You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: OTA39433.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: OTA39433.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Dothideomycetes; ; Teratosphaeriaceae; Hortaea; Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | OTA39433.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT41 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Chloride channel protein [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:A0A1Z5TTV6] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 1097 | 1227 | 5.3e-28 | 0.6476190476190476 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 239656 | ClC_3_like | 0.0 | 440 | 932 | 1 | 445 | ClC-3-like chloride channel proteins. This CD includes ClC-3, ClC-4, ClC-5 and ClC-Y1. ClC-3 was initially cloned from rat kidney. Expression of ClC-3 produces outwardly-rectifying Cl currents that are inhibited by protein kinase C activation. It has been suggested that ClC-3 may be a ubiquitous swelling-activated Cl channel that has very similar characteristics to those of native volume-regulated Cl currents. The function of ClC-4 is unclear. Studies of human ClC-4 have revealed that it gives rise to Cl currents that rapidly activate at positive voltages, and are sensitive to extracellular pH, with currents decreasing when pH falls below 6.5. ClC-4 is broadly distributed, especially in brain and heart. ClC-5 is predominantly expressed in the kidney, but can be found in the brain and liver. Mutations in the ClC-5 gene cause certain hereditary diseases, including Dent's disease, an X-chromosome linked syndrome characterised by proteinuria, hypercalciuria, and kidney stones (nephrolithiasis), leading to progressive renal failure. These proteins belong to the ClC superfamily of chloride ion channels, which share the unique double-barreled architecture and voltage-dependent gating mechanism. The gating is conferred by the permeating anion itself, acting as the gating charge. This domain is found in the eukaryotic halogen ion (Cl- and I-) channel proteins, that perform a variety of functions including cell volume regulation, the membrane potential stabilization, transepithelial chloride transport and charge compensation necessary for the acidification of intracellular organelles. |
| 238507 | ClC_euk | 2.65e-104 | 440 | 921 | 1 | 416 | Chloride channel, ClC. These domains are found in the eukaryotic halogen ion (Cl-, Br- and I-) channel proteins that perform a variety of functions including cell volume regulation, membrane potential stabilization, charge compensation necessary for the acidification of intracellular organelles, signal transduction and transepithelial transport. They are also involved in many pathophysiological processes and are responsible for a number of human diseases. These proteins belong to the ClC superfamily of chloride ion channels, which share the unique double-barreled architecture and voltage-dependent gating mechanism. The gating is conferred by the permeating anion itself, acting as the gating charge. Some proteins possess long C-terminal cytoplasmic regions containing two CBS (cystathionine beta synthase) domains of putative regulatory function. |
| 239657 | ClC_6_like | 7.30e-95 | 508 | 934 | 72 | 461 | ClC-6-like chloride channel proteins. This CD includes ClC-6, ClC-7 and ClC-B, C, D in plants. Proteins in this family are ubiquitous in eukarotes and their functions are unclear. They are expressed in intracellular organelles membranes. This family belongs to the ClC superfamily of chloride ion channels, which share the unique double-barreled architecture and voltage-dependent gating mechanism. The gating is conferred by the permeating anion itself, acting as the gating charge. ClC chloride ion channel superfamily perform a variety of functions including cellular excitability regulation, cell volume regulation, membrane potential stabilization, acidification of intracellular organelles, signal transduction, and transepithelial transport in animals. |
| 239655 | ClC_1_like | 2.06e-87 | 432 | 932 | 1 | 424 | ClC-1-like chloride channel proteins. This CD includes isoforms ClC-0, ClC-1, ClC-2 and ClC_K. ClC-1 is expressed in skeletal muscle and its mutation leads to both recessively and dominantly-inherited forms of muscle stiffness or myotonia. ClC-K is exclusively expressed in kidney. Similarly, mutation of ClC-K leads to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in mice and Bartter's syndrome in human. These proteins belong to the ClC superfamily of chloride ion channels, which share the unique double-barreled architecture and voltage-dependent gating mechanism. The gating is conferred by the permeating anion itself, acting as the gating charge. This domain is found in the eukaryotic halogen ion (Cl-, Br- and I-) channel proteins, that perform a variety of functions including cell volume regulation, regulation of intracelluar chloride concentration, membrane potential stabilization, charge compensation necessary for the acidification of intracellular organelles and transepithelial chloride transport. |
