You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAG5438295.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAG5438295.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
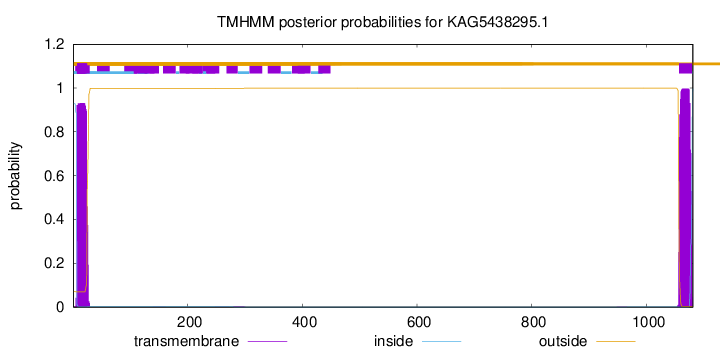
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Pneumocystis canis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Pneumocystidomycetes; ; Pneumocystidaceae; Pneumocystis; Pneumocystis canis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAG5438295.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 46206; End:50260 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MEFRCQALVL HALIYVTLFV YGRVETIQRR GNFLFYSNGE RFFIKGIAYQ PQPSLGSTKH | 60 |
| YTDPLGDPKI CSRDLPYFLD LGINTLRVYT VDPELDHTYC MNLFAESGIY VLLDLSEPRV | 120 |
| SIISTNPSWD VILLYRYIKV IDSMINYPNL IGFFAGNEVV LDTQNTHAAA FVKAAIRDIK | 180 |
| AYIKHKKYRN VLVGYAANDH HHTRIPSANY FACGDSDSAA DFFGINIYEW CEPTTYETSG | 240 |
| YKDRVNDFSN FGIPLFFSEY GCNIVNGNLG VRTFKQIQYI YSRYMTSVFS GGIVYEWFQG | 300 |
| ENSYGLVDLL NDGTISPRKD YLNLKMQLNL LKSSPPDNLG DRPTFSSPQC PSINEYWSAS | 360 |
| TSLPPVPNSE LCSCASSASS CVAVSDITNK EMEDIFSYVC SKISCRAISK DGKAGVYGAY | 420 |
| SVCNPIDQLN VILGLYHSNF NDDSACNFKG TTYPTEPRVS KTCSSLLRMV GPDGTGTITG | 480 |
| PPYATEHTKG DASQKHKGGS EKELSMKWKL ILGLEIAIRR KIENELSKKK PTAARMHPSR | 540 |
| KMDPKTVLSL SPSPPLTVQS GITVSEASQL MAAKREDCVL VVDDNQHLMG IFTAKDLAFR | 600 |
| VVGMDMDPRN LLIEDIMTKN PLCARNDTSA TDALDLMVHK GFRHLPVCDE DGNVSGILDI | 660 |
| TKCFHEAMKK VERAYTSSRQ LYDALEGVQT EWGQIEQSEQ IIQYVETLKQ KMSGPNLASA | 720 |
| LDGTTPITVN IRTSVRDAAF LMRENHTTAV LVMDQMNISG IFTSKDIVLR VIAPGLDPAN | 780 |
| CSVVRVMTPH PDCVPMDMSI QEALKKMDEG RYLNLPVLDQ ESQVIGMVDV MKLTYLILEQ | 840 |
| IKNIGSPDGE GLIWNRFWNN LEDGDSESIL SDNQLSTSQN YQSLLYASLP NNQQDIQVLS | 900 |
| PDTSATKLPQ KNEWTSPTER PTFSGKNSPL LSQIPFVFKF KSLYGKTHRI QLIPQAGYAS | 960 |
| LRLAIIERLR SELEKLGGSD DLAISFIDDE GDSVSMTTDD DMFHAVELAY KNAEDKVNLI | 1020 |
| IHHPNSSIIN QKSDDLSSIT ENHHNEKASQ SKSPKLTGYF VSISIAFCIT TIAIVYKYIR | 1080 |
| K | 1081 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.-:30 | 2.4.1.-:33 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH72 | 23 | 329 | 6.7e-120 | 0.9807692307692307 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397351 | Glyco_hydro_72 | 2.56e-140 | 24 | 329 | 9 | 312 | Glucanosyltransferase. This is a family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored beta(1-3)glucanosyltransferases. The active site residues in the Aspergillus fumigatus example are the two glutamate residues at 160 and 261. |
| 341417 | CBS_pair_MUG70_1 | 1.33e-69 | 552 | 669 | 1 | 118 | Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domains similar to MUG70 repeat1. Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domain, present in MUG70. The MUG70 protein, encoded by the Meiotically Up-regulated Gene 70, plays a role in meiosis and contains, beside the two CBS pairs, a PB1 domain. The CBS domain, named after human CBS, is a small domain originally identified in cystathionine beta-synthase and is subsequently found in a wide range of different proteins. CBS domains usually occur in tandem repeats. They associate to form a so-called Bateman domain or a CBS pair based on crystallographic studies in bacteria. The CBS pair was used as a basis for this cd hierarchy since the human CBS proteins can adopt the typical core structure and form an intramolecular CBS pair. The interface between the two CBS domains forms a cleft that is a potential ligand binding site. The CBS pair coexists with a variety of other functional domains and this has been used to help in its classification here. It has been proposed that the CBS domain may play a regulatory role, although its exact function is unknown. Mutations of conserved residues within this domain are associated with a variety of human hereditary diseases, including congenital myotonia, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis, and classic Bartter syndrome (CLC chloride channel family members), Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (gamma 2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase), retinitis pigmentosa (IMP dehydrogenase-1), and homocystinuria (cystathionine beta-synthase). |
