You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: M747DRAFT_366860-t43_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: M747DRAFT_366860-t43_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
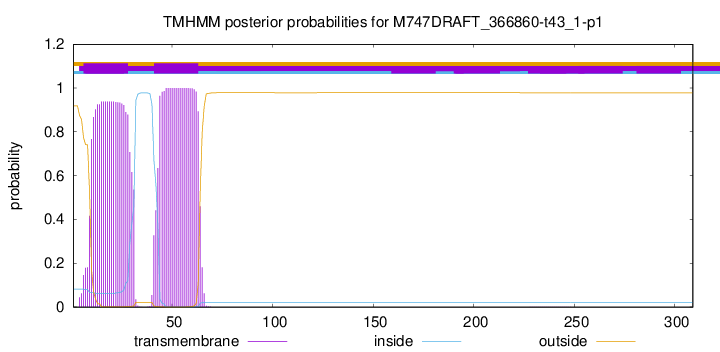
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus niger | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus niger | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | M747DRAFT_366860-t43_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT31 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | glycoside hydrolase/deacetylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE4 | 95 | 233 | 5e-21 | 0.9615384615384616 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200581 | CE4_NodB_like_2 | 1.97e-80 | 100 | 292 | 1 | 189 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized chitin deacetylases and hypothetical proteins. This family includes some uncharacterized chitin deacetylases and hypothetical proteins, mainly from eukaryotes. Although their biological function is unknown, members in this family show high sequence homology to the catalytic NodB homology domain of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum chitin deacetylase (endo-chitin de-N-acetylase, ClCDA, EC 3.5.1.41), which catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-acetamido groups of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitin, converting it to chitosan in fungal cell walls. Like ClCDA, this family is a member the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. |
| 213022 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 2.08e-39 | 100 | 281 | 1 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| 200578 | CE4_CtAXE_like | 1.63e-38 | 100 | 292 | 1 | 179 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase and its bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase (CtAXE, EC 3.1.1.72), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. CtAXE deacetylates O-acetylated xylan, a key component of plant cell walls. It shows no detectable activity on generic esterase substrates including para-nitrophenyl acetate. It is specific for sugar-based substrates and will precipitate acetylxylan, as a consequence of deacetylation. CtAXE is a monomeric protein containing a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold as other CE4 esterases. However, due to differences in the topography of the substrate-binding groove, the chemistry of the active center, and metal ion coordination, CtAXE has different metal ion preference and lacks activity on N-acetyl substrates. It is significantly activated by Co2+. Moreover, CtAXE displays distinctly different ligand coordination to the metal ion, utilizing an aspartate, a histidine, and four water molecules, as opposed to the conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad of other CE4 esterases. |
| 200582 | CE4_NodB_like_3 | 6.63e-31 | 100 | 290 | 1 | 187 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases. This family includes many uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases. Although their biological function still remains unknown, members in this family show high sequence homology to the catalytic NodB homology domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide deacetylase PgdA (SpPgdA), which is an extracellular metal-dependent polysaccharide deacetylase with de-N-acetylase activity toward a hexamer of chitooligosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine, but not shorter chitooligosaccharides or a synthetic peptidoglycan tetrasaccharide. Like SpPgdA, this family is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. |
