You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAG6623040.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAG6623040.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phytophthora cinnamomi | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Peronosporaceae; Phytophthora; Phytophthora cinnamomi | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAG6623040.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | putative glycoside hydrolase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.26:2 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH32 | 47 | 376 | 1.7e-62 | 0.9590443686006825 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350133 | GH32_XdINV-like | 4.85e-128 | 54 | 376 | 2 | 335 | glycoside hydrolase family 32 protein such as Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous beta-fructofuranosidase (Inv;Xd-INV;XdINV). This subfamily of glycosyl hydrolase family GH32 includes fructan:fructan 1-fructosyltransferase (FT, EC 2.4.1.100) and beta-fructofuranosidase (invertase or Inv, EC 3.2.1.26), among others. These enzymes cleave sucrose into fructose and glucose via beta-fructofuranosidase activity, producing invert sugar that is a mixture of dextrorotatory D-glucose and levorotatory D-fructose, thus named invertase (EC 3.2.1.26). These retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous beta-fructofuranosidase (XdINV) also catalyzes the synthesis of fructooligosaccharides (FOS, a beneficial prebiotic), producing neo-FOS, making it an interesting biotechnology target. Structural studies show plasticity of its active site, having a flexible loop that is essential in binding sucrose and beta(2-1)-linked oligosaccharide, making it a valuable biocatalyst to produce novel bioconjugates. The breakdown of sucrose is widely used as a carbon or energy source by bacteria, fungi, and plants. Invertase is used commercially in the confectionery industry, since fructose has a sweeter taste than sucrose and a lower tendency to crystallize. A common structural feature of all these enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain, similar to GH43, that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 214757 | Glyco_32 | 3.81e-71 | 47 | 568 | 1 | 436 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 32. |
| 350110 | GH32_FFase | 1.22e-68 | 54 | 376 | 2 | 281 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 32, beta-fructosidases. Glycosyl hydrolase family GH32 cleaves sucrose into fructose and glucose via beta-fructofuranosidase activity, producing invert sugar that is a mixture of dextrorotatory D-glucose and levorotatory D-fructose, thus named invertase (EC 3.2.1.26). This family also contains other fructofuranosidases such as inulinase (EC 3.2.1.7), exo-inulinase (EC 3.2.1.80), levanase (EC 3.2.1.65), and transfructosidases such sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.99), fructan:fructan 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.100), sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.10), fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.243) and levan fructosyltransferases (EC 2.4.1.