| 341418 | CBS_pair_MUG70_2 | 6.01e-63 | 723 | 839 | 1 | 118 | Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domains similar to MUG70 repeat2. Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domain, present in MUG70. The MUG70 protein, encoded by the Meiotically Up-regulated Gene 70, plays a role in meiosis and contains, beside the two CBS pairs, a PB1 domain. The CBS domain, named after human CBS, is a small domain originally identified in cystathionine beta-synthase and is subsequently found in a wide range of different proteins. CBS domains usually occur in tandem repeats. They associate to form a so-called Bateman domain or a CBS pair based on crystallographic studies in bacteria. The CBS pair was used as a basis for this cd hierarchy since the human CBS proteins can adopt the typical core structure and form an intramolecular CBS pair. The interface between the two CBS domains forms a cleft that is a potential ligand binding site. The CBS pair coexists with a variety of other functional domains and this has been used to help in its classification here. It has been proposed that the CBS domain may play a regulatory role, although its exact function is unknown. Mutations of conserved residues within this domain are associated with a variety of human hereditary diseases, including congenital myotonia, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis, and classic Bartter syndrome (CLC chloride channel family members), Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (gamma 2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase), retinitis pigmentosa (IMP dehydrogenase-1), and homocystinuria (cystathionine beta-synthase). |
| 341417 | CBS_pair_MUG70_1 | 1.23e-33 | 726 | 832 | 4 | 111 | Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domains similar to MUG70 repeat1. Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domain, present in MUG70. The MUG70 protein, encoded by the Meiotically Up-regulated Gene 70, plays a role in meiosis and contains, beside the two CBS pairs, a PB1 domain. The CBS domain, named after human CBS, is a small domain originally identified in cystathionine beta-synthase and is subsequently found in a wide range of different proteins. CBS domains usually occur in tandem repeats. They associate to form a so-called Bateman domain or a CBS pair based on crystallographic studies in bacteria. The CBS pair was used as a basis for this cd hierarchy since the human CBS proteins can adopt the typical core structure and form an intramolecular CBS pair. The interface between the two CBS domains forms a cleft that is a potential ligand binding site. The CBS pair coexists with a variety of other functional domains and this has been used to help in its classification here. It has been proposed that the CBS domain may play a regulatory role, although its exact function is unknown. Mutations of conserved residues within this domain are associated with a variety of human hereditary diseases, including congenital myotonia, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis, and classic Bartter syndrome (CLC chloride channel family members), Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (gamma 2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase), retinitis pigmentosa (IMP dehydrogenase-1), and homocystinuria (cystathionine beta-synthase). |
| 341358 | CBS_pair_SF | 5.67e-30 | 553 | 661 | 2 | 109 | Two tandem repeats of the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS pair) domains superfamily. The CBS domain, named after human CBS, is a small domain originally identified in cystathionine beta-synthase and is subsequently found in a wide range of different proteins. CBS domains usually occur in tandem repeats. They associate to form a so-called Bateman domain or a CBS pair based on crystallographic studies in bacteria. The CBS pair was used as a basis for this cd hierarchy since the human CBS proteins can adopt the typical core structure and form an intramolecular CBS pair. The interface between the two CBS domains forms a cleft that is a potential ligand binding site. The CBS pair coexists with a variety of other functional domains and this has been used to help in its classification here. It has been proposed that the CBS domain may play a regulatory role, although its exact function is unknown. Mutations of conserved residues within this domain are associated with a variety of human hereditary diseases, including congenital myotonia, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis, and classic Bartter syndrome (CLC chloride channel family members), Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (gamma 2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase), retinitis pigmentosa (IMP dehydrogenase-1), and homocystinuria (cystathionine beta-synthase). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSL64406.1|CBM43|GH72 | 8.91e-215 | 53 | 514 | 12 | 474 |
