You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KZZ92659.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KZZ92659.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
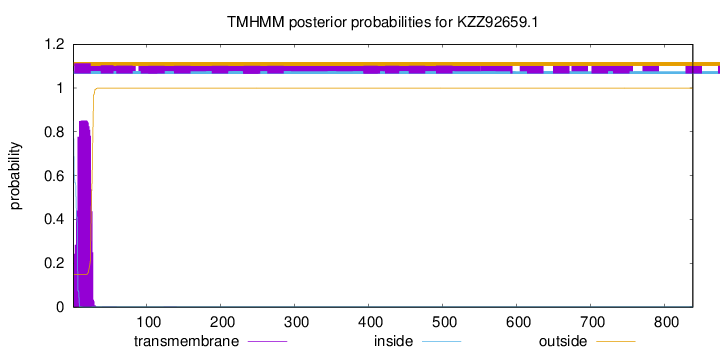
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Ascosphaera apis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Ascosphaeraceae; Ascosphaera; Ascosphaera apis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KZZ92659.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH72 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Laccase TilA [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:A0A167ZHC5] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 157265; End:161590 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MLALSSSMFL LLLNIFILSI TALPLSLKHT PTPRSLTNKT ITLIIENQIV SPNGIPRMGI | 60 |
| TVNGQTPGPT YTFDQDDEIT VEVINHLDED TSVHFHGIEQ WGTPWSDGVP GVTQRPIAPG | 120 |
| QTFLYQWKAT AAGAYWYHSH YKGQIADGLH GAILINPRNG TANPFGVIAG NDTVELEKLE | 180 |
| RAERDSRVIV LGDWTNFTYH EVMDIEYASG VDYFCIDSLT INGKGKNICK SQEELNELER | 240 |
| PNQLALTKNR DLTLKGCLPA DKYQALHPYP YDLSKLPRAS FDECTPSENE PEVIEVDPND | 300 |
| GWVSLTLIAA SPATQPLFTI DNHSMWIYAV DGPYVHPRFV NGVQVPASRR YQVFVKLDQK | 360 |
| PGDYTIRVPS LTGSQIISGY GVFRYKEGGN STAEYNSTAG YNSTAGDVYN ATAPPANATF | 420 |
| AAGNTTLGVA NMTKRDVGES TPWVGYNGLN LTETFIMNED IDLKPFPPHK PASTAQRTII | 480 |
| FDAGFFHHDW EWTLSGKAAI NDTYDTPALF DPKPDNELIF ETKMGEWVDV IIRQPNGQPA | 540 |
| HPIHKHSIKF YVIGRGNFFF NYSSVEEAME VHPEAFDLET PPFADTFLTP QTRTGPGFLA | 600 |
| LRYHVENPGA FMMHCHIQTH LDGGMGVVFL DAMDELPAIP ERYDYLFKLL LIGDSGVGKS | 660 |
| CLLLRFADDT YTESYISTIG VDFKIRTIEL DGKTVKLQIW DTAGQERFRT ITSSYYRGAH | 720 |
| GICVVYDVTD MDSFNNVRQW LQEIDRYATE GVNKLLVGNK SDMEDKKVVE YSVAKEFADS | 780 |
| LGIPFLETSA KNASNVEQAF LTMARQIKER MGSNTVNNKP TVQVTGRDVP SNNSSGCC | 838 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA1 | 56 | 625 | 1.7e-77 | 0.9748603351955307 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 206661 | Rab1_Ypt1 | 4.54e-129 | 645 | 810 | 1 | 166 | Rab GTPase family 1 includes the yeast homolog Ypt1. Rab1/Ypt1 subfamily. Rab1 is found in every eukaryote and is a key regulatory component for the transport of vesicles from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. Studies on mutations of Ypt1, the yeast homolog of Rab1, showed that this protein is necessary for the budding of vesicles of the ER as well as for their transport to, and fusion with, the Golgi apparatus. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) interact with GTP-bound Rab and accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) interact with GDP-bound Rabs to promote the formation of the GTP-bound state. Rabs are further regulated by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which facilitate Rab recycling by masking C-terminal lipid binding and promoting cytosolic localization. Most Rab GTPases contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with sequence motifs CC, CXC, or CCX. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rab proteins. Due to the presence of truncated sequences in this CD, the lipid modification site is not available for annotation. |
