You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: OTA39661.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: OTA39661.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Dothideomycetes; ; Teratosphaeriaceae; Hortaea; Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | OTA39661.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT61 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | MFS domain-containing protein [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:A0A1Z5TUS2] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 514445; End:517646 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MAGDWYTFGV ALFAAIGTFL FGFDTGIATT TIAHESWIEY MGHPSEGLTG AVVAVYIAGE | 60 |
| ACGALTQTFL GDRLGRIRFM QMMCVVVTIG TVIQTAAVNM GMFLAGRALA GYAVGGLVGT | 120 |
| VPIYLSEISS PHQRGLIGGI SGCGISFGTM ASNWVGMACG YAPYGATQWR LPLGIQIPWG | 180 |
| IILFIGLATF MPNSPRLLIR KGKIEPAREE FLKIRRDLQS HEALEEFALM HAQIEYEMER | 240 |
| EITSYSEIFK LFRHRALVSI AVQTMTSLTG VNVIQYYQTI LYKSLGIDQK TILALAGVYG | 300 |
| TIAFLSNALT TRFLTDQWGR RKMILTGLAG IIVIEIYAAV MQLEFQNSDN RIGKGFAVLG | 360 |
| IYLFVVTYYG MLNSTTWLYG AEVLPMALRS KVMGLAAASH FIVNVGITEA GPSAFANIKQ | 420 |
| NYYYVFVGCT AFFLTIAWFY FPETRHKTLE EVAAAFGDRV VSLTDRDLVA EQTVFEEKVA | 480 |
| MSHVEKSDAD ADRPGSQMSR RTTHQYGQQR MPGDIWDKSE DDWGMPVNRR ITSKDFSIWS | 540 |
| PRRHRRSWPY LGFGLLVLIW WMWPASTAVD WSRYAYVTYA TNDANMCNAF MMFESLHRLG | 600 |
| SKADRVLLHN PQWIDRAQGG MDRNAQLMSL AAKRYNVKLR PARLLDERGE HTEVTSDGIS | 660 |
| TWDTSVTKLR AFELTEYDRV LHIDSDSTIL QHMDELFLAP KAPIAMPRAY WTDEVVGRWP | 720 |
| LTSLMMLIEP NPLELRGMLD TLRSWWMDQS PDKTHGYDME LLNQRFGASA MVLPHRPYAL | 780 |
| LTSEFRNTDH SAYLGTINAP APMRHKWDPD AVLKEAKLVH FSDWPLPKPW VMWPHDAVTE | 840 |
| IQPNCTKMGS DSYQYSCRER EIWKDLYNDF RKRRKDHCRL LSATAPNWPS WKKTVGAE | 898 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT8 | 572 | 832 | 1.1e-21 | 0.8871595330739299 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395036 | Sugar_tr | 3.02e-81 | 10 | 456 | 1 | 452 | Sugar (and other) transporter. |
| 340914 | MFS_HXT | 2.43e-79 | 10 | 452 | 2 | 399 | Fungal Hexose transporter subfamily of the Major Facilitator Superfamily of transporters and similar proteins. The fungal hexose transporter (HXT) subfamily is comprised of functionally redundant proteins that function mainly in the transport of glucose, as well as other sugars such as galactose and fructose. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has 20 genes that encode proteins in this family (HXT1 to HXT17, GAL2, SNF3, and RGT2). Seven of these (HXT1-7) encode functional glucose transporters. Gal2p is a galactose transporter, while Rgt2p and Snf3p act as cell surface glucose receptors that initiate signal transduction in response to glucose, functioning in an induction pathway responsible for glucose uptake. Rgt2p is activated by high levels of glucose and stimulates expression of low affinity glucose transporters such as Hxt1p and Hxt3p, while Snf3p generates a glucose signal in response to low levels of glucose, stimulating the expression of high affinity glucose transporters such as Hxt2p and Hxt4p. Schizosaccharomyces pombe contains eight GHT genes (GHT1-8) belonging to this family. Ght1, Ght2, and Ght5 are high-affinity glucose transporters; Ght3 is a high-affinity gluconate transporter; and Ght6 high-affinity fructose transporter. The substrate specificities for Ght4, Ght7, and Ght8 remain undetermined. The HXT subfamily belongs to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 133064 | GT8_GNT1 | 7.16e-79 | 574 | 870 | 1 | 278 | GNT1 is a fungal enzyme that belongs to the GT 8 family. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is a fungal enzyme that catalyzes the addition of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine to mannotetraose side chains by an alpha 1-2 linkage during the synthesis of mannan. The N-acetyl-D-glucosamine moiety in mannan plays a role in the attachment of mannan to asparagine residues in proteins. The mannotetraose and its N-acetyl-D-glucosamine derivative side chains of mannan are the principle immunochemical determinants on the cell surface. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is a member of glycosyltransferase family 8, which are, based on the relative anomeric stereochemistry of the substrate and product in the reaction catalyzed, retaining glycosyltransferases. |