| AAF05967.1|CBM43|GH72 | 1.53e-212 | 14 | 514 | 14 | 531 |
| AWU75603.1|CBM43|GH72 | 7.76e-142 | 26 | 480 | 28 | 478 |
| AWU49727.1|CBM43|GH72 | 5.41e-138 | 26 | 480 | 28 | 478 |
| AOA61229.1|CBM43|GH72 | 4.58e-137 | 26 | 480 | 18 | 472 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2W62_A | 9.95e-106 | 21 | 508 | 30 | 522 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gas2p in complex with laminaripentaose [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],2W63_A Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Gas2p In Complex With Laminaritriose And Laminaritetraose [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],5O9O_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 7. [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9P_A Crystal structure of Gas2 in complex with compound 10 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9Q_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 6 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9R_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 9 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5O9Y_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 11 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_B Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA2_C Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 8 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C],5OA6_A Crystal structure of ScGas2 in complex with compound 12 [Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C] |
| 2W61_A | 2.69e-105 | 21 | 508 | 30 | 522 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gas2p apostructure (E176Q mutant) [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
| 5FIH_A | 7.26e-105 | 21 | 508 | 30 | 522 | SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE GAS2P (E176Q MUTANT) IN COMPLEX WITH LAMINARITETRAOSE AND LAMINARIPENTAOSE [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
| 3FHM_A | 7.74e-09 | 556 | 660 | 38 | 141 | Crystal structure of the CBS-domain containing protein ATU1752 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens [Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58],3FHM_B Crystal structure of the CBS-domain containing protein ATU1752 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens [Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58],3FHM_C Crystal structure of the CBS-domain containing protein ATU1752 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens [Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58],3FHM_D Crystal structure of the CBS-domain containing protein ATU1752 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens [Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58] |
| 4GQY_A | 6.58e-08 | 558 | 658 | 19 | 145 | Crystal structure of CBSX2 in complex with AMP [Arabidopsis thaliana],4GQY_B Crystal structure of CBSX2 in complex with AMP [Arabidopsis thaliana],4GQY_C Crystal structure of CBSX2 in complex with AMP [Arabidopsis thaliana],4GQY_D Crystal structure of CBSX2 in complex with AMP [Arabidopsis thaliana] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|O13318|PHR2_CANAL | 9.53e-131 | 24 | 480 | 25 | 478 | pH-responsive protein 2 OS=Candida albicans (strain SC5314 / ATCC MYA-2876) OX=237561 GN=PHR2 PE=2 SV=2 |
| sp|P56092|EPD1_CANMA | 1.00e-126 | 9 | 480 | 10 | 478 | Protein EPD1 OS=Candida maltosa OX=5479 GN=EPD1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P22146|GAS1_YEAST | 7.73e-125 | 24 | 480 | 25 | 479 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase GAS1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=GAS1 PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|Q9P378|GAS1_SCHPO | 3.63e-123 | 24 | 479 | 21 | 473 | 1,3-beta-glucanosyltransferase gas1 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=gas1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|O74137|EPD2_CANMA | 3.71e-120 | 31 | 451 | 33 | 461 | Protein EPD2 OS=Candida maltosa OX=5479 GN=EPD2 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
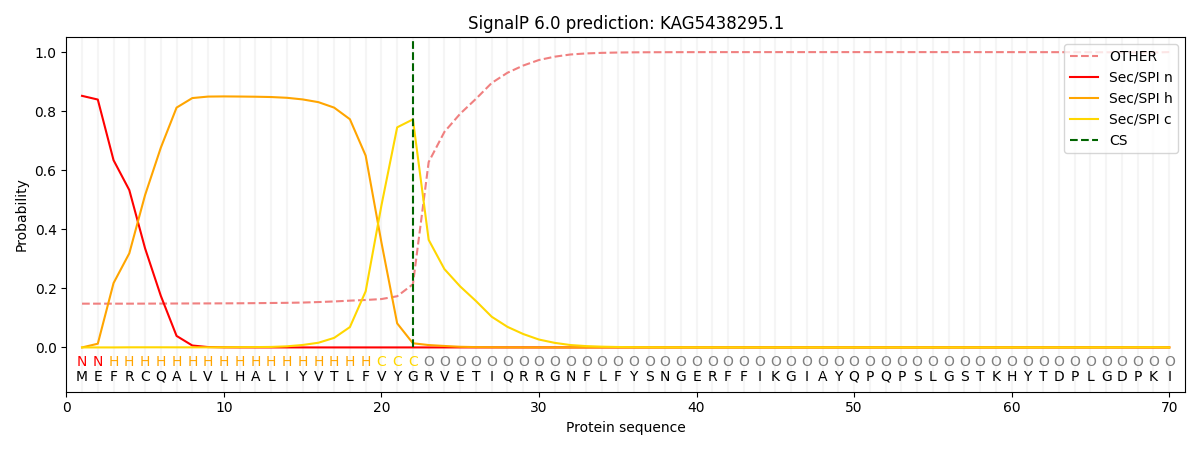
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.162451 | 0.837541 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.7721 |