You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: P174DRAFT_418746-t37_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: P174DRAFT_418746-t37_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus novofumigatus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus novofumigatus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | P174DRAFT_418746-t37_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13|GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA1 | 65 | 198 | 3.4e-32 | 0.35195530726256985 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 259919 | CuRO_1_Abr2_like | 1.45e-41 | 65 | 153 | 23 | 112 | The first cupredoxin domain of a group of fungal Laccases similar to Abr2 from Aspergillus fumigatus. Abr2 is involved in conidial pigment biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. Laccase is a blue multi-copper enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of a variety aromatic - notably phenolic and inorganic substances coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. Laccase has been implicated in a wide spectrum of biological activities and, in particular, plays a key role in morphogenesis, development and lignin metabolism in fungi and plants. Like other related multicopper oxidases (MCOs), laccase is composed of three cupredoxin domains that include one mononuclear and one trinuclear copper center. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. |
| 259927 | CuRO_1_tcLCC2_insect_like | 2.35e-32 | 65 | 153 | 11 | 100 | The first cupredoxin domain of insect laccases similar to laccase 2 in Tribolium castaneum. This multicopper oxidase (MCO) family includes the majority of insect laccases. One member of the family is laccase 2 from Tribolium castaneum. Laccase 2 is required for beetle cuticle tanning. Laccase (polyphenol oxidase EC 1.10.3.2) is a blue multi-copper enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of a variety of organic substrates coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. It displays broad substrate specificity, catalyzing the oxidation of a wide variety of aromatic - notably phenolic and inorganic substances. Laccase has been implicated in a wide spectrum of biological activities and, in particular, plays a key role in morphogenesis, development and lignin metabolism in fungi, plants and insects. Although MCOs have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats that include one mononuclear and one trinuclear copper center. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. |
| 259944 | CuRO_2_Abr2_like | 1.28e-30 | 302 | 391 | 45 | 138 | The second cupredoxin domain of a group of fungal Laccases similar to Abr2 from Aspergillus fumigatus. Abr2 is involved in conidial pigment biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. Laccase is a blue multi-copper enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of a variety aromatic - notably phenolic and inorganic substances coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. Laccase has been implicated in a wide spectrum of biological activities and, in particular, plays a key role in morphogenesis, development and lignin metabolism in fungi and plants. Like other related multicopper oxidases (MCOs), laccase is composed of three cupredoxin domains that include one mononuclear and one trinuclear copper center. The copper ions are bound in several sites: Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 2 of 3-domain MCOs has lost the ability to bind copper. |
| 400195 | Cu-oxidase_3 | 2.63e-30 | 65 | 153 | 21 | 110 | Multicopper oxidase. This entry contains many divergent copper oxidase-like domains that are not recognized by the pfam00394 model. |
| 259869 | CuRO_1_LCC_like | 7.53e-30 | 65 | 153 | 25 | 115 | Cupredoxin domain 1 of laccase-like multicopper oxidases; including laccase, CueO, spore coat protein A, ascorbate oxidase and similar proteins. Laccase-like multicopper oxidases (MCOs) in this family contain three cupredoxin domains. They are able to couple oxidation of substrates with reduction of dioxygen to water. MCOs are capable of oxidizing a vast range of substrates, varying from aromatic to inorganic compounds such as metals. Although the members of this family have diverse functions, majority of them have three cupredoxin domain repeats. The copper ions are bound in several sites; Type 1, Type 2, and/or Type 3. The ensemble of types 2 and 3 copper is called a trinuclear cluster. MCOs oxidize their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper center and transferring them to the active site trinuclear copper center. The cupredoxin domain 1 of 3-domain MCOs contains part the trinuclear copper binding site, which is located at the interface of domains 1 and 3. Also included in this family are cupredoxin domains 1, 3, and 5 of the 6-domain MCO ceruloplasmin and similar proteins. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.91e-133 | 65 | 412 | 54 | 398 | |