| 206659 | Rab8_Rab10_Rab13_like | 2.78e-107 | 644 | 810 | 1 | 167 | Rab GTPase families 8, 10, 13 (Rab8, Rab10, Rab13). Rab8/Sec4/Ypt2 are known or suspected to be involved in post-Golgi transport to the plasma membrane. It is likely that these Rabs have functions that are specific to the mammalian lineage and have no orthologs in plants. Rab8 modulates polarized membrane transport through reorganization of actin and microtubules, induces the formation of new surface extensions, and has an important role in directed membrane transport to cell surfaces. The Ypt2 gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a member of the Ypt/Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins, related in sequence to Sec4p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae but closer to mammalian Rab8. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) interact with GTP-bound Rab and accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) interact with GDP-bound Rabs to promote the formation of the GTP-bound state. Rabs are further regulated by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which facilitate Rab recycling by masking C-terminal lipid binding and promoting cytosolic localization. Most Rab GTPases contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with sequence motifs CC, CXC, or CCX. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rab proteins. Due to the presence of truncated sequences in this CD, the lipid modification site is not available for annotation. |
| 197555 | RAB | 1.20e-96 | 647 | 810 | 1 | 164 | Rab subfamily of small GTPases. Rab GTPases are implicated in vesicle trafficking. |
| 395024 | Ras | 1.69e-94 | 648 | 809 | 1 | 162 | Ras family. Includes sub-families Ras, Rab, Rac, Ral, Ran, Rap Ypt1 and more. Shares P-loop motif with GTP_EFTU, arf and myosin_head. See pfam00009 pfam00025, pfam00063. As regards Rab GTPases, these are important regulators of vesicle formation, motility and fusion. They share a fold in common with all Ras GTPases: this is a six-stranded beta-sheet surrounded by five alpha-helices. |
| 206640 | Rab | 2.85e-91 | 647 | 805 | 1 | 159 | Ras-related in brain (Rab) family of small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Rab GTPases form the largest family within the Ras superfamily. There are at least 60 Rab genes in the human genome, and a number of Rab GTPases are conserved from yeast to humans. Rab GTPases are small, monomeric proteins that function as molecular switches to regulate vesicle trafficking pathways. The different Rab GTPases are localized to the cytosolic face of specific intracellular membranes, where they regulate distinct steps in membrane traffic pathways. In the GTP-bound form, Rab GTPases recruit specific sets of effector proteins onto membranes. Through their effectors, Rab GTPases regulate vesicle formation, actin- and tubulin-dependent vesicle movement, and membrane fusion. