suffering allergenic response to this allergen, were mainly located on the helical domain II; the best-conserved IgE-binding epitope predicted for TLPs corresponds to this region. Some TLPs hydrolyze the beta-1,3-glucans of the type commonly found in fungal walls. Most TLPs contain 16 conserved Cys residues. A deletion within the third domain (domain II) of the Triticum aestivum thaumatin-like xylanase inhibitor is observed, thus, only 10 conserved Cys residues are present within this smaller TLP and similar homologs. |
| 185757 | TLP-PA | 8.86e-19 | 24 | 157 | 1 | 133 | allergenic/antifungal thaumatin-like proteins: plant and animal homologs. This subfamily is represented by the thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs), Cherry Allergen Pru Av 2 TLP, Peach PpAZ44 TLP (a propylene-induced TLP in abscission), the Caenorhabditis elegans thaumatin family member (thn-6), and other plant and animal homologs. TLPs are involved in host defense and a wide range of developmental processes in fungi, plants, and animals. Due to their inducible expression by environmental stresses such as pathogen/pest attack, drought and cold, plant TLPs are classified as the pathogenesis-related (PR) protein family 5 (PR5). Several members of the plant TLP family have been reported as food allergens from fruits (i.e., cherry, Pru av 2; bell pepper, Cap a1; tomatoes, Lyc e NP24) and pollen allergens from conifers (i.e., mountain cedar, Jun a 3; Arizona cypress, Cup a3; Japanese cedar, Cry j3). TLPs are three-domain, crescent-fold structures with either an electronegative, electropositive, or neutral cleft occurring between domains I and II. It has been proposed that the antifungal activity of plant PR5 proteins relies on the strong electronegative character of this cleft. Some TLPs hydrolyze the beta-1,3-glucans of the type commonly found in fungal walls. TLPs within this subfamily contain 16 conserved Cys residues. |
| 128501 | THN | 2.75e-17 | 27 | 174 | 3 | 149 | Thaumatin family. The thaumatin family gathers proteins related to plant pathogenesis. The thaumatin family includes very basic members with extracellular and vacuolar localization. Thaumatin itsel is a potent sweet-tasting protein. Several members of this family display significant in vitro activity of inhibiting hyphal growth or spore germination of various fungi probably by a membrane permeabilizing mechanism. |
| 395248 | Thaumatin | 2.87e-17 | 29 | 157 | 1 | 124 | Thaumatin family. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.69e-60 | 8 | 183 | 4 | 177 | |
| 7.19e-14 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | |
| 7.19e-14 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | |
| 7.19e-14 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | |
| 7.19e-14 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.28e-14 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | Thaumatin-like protein PWIR2 OS=Triticum aestivum OX=4565 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 3.63e-13 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | Pathogenesis-related protein 1C OS=Hordeum vulgare OX=4513 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.37e-12 | 24 | 183 | 22 | 172 | Pathogenesis-related protein 1A/1B OS=Hordeum vulgare OX=4513 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 5.54e-08 | 24 | 169 | 25 | 167 | Thaumatin-like protein 2 OS=Prunus persica OX=3760 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
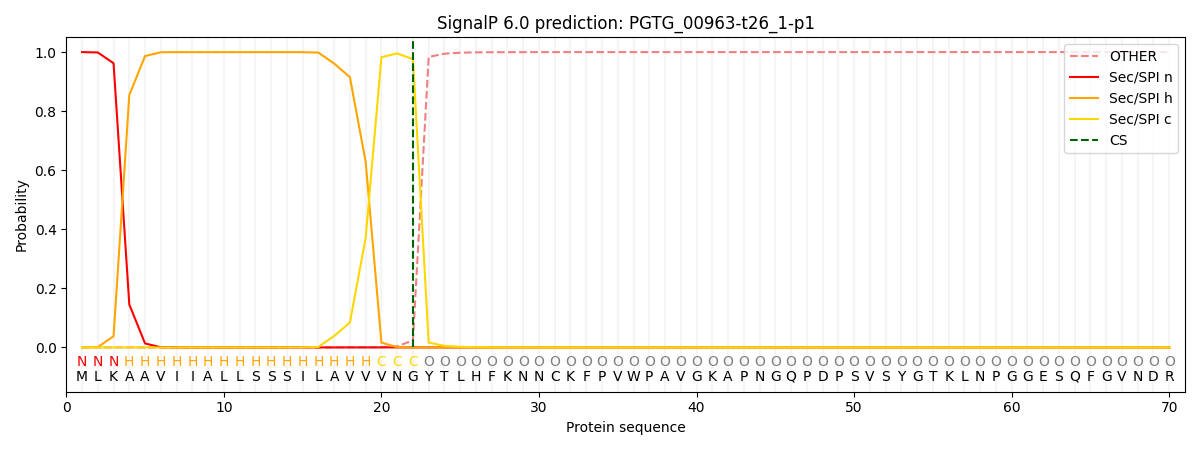
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000209 | 0.999768 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.9762 |