| 1.01e-92 | 65 | 415 | 49 | 407 | |
| 1.44e-89 | 65 | 393 | 49 | 380 | |
| 1.44e-89 | 65 | 393 | 49 | 380 | |
| 3.93e-87 | 65 | 400 | 48 | 381 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.47e-22 | 65 | 368 | 28 | 274 | Refined Crystal Structure Of Ascorbate Oxidase At 1.9 Angstroms Resolution [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1AOZ_B Refined Crystal Structure Of Ascorbate Oxidase At 1.9 Angstroms Resolution [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASO_A X-Ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-Forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASO_B X-Ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-Forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASP_A X-ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASP_B X-ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASQ_A X-Ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-Forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo],1ASQ_B X-Ray Structures And Mechanistic Implications Of Three Functional Derivatives Of Ascorbate Oxidase From Zucchini: Reduced-, Peroxide-, And Azide-Forms [Cucurbita pepo var. melopepo] |
|
| 8.68e-19 | 65 | 199 | 29 | 157 | Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data1) [uncultured bacterium],4E9V_B Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data1) [uncultured bacterium],4E9V_C Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data1) [uncultured bacterium],4E9W_A Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data2) [uncultured bacterium],4E9W_B Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data2) [uncultured bacterium],4E9W_C Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data2) [uncultured bacterium],4E9X_A Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data3) [uncultured bacterium],4E9X_B Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data3) [uncultured bacterium],4E9X_C Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data3) [uncultured bacterium],4E9Y_A Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data4) [uncultured bacterium],4E9Y_B Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data4) [uncultured bacterium],4E9Y_C Multicopper Oxidase mgLAC (data4) [uncultured bacterium] |
|
| 1.68e-18 | 65 | 189 | 28 | 146 | Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea],3G5W_B Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea],3G5W_C Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea],3G5W_D Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea],3G5W_E Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea],3G5W_F Crystal structure of Blue Copper Oxidase from Nitrosomonas europaea [Nitrosomonas europaea] |
|
| 1.32e-16 | 65 | 191 | 92 | 207 | Structure of the L499M mutant of the laccase from B.aclada [Botrytis aclada] |
|
| 1.32e-16 | 65 | 191 | 92 | 207 | Crystal structure of laccase from Botrytis aclada at 1.67 A resolution [Botrytis aclada],4X4K_A Structure of laccase from Botrytis aclada with full copper content [Botrytis aclada] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.25e-179 | 65 | 414 | 44 | 390 | Multicopper oxidase VdtB OS=Byssochlamys spectabilis OX=264951 GN=VdtB PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.55e-90 | 65 | 393 | 49 | 380 | Multicopper oxidase GIP1 OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=GIP1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.43e-84 | 65 | 393 | 48 | 372 | Multicopper oxidase MCE OS=Talaromyces pinophilus OX=128442 GN=MCE PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 5.21e-82 | 65 | 394 | 47 | 375 | Laccase ustL OS=Ustilaginoidea virens OX=1159556 GN=ustL PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.17e-72 | 65 | 391 | 48 | 377 | Laccase 1 OS=Metarhizium majus (strain ARSEF 297) OX=1276143 GN=Mlac1 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
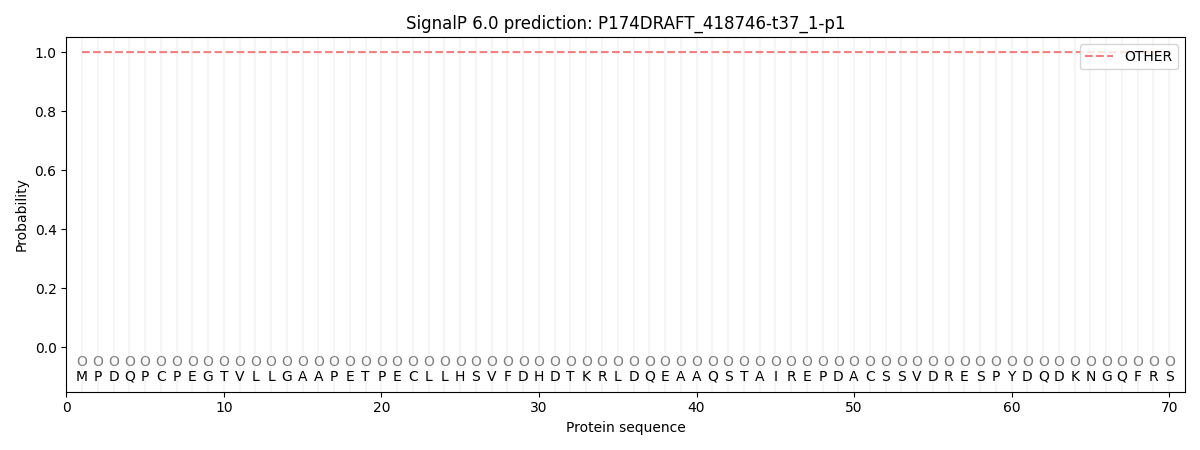
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000043 | 0.000000 |