| 395529 | Voltage_CLC | 1.04e-83 | 523 | 912 | 1 | 343 | Voltage gated chloride channel. This family of ion channels contains 10 or 12 transmembrane helices. Each protein forms a single pore. It has been shown that some members of this family form homodimers. In terms of primary structure, they are unrelated to known cation channels or other types of anion channels. Three ClC subfamilies are found in animals. ClC-1 is involved in setting and restoring the resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle, while other channels play important parts in solute concentration mechanisms in the kidney. These proteins contain two pfam00571 domains. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.64e-53 | 1098 | 1254 | 101 | 249 | |
| 1.35e-40 | 1098 | 1253 | 101 | 253 | |
| 3.76e-37 | 1098 | 1236 | 110 | 241 | |
| 1.79e-36 | 1074 | 1233 | 83 | 239 | |
| 2.26e-36 | 1081 | 1253 | 82 | 249 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.24e-55 | 433 | 1089 | 127 | 787 | CLC-7/Ostm1 membrane protein complex [Homo sapiens],7BXU_B CLC-7/Ostm1 membrane protein complex [Homo sapiens],7JM7_A Structure of human CLC-7/OSTM1 complex [Homo sapiens],7JM7_C Structure of human CLC-7/OSTM1 complex [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.02e-54 | 433 | 1089 | 147 | 807 | Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex with ATP [Homo sapiens],7CQ5_D Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex with ATP [Homo sapiens],7CQ6_C Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex [Homo sapiens],7CQ6_D Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex [Homo sapiens],7CQ7_C Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex with ADP [Homo sapiens],7CQ7_D Structure of the human CLCN7-OSTM1 complex with ADP [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.07e-54 | 433 | 1089 | 123 | 784 | Structure of chicken CLC-7 [Gallus gallus],7JM6_B Structure of chicken CLC-7 [Gallus gallus] |
|
| 9.52e-47 | 510 | 1091 | 55 | 621 | Crystal Structure of a eukaryotic CLC transporter [Cyanidioschyzon merolae],3ORG_B Crystal Structure of a eukaryotic CLC transporter [Cyanidioschyzon merolae],3ORG_C Crystal Structure of a eukaryotic CLC transporter [Cyanidioschyzon merolae],3ORG_D Crystal Structure of a eukaryotic CLC transporter [Cyanidioschyzon merolae] |
|
| 5.52e-45 | 512 | 1017 | 162 | 673 | Human CLC-1 chloride ion channel, transmembrane domain [Homo sapiens],6COY_B Human CLC-1 chloride ion channel, transmembrane domain [Homo sapiens],6COZ_A Human CLC-1 chloride ion channel, C-terminal cytosolic domain [Homo sapiens],6COZ_B Human CLC-1 chloride ion channel, C-terminal cytosolic domain [Homo sapiens],6QV6_A CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, membrane domain [Homo sapiens],6QV6_B CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, membrane domain [Homo sapiens],6QVB_A CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 3 [Homo sapiens],6QVB_B CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 3 [Homo sapiens],6QVC_A CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 1 [Homo sapiens],6QVC_B CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 1 [Homo sapiens],6QVD_A CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 2 [Homo sapiens],6QVD_B CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 2 [Homo sapiens],6QVU_A CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, low pH [Homo sapiens],6QVU_B CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, low pH [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.20e-188 | 362 | 1089 | 60 | 800 | H(+)/Cl(-) exchange transporter 3 OS=Rattus norvegicus OX=10116 GN=Clcn3 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 5.20e-188 | 362 | 1089 | 60 | 800 | H(+)/Cl(-) exchange transporter 3 OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=CLCN3 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 5.20e-188 | 362 | 1089 | 60 | 800 | H(+)/Cl(-) exchange transporter 3 OS=Oryctolagus cuniculus OX=9986 GN=CLCN3 PE=2 SV=3 |
|
| 1.44e-187 | 362 | 1089 | 60 | 800 | H(+)/Cl(-) exchange transporter 3 OS=Cavia porcellus OX=10141 GN=CLCN3 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 5.63e-187 | 362 | 1089 | 60 | 800 | H(+)/Cl(-) exchange transporter 3 OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Clcn3 PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000076 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
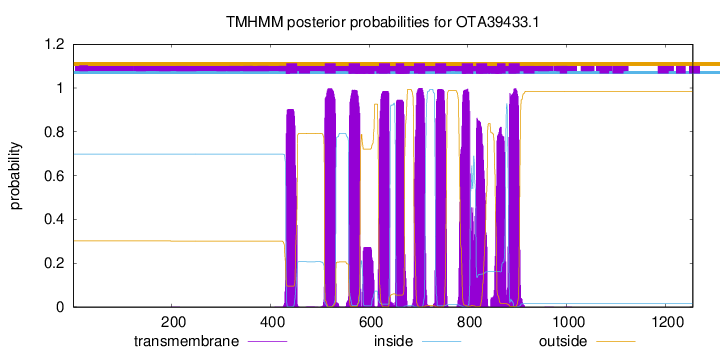
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 432 | 454 |
| 510 | 532 |
| 559 | 581 |
| 620 | 642 |
| 654 | 671 |
| 691 | 713 |
| 734 | 756 |
| 788 | 810 |
| 817 | 839 |
| 859 | 876 |
| 883 | 905 |