| 200584 | CE4_GT2-like | 9.43e-30 | 100 | 294 | 1 | 195 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial glycosyl transferase, group 2-like family proteins. This family includes many uncharacterized bacterial proteins containing an N-terminal GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) domain, a middle NodB-like homology domain, and a C-terminal GT2-like (glycosyl transferase group 2) domain. Although their biological function is unknown, members in this family contain a middle NodB homology domain that is similar to the catalytic domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide deacetylase PgdA (SpPgdA), an extracellular metal-dependent polysaccharide deacetylase with de-N-acetylase activity toward a hexamer of chitooligosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine, but not shorter chitooligosaccharides or a synthetic peptidoglycan tetrasaccharide. Like SpPgdA, this family is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. The presence of three domains suggests that members of this family may be multifunctional. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.94e-213 | 1 | 309 | 1 | 309 | |
| 2.83e-88 | 59 | 302 | 14 | 251 | |
| 1.02e-84 | 25 | 303 | 8 | 268 | |
| 3.85e-82 | 59 | 305 | 14 | 246 | |
| 3.85e-82 | 59 | 305 | 14 | 246 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.40e-21 | 80 | 295 | 95 | 301 | Chain A, Predicted xylanase/chitin deacetylase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus subsp. tengcongensis MB4] |
|
| 3.94e-17 | 99 | 295 | 3 | 187 | Crystal structure of the Xyl-CE4 domain of a multidomain xylanase from the hindgut metagenome of Trinervitermes trinervoides [uncultured bacterium] |
|
| 2.06e-16 | 96 | 294 | 232 | 416 | Structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase (SpPgdA) [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6] |
|
| 5.49e-16 | 94 | 295 | 79 | 268 | Crystal structure of a BA3943 mutant,a CE4 family pseudoenzyme with restored enzymatic activity. [Bacillus anthracis] |
|
| 7.02e-16 | 87 | 294 | 20 | 221 | Chain A, CHITIN DEACETYLASE [Aspergillus nidulans],2Y8U_B Chain B, CHITIN DEACETYLASE [Aspergillus nidulans] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.57e-27 | 83 | 294 | 15 | 209 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase BC_3618 OS=Bacillus cereus (strain ATCC 14579 / DSM 31 / CCUG 7414 / JCM 2152 / NBRC 15305 / NCIMB 9373 / NCTC 2599 / NRRL B-3711) OX=226900 GN=BC_3618 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 6.49e-16 | 97 | 292 | 263 | 444 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase PgdA OS=Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a (strain EGD / Mackaness) OX=1334565 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 6.49e-16 | 97 | 292 | 263 | 444 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase PgdA OS=Listeria monocytogenes serovar 1/2a (strain ATCC BAA-679 / EGD-e) OX=169963 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 6.49e-16 | 97 | 292 | 263 | 444 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase PgdA OS=Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a (strain 10403S) OX=393133 GN=pgdA PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.17e-15 | 96 | 294 | 264 | 448 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) OX=171101 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
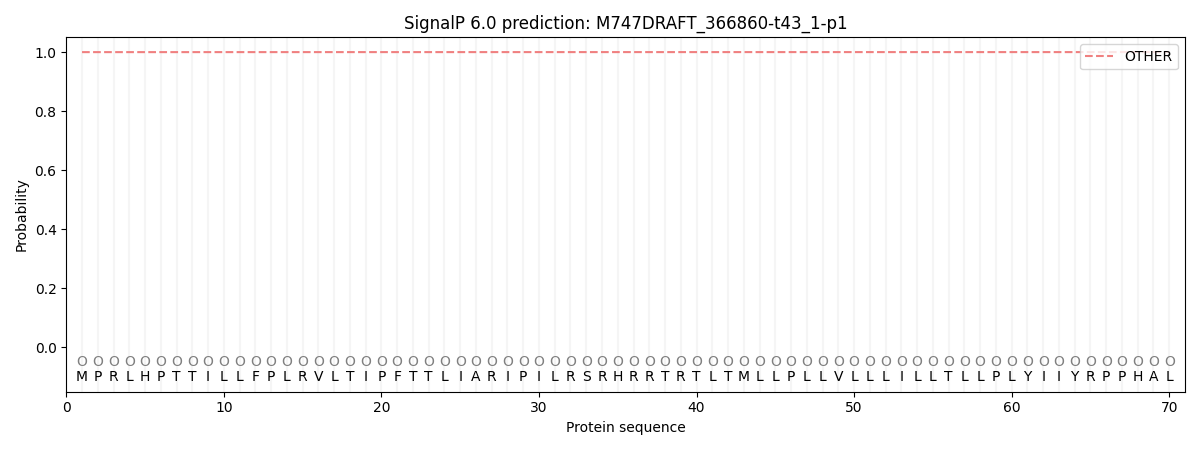
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999980 | 0.000019 |