-). These retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. These enzymes are predicted to display a 5-fold beta-propeller fold as found for GH43 and CH68. The breakdown of sucrose is widely used as a carbon or energy source by bacteria, fungi, and plants. Invertase is used commercially in the confectionery industry, since fructose has a sweeter taste than sucrose and a lower tendency to crystallize. A common structural feature of all these enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain, similar to GH43, that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 224536 | SacC | 1.82e-63 | 40 | 600 | 26 | 479 | Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase SacC, GH32 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 395193 | Glyco_hydro_32N | 6.96e-48 | 47 | 374 | 1 | 295 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 32 N-terminal domain. This domain corresponds to the N-terminal domain of glycosyl hydrolase family 32 which forms a five bladed beta propeller structure. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 620 | 1 | 619 | |
| 4.08e-176 | 12 | 617 | 7 | 598 | |
| 5.38e-143 | 38 | 611 | 28 | 595 | |
| 6.42e-88 | 27 | 614 | 25 | 618 | |
| 6.50e-86 | 54 | 191 | 1 | 138 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.71e-50 | 34 | 614 | 18 | 634 | Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (wild-type) from A. japonicus [Aspergillus japonicus],3LFI_A Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (wild-type) from A. japonicus in complex with glucose [Aspergillus japonicus],3LFI_B Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (wild-type) from A. japonicus in complex with glucose [Aspergillus japonicus] |
|
| 1.89e-50 | 38 | 616 | 61 | 643 | Chain A, Beta-fructofuranosidase [Phaffia rhodozyma],6S82_B Chain B, Beta-fructofuranosidase [Phaffia rhodozyma] |
|
| 1.89e-50 | 38 | 616 | 61 | 643 | Chain A, Beta-fructofuranosidase [Phaffia rhodozyma],5ANN_B Chain B, Beta-fructofuranosidase [Phaffia rhodozyma] |
|
| 2.91e-50 | 34 | 615 | 18 | 604 | Aspergillus kawachii beta-fructofuranosidase complexed with glycerol [Aspergillus luchuensis IFO 4308],5XH9_A Aspergillus kawachii beta-fructofuranosidase [Aspergillus luchuensis IFO 4308],5XHA_A Aspergillus kawachii beta-fructofuranosidase complexed with fructose [Aspergillus luchuensis IFO 4308] |
|
| 2.15e-49 | 34 | 614 | 18 | 634 | Crystal Structure of A. japonicus CB05 [Aspergillus japonicus],3LDR_A Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (D191A) from A. japonicus in complex with 1-Kestose [Aspergillus japonicus],3LEM_A Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (D191A) from A. japonicus in complex with Nystose [Aspergillus japonicus],3LIG_A Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (D191A) from A. japonicus [Aspergillus japonicus],3LIH_A Crystal structure of fructosyltransferase (D191A) from A. japonicus in complex with raffinose [Aspergillus japonicus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.95e-36 | 25 | 605 | 11 | 498 | Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase OS=Zymomonas mobilis subsp. mobilis (strain ATCC 10988 / DSM 424 / LMG 404 / NCIMB 8938 / NRRL B-806 / ZM1) OX=555217 GN=sacA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 4.17e-35 | 32 | 604 | 116 | 646 | Beta-fructofuranosidase, soluble isoenzyme I OS=Daucus carota OX=4039 GN=INV*DC4 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 8.46e-35 | 25 | 605 | 11 | 498 | Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase OS=Zymomonas mobilis subsp. mobilis (strain ATCC 31821 / ZM4 / CP4) OX=264203 GN=sacA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 8.23e-34 | 43 | 614 | 121 | 656 | Acid beta-fructofuranosidase 4, vacuolar OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=BFRUCT4 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 1.68e-33 | 43 | 605 | 104 | 622 | Acid beta-fructofuranosidase OS=Solanum lycopersicum OX=4081 GN=TIV1 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
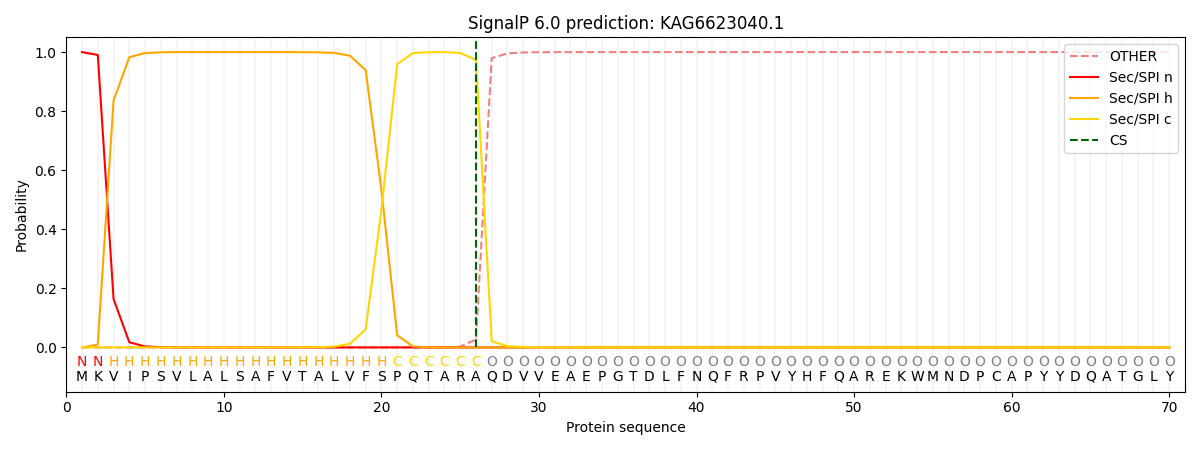
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000232 | 0.999765 | CS pos: 26-27. Pr: 0.9733 |
