You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KFA56039.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KFA56039.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Stachybotrys chartarum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Stachybotryaceae; Stachybotrys; Stachybotrys chartarum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KFA56039.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT32 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 1.1.3.9:34 | 1.1.3.13:3 | 1.1.3.-:1 | 1.1.3.7:1 | 1.1.3.47:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA5 | 83 | 629 | 5.7e-214 | 0.9047619047619048 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 199882 | E_set_GO_C | 4.87e-26 | 530 | 629 | 1 | 103 | C-terminal Early set domain associated with the catalytic domain of galactose oxidase. E or "early" set domains are associated with the catalytic domain of galactose oxidase at the C-terminal end. Galactose oxidase is an extracellular monomeric enzyme which catalyzes the stereospecific oxidation of a broad range of primary alcohol substrates and possesses a unique mononuclear copper site essential for catalyzing a two-electron transfer reaction during the oxidation of primary alcohols to corresponding aldehydes. The second redox active center necessary for the reaction was found to be situated at a tyrosine residue. The C-terminal domain of galactose oxidase may be related to the immunoglobulin and/or fibronectin type III superfamilies. These domains are associated with different types of catalytic domains at either the N-terminal or C-terminal end and may be involved in homodimeric/tetrameric/dodecameric interactions. Members of this family include members of the alpha amylase family, sialidase, galactose oxidase, cellulase, cellulose, hyaluronate lyase, chitobiase, and chitinase, among others. |
| 401164 | DUF1929 | 1.93e-23 | 545 | 629 | 5 | 91 | Domain of unknown function (DUF1929). Members of this family adopt a secondary structure consisting of a bundle of seven, mostly antiparallel, beta-strands surrounding a hydrophobic core. The 7 strands are arranged in 2 sheets, in a Greek-key topology. Their precise function, has not, as yet, been defined, though they are mostly found in sugar-utilising enzymes, such as galactose oxidase. |
| 276965 | Kelch | 5.79e-11 | 223 | 309 | 10 | 93 | Kelch repeat. Kelch repeats are 44 to 56 amino acids in length and form a four-stranded beta-sheet corresponding to a single blade of five to seven bladed beta propellers. The Kelch superfamily is a large evolutionary conserved protein family whose members are present throughout the cell and extracellularly, and have diverse activities. Kelch repeats are often in combination with other domains, like BTB and BACK or F-box domains. |
| 276965 | Kelch | 2.44e-10 | 257 | 468 | 1 | 136 | Kelch repeat. Kelch repeats are 44 to 56 amino acids in length and form a four-stranded beta-sheet corresponding to a single blade of five to seven bladed beta propellers. The Kelch superfamily is a large evolutionary conserved protein family whose members are present throughout the cell and extracellularly, and have diverse activities. Kelch repeats are often in combination with other domains, like BTB and BACK or F-box domains. |
| 276965 | Kelch | 4.70e-10 | 223 | 309 | 57 | 140 | Kelch repeat. Kelch repeats are 44 to 56 amino acids in length and form a four-stranded beta-sheet corresponding to a single blade of five to seven bladed beta propellers. The Kelch superfamily is a large evolutionary conserved protein family whose members are present throughout the cell and extracellularly, and have diverse activities. Kelch repeats are often in combination with other domains, like BTB and BACK or F-box domains. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.35e-289 | 17 | 631 | 98 | 711 | |
| 2.44e-283 | 34 | 631 | 292 | 895 | |
| 7.90e-274 | 42 | 631 | 119 | 710 | |
| 2.25e-273 | 42 | 631 | 119 | 710 | |
| 2.25e-273 | 42 | 631 | 119 | 710 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.82e-291 | 17 | 631 | 78 | 691 | Copper oxidase from Colletotrichum graminicola [Colletotrichum graminicola M1.001] |
|
| 5.18e-291 | 17 | 631 | 78 | 691 | Copper oxidase from Colletotrichum graminicola [Colletotrichum graminicola M1.001],6STX_C Copper oxidase from Colletotrichum graminicola [Colletotrichum graminicola M1.001] |
|
| 1.04e-290 | 17 | 631 | 78 | 691 | Copper oxidase from Colletotrichum graminicola [Colletotrichum graminicola M1.001] |
|
| 1.52e-142 | 139 | 629 | 177 | 659 | Chain A, GALACTOSE OXIDASE [Fusarium graminearum] |
|
| 3.12e-142 | 139 | 629 | 155 | 637 | Chain A, Galactose oxidase [Fusarium graminearum] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.67e-141 | 139 | 629 | 196 | 678 | Galactose oxidase OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=GAOA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 3.04e-140 | 139 | 629 | 196 | 678 | Galactose oxidase OS=Gibberella zeae OX=5518 GN=GAOA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.19e-10 | 212 | 630 | 94 | 522 | Aldehyde oxidase GLOX OS=Vitis pseudoreticulata OX=231512 GN=GLOX PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.92e-09 | 410 | 630 | 386 | 615 | Aldehyde oxidase GLOX1 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=GLOX1 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 8.74e-06 | 223 | 300 | 777 | 854 | Kelch-like protein 29 OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Klhl29 PE=2 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
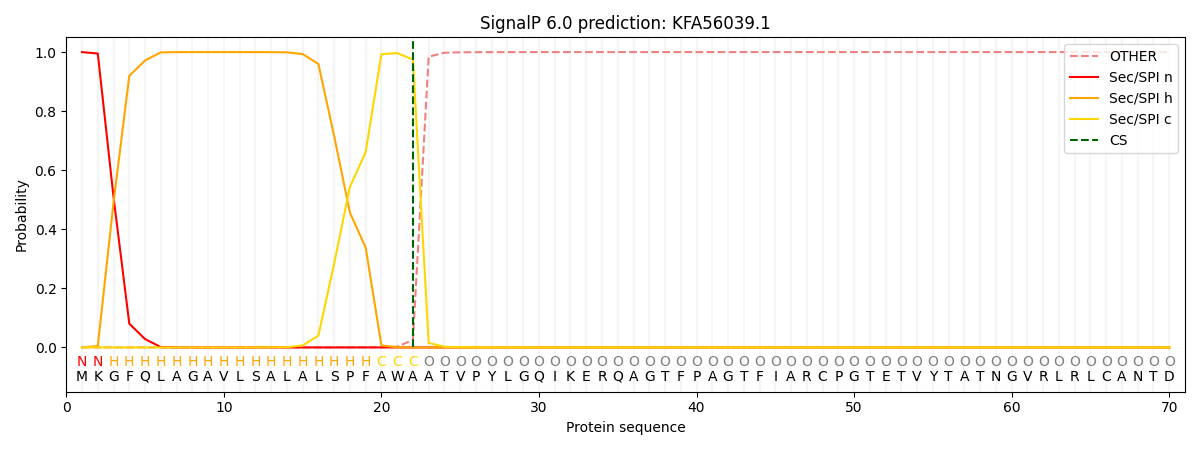
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000334 | 0.999674 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.9748 |