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) interact with GTP-bound Rab and accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) interact with GDP-bound Rabs to promote the formation of the GTP-bound state. Rabs are further regulated by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which mask C-terminal lipid binding and promote cytosolic localization. While most unicellular organisms possess 5-20 Rab members, several have been found to possess 60 or more Rabs; for many of these Rab isoforms, homologous proteins are not found in other organisms. Most Rab GTPases contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with sequence motifs CC, CXC, or CCX. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rab proteins. Since crystal structures often lack C-terminal residues, the lipid modification site is not available for annotation in many of the CDs in the hierarchy, but is included where possible. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSS52076.1|AA1 | 1.40e-165 | 51 | 643 | 44 | 599 |
| QSS70055.1|AA1 | 1.98e-165 | 51 | 643 | 44 | 599 |
| CAK37372.1|AA1 | 3.11e-152 | 50 | 643 | 35 | 589 |
| BCR93223.1|AA1 | 4.23e-149 | 50 | 643 | 35 | 589 |
| BCS05875.1|AA1 | 4.23e-149 | 50 | 643 | 35 | 589 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3TKL_A | 1.66e-100 | 633 | 812 | 3 | 182 | Crystal structure of the GTP-bound Rab1a in complex with the coiled-coil domain of LidA from Legionella pneumophila [Homo sapiens] |
| 4JVS_B | 1.94e-100 | 636 | 812 | 5 | 181 | Crystal structure of LepB GAP domain from Legionella drancourtii in complex with Rab1-GDP and AlF3 [Homo sapiens] |
| 2FOL_A | 1.96e-100 | 636 | 812 | 15 | 191 | Crystal structure of human RAB1A in complex with GDP [Homo sapiens] |
| 4FMC_B | 1.48e-99 | 640 | 811 | 1 | 171 | EspG-Rab1 complex [Homo sapiens],4FMC_D EspG-Rab1 complex [Homo sapiens],4FMD_B EspG-Rab1 complex structure at 3.05 A [Homo sapiens],4FMD_D EspG-Rab1 complex structure at 3.05 A [Homo sapiens],4FME_B EspG-Rab1-Arf6 complex [Homo sapiens],4FME_E EspG-Rab1-Arf6 complex [Homo sapiens] |
| 3SFV_A | 2.09e-99 | 633 | 811 | 3 | 181 | Crystal structure of the GDP-bound Rab1a S25N mutant in complex with the coiled-coil domain of LidA from Legionella pneumophila [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|A0A1S7IUL2|MCE_TALPI | 1.18e-136 | 51 | 643 | 36 | 592 | Multicopper oxidase MCE OS=Talaromyces pinophilus OX=128442 GN=MCE PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|E9RBR0|ABR2_ASPFU | 3.46e-126 | 51 | 639 | 32 | 579 | Laccase abr2 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=abr2 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q0UHZ8|ELCG_PHANO | 4.38e-124 | 60 | 643 | 62 | 614 | Multicopper oxidase elcG OS=Phaeosphaeria nodorum (strain SN15 / ATCC MYA-4574 / FGSC 10173) OX=321614 GN=elcG PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|A0A443HK79|VDTB1_BYSSP | 3.50e-123 | 51 | 643 | 32 | 597 | Multicopper oxidase VdtB OS=Byssochlamys spectabilis OX=264951 GN=VdtB PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|I1RF62|GIP1_GIBZE | 8.92e-121 | 51 | 643 | 37 | 600 | Multicopper oxidase GIP1 OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=GIP1 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
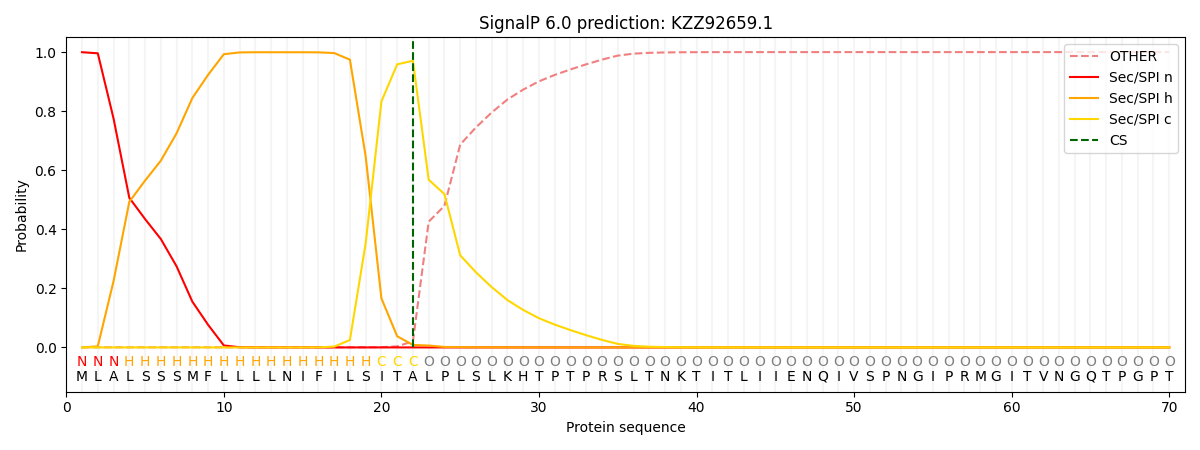
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000958 | 0.999033 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.9708 |