You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: OTA33807.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: OTA33807.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Dothideomycetes; ; Teratosphaeriaceae; Hortaea; Hortaea werneckii | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | OTA33807.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH47 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Expansin-like EG45 domain-containing protein [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:A0A1Z5TCM8] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBM63 | 147 | 217 | 1.3e-18 | 0.8717948717948718 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 409004 | DPBB_RlpA_EXP_N-like | 1.52e-34 | 36 | 131 | 2 | 94 | double-psi beta-barrel fold of RlpA, N-terminal domain of expansins, and similar domains. The double-psi beta-barrel (DPBB) fold is found in a divergent group of proteins, including endolytic peptidoglycan transglycosylase RlpA (rare lipoprotein A), EG45-like domain containing proteins, kiwellins, Streptomyces papain inhibitor (SPI), and the N-terminal domain of plant and bacterial expansins. RlpA may work in tandem with amidases to degrade peptidoglycan (PG) in the division septum and lateral wall to facilitate daughter cell separation. An EG45-like domain containing protein from Arabidopsis thaliana, called plant natriuretic peptide A (AtPNP-A), functions in cell volume regulation. Kiwellin proteins comprise a widespread family of plant-defense proteins that target pathogenic bacterial/fungal effectors that down-regulate plant defense responses. SPI is a stress protein produced under hyperthermal stress conditions that serves as a glutamine and lysine donor substrate for microbial transglutaminase (MTG, EC 2.3.2.13) from Streptomycetes. Some expansin family proteins display cell wall loosening activity and are involved in cell expansion and other developmental events during which cell wall modification occurs. |
| 409008 | DPBB_EXP_N-like | 5.06e-24 | 35 | 134 | 1 | 117 | N-terminal double-psi beta-barrel fold domain of the expansin family and similar domains. The plant expansin family consists of four subfamilies, alpha-expansin (EXPA), beta-expansin (EXPB), expansin-like A (EXLA), and expansin-like B (EXLB). EXPA and EXPB display cell wall loosening activity and are involved in cell expansion and other developmental events during which cell wall modification occurs. EXPA proteins function more efficiently on dicotyledonous cell walls, whereas EXPB proteins exhibit specificity for the cell walls of monocotyledons. Expansins also affect environmental stress responses. Expansin family proteins contain an N-terminal domain (D1) homologous to the catalytic domain of glycoside hydrolase family 45 (GH45) proteins but with no hydrolytic activity, and a C-terminal domain (D2) homologous to group-2 grass pollen allergens. This family also includes GH45 endoglucanases from mollusks. This model represents the N-terminal domain of expansins and similar proteins, which adopts a double-psi beta-barrel (DPBB) fold. |
| 409010 | DPBB_SPI-like | 2.55e-18 | 36 | 131 | 2 | 101 | double-psi beta-barrel fold of Streptomyces papain inhibitor and similar proteins. Streptomyces papain inhibitor (SPI) adopts a rigid, thermo-resistant double-psi-beta-barrel (DPBB) fold that is stabilized by two cysteine bridges. SPI serves as a glutamine and lysine donor substrate for microbial transglutaminase (MTG, EC 2.3.2.13) from Streptomycetes, that is used to covalently and specifically link functional amines to glutamine donor sites of therapeutic proteins. SPI is a stress protein produced under hyperthermal stress conditions, and is able to inhibit the cysteine proteases, papain and bromelain, as well as the bovine serine protease trypsin. |
| 226755 | YoaJ | 4.35e-11 | 34 | 216 | 30 | 206 | Peptidoglycan-binding domain, expansin [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 409009 | DPBB_EXLX1-like | 9.40e-10 | 36 | 129 | 4 | 99 | N-terminal double-psi beta-barrel fold domain of bacterial expansins similar to Bacillus subtilis EXLX1. This subfamily is composed of bacterial expansins including Bacillus subtilis EXLX1, also called expansin-YoaJ. Similar to plant expansins, EXLX1 contains an N-terminal domain (D1) homologous to the catalytic domain of glycoside hydrolase family 45 (GH45) proteins but with no hydrolytic activity, and a C-terminal domain (D2) homologous to group-2 grass pollen allergens. It strongly binds to crystalline cellulose via D2, and weakly binds soluble cellooligosaccharides. Bacterial expansins, which are present in some plant pathogens, have the ability to loosen plant cell walls, but with weaker activity compared to plant expansins. They may have a role in plant-bacterial interactions. This model represents the N-terminal domain of EXLX1 and similar bacterial expansins, which adopts a double-psi beta-barrel (DPBB) fold. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.97e-76 | 13 | 224 | 11 | 213 | |
| 6.46e-75 | 30 | 221 | 23 | 209 | |
| 6.46e-75 | 30 | 221 | 23 | 209 | |
| 2.11e-70 | 51 | 235 | 2 | 182 | |
| 8.71e-68 | 35 | 235 | 182 | 378 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.11e-06 | 36 | 134 | 29 | 151 | Expansin-A11 OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=EXPA11 PE=2 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
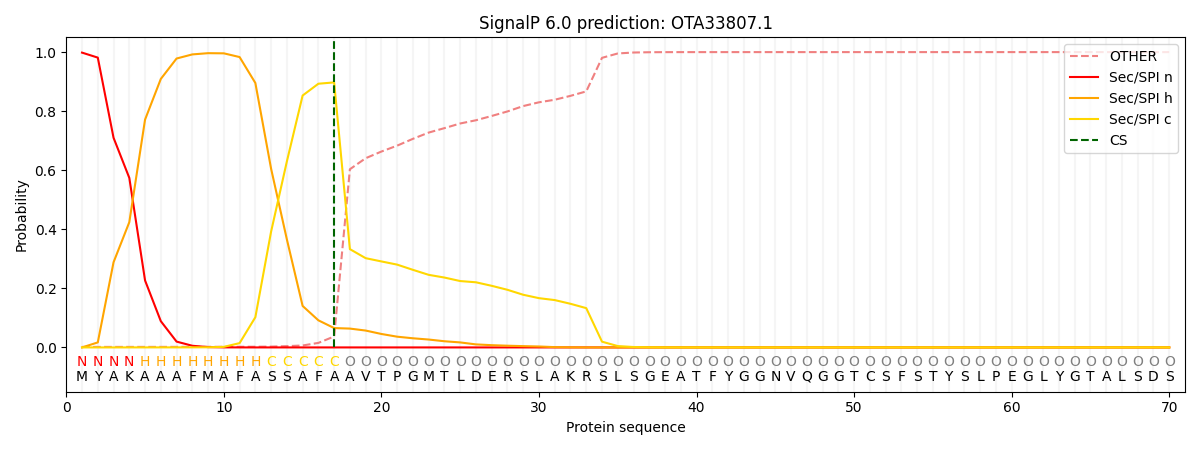
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.002880 | 0.997113 | CS pos: 17-18. Pr: 0.8974 |
