You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: NCU03657-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: NCU03657-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
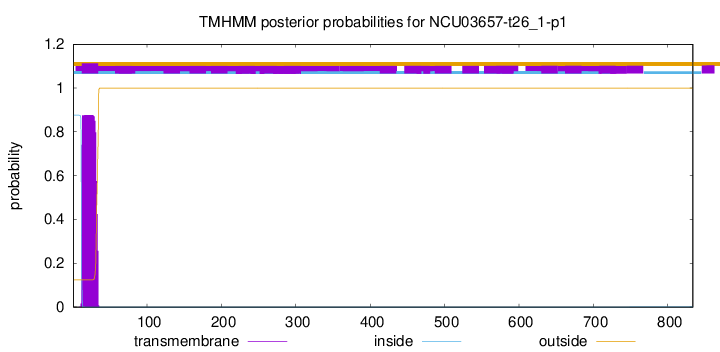
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Neurospora crassa | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Sordariaceae; Neurospora; Neurospora crassa | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | NCU03657-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH105 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.106:25 | 3.2.1.-:4 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH63 | 601 | 810 | 3e-32 | 0.4298245614035088 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397353 | Glyco_hydro_63 | 0.0 | 315 | 813 | 1 | 494 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 63 C-terminal domain. This is a family of eukaryotic enzymes belonging to glycosyl hydrolase family 63. They catalyze the specific cleavage of the non-reducing terminal glucose residue from Glc(3)Man(9)GlcNAc(2). Mannosyl oligosaccharide glucosidase EC:3.2.1.106 is the first enzyme in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway. This family represents the C-terminal catalytic domain. |
| 407154 | Glyco_hydro_63N | 2.63e-105 | 52 | 273 | 1 | 221 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 63 N-terminal domain. This is a family of eukaryotic enzymes belonging to glycosyl hydrolase family 63. They catalyze the specific cleavage of the non-reducing terminal glucose residue from Glc(3)Man(9)GlcNAc(2). Mannosyl oligosaccharide glucosidase EC:3.2.1.106 is the first enzyme in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway. This family represents the N-terminal beta sandwich domain. |
| 225942 | GDB1 | 3.27e-06 | 612 | 765 | 427 | 565 | Glycogen debranching enzyme (alpha-1,6-glucosidase) [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 283786 | GDE_C | 3.46e-06 | 614 | 766 | 179 | 333 | Amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase. This family includes human glycogen branching enzyme AGL. This enzyme contains a number of distinct catalytic activities. It has been shown for the yeast homolog GDB1 that mutations in this region disrupt the enzymes Amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase (EC:3.2.1.33). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 828 | 1 | 828 | |
| 0.0 | 13 | 816 | 17 | 822 | |
| 0.0 | 10 | 823 | 5 | 831 | |
| 0.0 | 30 | 830 | 28 | 830 | |
| 0.0 | 30 | 830 | 28 | 830 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.54e-177 | 43 | 811 | 6 | 800 | Crystal structure of Processing alpha-Glucosidase I [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C] |
|
| 3.66e-135 | 52 | 814 | 37 | 778 | Murine endoplasmic reticulum alpha-glucosidase I with N-9'-methoxynonyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [Mus musculus],5MHF_B Murine endoplasmic reticulum alpha-glucosidase I with N-9'-methoxynonyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [Mus musculus],5MHF_C Murine endoplasmic reticulum alpha-glucosidase I with N-9'-methoxynonyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [Mus musculus],5MHF_D Murine endoplasmic reticulum alpha-glucosidase I with N-9'-methoxynonyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [Mus musculus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.28e-233 | 43 | 812 | 33 | 805 | Probable mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPAC6G10.09 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 7.48e-176 | 43 | 811 | 36 | 830 | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=CWH41 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 8.41e-137 | 52 | 814 | 92 | 833 | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Mogs PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.05e-133 | 54 | 814 | 94 | 833 | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Rattus norvegicus OX=10116 GN=Mogs PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.62e-127 | 52 | 812 | 94 | 834 | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=MOGS PE=1 SV=5 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
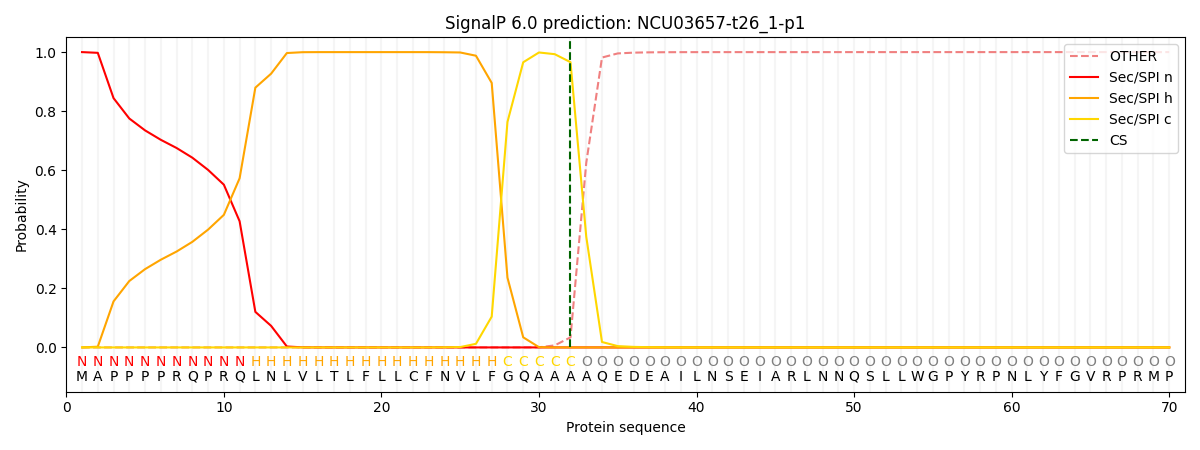
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000258 | 0.999711 | CS pos: 32-33. Pr: 0.9659 |