| 340873 | MFS_GLUT_like | 3.39e-53 | 13 | 443 | 1 | 365 | Glucose transporters (GLUTs) and other similar sugar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This family is composed of glucose transporters (GLUTs) and other sugar transporters including fungal hexose transporters (HXT), bacterial xylose transporter (XylE), plant sugar transport proteins (STP) and polyol transporters (PLT), H(+)-myo-inositol cotransporter (HMIT), and similar proteins. GLUTs, also called Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporters (SLC2A), are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. The GLUT-like family belongs to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 340915 | MFS_GLUT_Class1_2_like | 4.16e-50 | 14 | 447 | 5 | 447 | Class 1 and Class 2 Glucose transporters (GLUTs) of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This subfamily includes Class 1 and Class 2 glucose transporters (GLUTs) including Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1, also called glucose transporter type 1 or GLUT1), SLC2A2-5 (GLUT2-5), SLC2A7 (GLUT7), SLC2A9 (GLUT9), SLC2A11 (GLUT11), SLC2A14 (GLUT14), and similar proteins. GLUTs are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). GLUTs 1-5 are the most thoroughly studied and are well-established as glucose and/or fructose transporters in various tissues and cell types. GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. They belong to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UJO21534.1|GT8 | 3.97e-141 | 521 | 892 | 6 | 389 |
| QDS73023.1|GT8 | 8.43e-123 | 554 | 897 | 51 | 393 |
| SMR53728.1|GT8 | 1.55e-122 | 521 | 892 | 14 | 399 |
| SMQ51594.1|GT8 | 1.55e-122 | 521 | 892 | 14 | 399 |
| SMR56054.1|GT8 | 1.55e-122 | 521 | 892 | 14 | 399 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4LDS_A | 3.29e-34 | 10 | 465 | 8 | 446 | The inward-facing structure of the glucose transporter from Staphylococcus epidermidis [Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228],4LDS_B The inward-facing structure of the glucose transporter from Staphylococcus epidermidis [Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228] |
| 4ZW9_A | 1.35e-31 | 14 | 456 | 39 | 487 | Crystal structure of human GLUT3 bound to D-glucose in the outward-occluded conformation at 1.5 angstrom [Homo sapiens],4ZWB_A Crystal structure of maltose-bound human GLUT3 in the outward-occluded conformation at 2.4 angstrom [Homo sapiens],4ZWC_A Crystal structure of maltose-bound human GLUT3 in the outward-open conformation at 2.6 angstrom [Homo sapiens],4ZWC_B Crystal structure of maltose-bound human GLUT3 in the outward-open conformation at 2.6 angstrom [Homo sapiens],7CRZ_A Chain A, Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 [Homo sapiens] |
| 7SPS_A | 1.43e-31 | 14 | 456 | 44 | 492 | Chain A, Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 [Homo sapiens],7SPS_B Chain B, Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 [Homo sapiens] |
| 5C65_A | 1.54e-31 | 14 | 456 | 17 | 465 | Structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT3 / SLC2A3 [Homo sapiens],5C65_B Structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT3 / SLC2A3 [Homo sapiens] |
| 7SPT_A | 1.92e-31 | 14 | 456 | 44 | 492 | Chain A, Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q4WBL2|GNT1_ASPFU | 2.27e-86 | 543 | 875 | 39 | 371 | Glucose N-acetyltransferase 1 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=gnt1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q4HVS2|GNT1_GIBZE | 3.36e-78 | 569 | 893 | 150 | 449 | Glucose N-acetyltransferase 1 OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=GNT1 PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|P39932|STL1_YEAST | 1.27e-47 | 1 | 457 | 22 | 489 | Sugar transporter STL1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=STL1 PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|K0E3U9|ECDD_ASPRU | 6.66e-47 | 5 | 452 | 16 | 484 | Major facilitator-type transporter ecdD OS=Aspergillus rugulosus OX=41736 GN=ecdD PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P38695|HXT5_YEAST | 2.06e-46 | 12 | 461 | 91 | 554 | Probable glucose transporter HXT5 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=HXT5 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000078 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
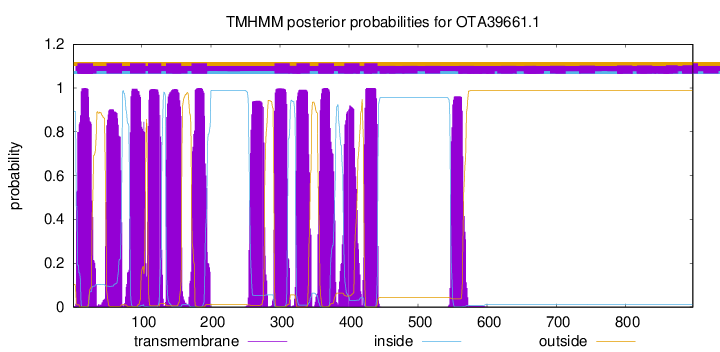
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 7 | 29 |
| 49 | 71 |
| 83 | 105 |
| 109 | 128 |
| 135 | 157 |
| 172 | 194 |
| 292 | 314 |
| 324 | 343 |
| 356 | 378 |
| 393 | 415 |
| 422 | 441 |
