You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: OCF70739.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: OCF70739.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
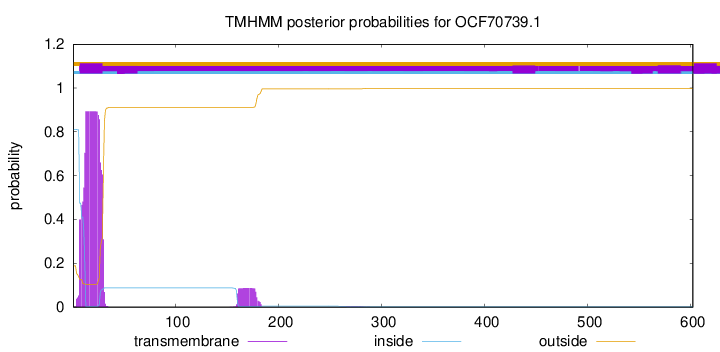
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Kwoniella mangrovensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Tremellomycetes; ; Cryptococcaceae; Kwoniella; Kwoniella mangrovensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | OCF70739.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL35 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | glycosyltransferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 274303 | tolA_full | 5.90e-06 | 538 | 583 | 102 | 158 | TolA protein. TolA couples the inner membrane complex of itself with TolQ and TolR to the outer membrane complex of TolB and OprL (also called Pal). Most of the length of the protein consists of low-complexity sequence that may differ in both length and composition from one species to another, complicating efforts to discriminate TolA (the most divergent gene in the tol-pal system) from paralogs such as TonB. Selection of members of the seed alignment and criteria for setting scoring cutoffs are based largely conserved operon struction. //The Tol-Pal complex is required for maintaining outer membrane integrity. Also involved in transport (uptake) of colicins and filamentous DNA, and implicated in pathogenesis. Transport is energized by the proton motive force. TolA is an inner membrane protein that interacts with periplasmic TolB and with outer membrane porins ompC, phoE and lamB. [Transport and binding proteins, Other, Cellular processes, Pathogenesis] |
| 225606 | TolA | 7.71e-06 | 541 | 583 | 133 | 175 | Membrane protein involved in colicin uptake [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 180240 | PRK05759 | 5.47e-05 | 541 | 583 | 70 | 113 | F0F1 ATP synthase subunit B; Validated |
| 274303 | tolA_full | 7.85e-05 | 540 | 582 | 135 | 176 | TolA protein. TolA couples the inner membrane complex of itself with TolQ and TolR to the outer membrane complex of TolB and OprL (also called Pal). Most of the length of the protein consists of low-complexity sequence that may differ in both length and composition from one species to another, complicating efforts to discriminate TolA (the most divergent gene in the tol-pal system) from paralogs such as TonB. Selection of members of the seed alignment and criteria for setting scoring cutoffs are based largely conserved operon struction. //The Tol-Pal complex is required for maintaining outer membrane integrity. Also involved in transport (uptake) of colicins and filamentous DNA, and implicated in pathogenesis. Transport is energized by the proton motive force. TolA is an inner membrane protein that interacts with periplasmic TolB and with outer membrane porins ompC, phoE and lamB. [Transport and binding proteins, Other, Cellular processes, Pathogenesis] |
| 349951 | ATP-synt_Fo_b | 8.06e-05 | 541 | 583 | 40 | 80 | F-type ATP synthase, membrane subunit b. Membrane subunit b is a component of the Fo complex of FoF1-ATP synthase. The F-type ATP synthases (FoF1-ATPase) consist of two structural domains: the F1 (assembly factor one) complex containing the soluble catalytic core, and the Fo (oligomycin sensitive factor) complex containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. F1 is composed of alpha (or A), beta (B), gamma (C), delta (D) and epsilon (E) subunits with a stoichiometry of 3:3:1:1:1, while Fo consists of the three subunits a, b, and c (1:2:10-14). An oligomeric ring of 10-14 c subunits (c-ring) make up the Fo rotor. The flux of protons through the ATPase channel (Fo) drives the rotation of the c-ring, which in turn is coupled to the rotation of the F1 complex gamma subunit rotor due to the permanent binding between the gamma and epsilon subunits of F1 and the c-ring of Fo. The F-ATP synthases are primarily found in the inner membranes of eukaryotic mitochondria, in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts or in the plasma membranes of bacteria. The F-ATP synthases are the primary producers of ATP, using the proton gradient generated by oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria) or photosynthesis (chloroplasts). Alternatively, under conditions of low driving force, ATP synthases function as ATPases, thus generating a transmembrane proton or Na(+) gradient at the expense of energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. This group also includes F-ATP synthase that has also been found in the archaea Candidatus Methanoperedens. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.67e-248 | 32 | 533 | 32 | 543 | |
| 1.67e-248 | 32 | 533 | 32 | 543 | |
| 5.29e-247 | 25 | 533 | 27 | 542 | |
| 6.54e-246 | 32 | 530 | 32 | 540 | |
| 3.05e-244 | 32 | 525 | 32 | 535 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.10e-22 | 194 | 511 | 143 | 395 | Initiation-specific alpha-1,6-mannosyltransferase OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=och1 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 1.04e-16 | 180 | 521 | 86 | 385 | Initiation-specific alpha-1,6-mannosyltransferase OS=Candida albicans (strain SC5314 / ATCC MYA-2876) OX=237561 GN=OCH1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 5.81e-08 | 194 | 494 | 131 | 371 | Putative glycosyltransferase HOC1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=HOC1 PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.998321 | 0.001679 |