You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAG2008164.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAG2008164.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Coprinopsis cinerea | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Agaricomycetes; ; Psathyrellaceae; Coprinopsis; Coprinopsis cinerea | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAG2008164.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM21 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | alpha amylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 478973; End:481611 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKLPQLWSIS FALLGLVFSF ASASPAMPLS DTRHVKRAPQ VSLINHSYDN DVLSGTINVQ | 60 |
| NIAYSKVVVV HWASGDTWSD SQTIAATYSS SGSNNFETWS FSGRAPGATQ FYIRYVVSGQ | 120 |
| TYYDPGNYQN HQISRPPGGG NPSPPGPAPT GPANLPAILP SNVPYEAPAN PPSGCSNFNG | 180 |
| WDNCNGGNTE MVASSERRRW QTPPRGDPAY FESFQDYSHL VGYANIQYNS GRTSAVVTVN | 240 |
| AVHKEGAELT YSFNGVEQSS PSFEVDSSLQ GTLAITVTSS DGKKLVLEPL NFFWQHQSLS | 300 |
| AAQSNFNNGQ KGGIVELFGW PWKDIEKECE FLGKAGYMGV KVWPPTEHVW GSHHYEPDTQ | 360 |
| FRPWYQVYQP VSYRLTSRMG TRAELRSMIN SCRRHGVRVY ADAVINHMSG QGNDVQNHRN | 420 |
| TDCSLYSGRN ATDYSPYYTN GNTYLINPFT GTRPTLEFPA VPFGPTDFHC ERGINDWNNG | 480 |
| FLITRGWLVG LTDLNTAKPY VQDRIATFLV DLISIGFSGF RVDAAKHIGP NEMAQILGRV | 540 |
| KNKLGGSLPA DFLTWMEVII GGETQLNACG GGEYSWYTNF DNRLRANGFG NDDIQKVKIW | 600 |
| SSDYPASMPI CGHWILPPSR FAVQNDDHDQ QHEGSSPRWM GDKGSVLIKD KNVGAHRHFS | 660 |
| VNLFSRRDHD WHIKLLLSSY MFSHEGGNGF PDGLSDCNTH YTGTLPRSGC RGIGFDQAYV | 720 |
| ANACGYTMVP GKYTRPHRDI SIINAMRGWV GLPPTNAHDL GIPGCH | 766 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 336 | 634 | 1.9e-52 | 0.9144981412639405 |
| CBM21 | 43 | 133 | 4.6e-16 | 0.9345794392523364 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200456 | AmyAc_bac_euk_AmyA | 4.84e-129 | 311 | 752 | 1 | 329 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial and eukaryotic Alpha amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes AmyA proteins from bacteria, fungi, mammals, insects, mollusks, and nematodes. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 200454 | AmyAc_bac1_AmyA | 8.96e-39 | 318 | 592 | 8 | 251 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 214758 | Aamy | 1.95e-20 | 322 | 412 | 18 | 99 | Alpha-amylase domain. |
| 397445 | CBM_21 | 3.40e-17 | 37 | 134 | 3 | 113 | Carbohydrate/starch-binding module (family 21). This family consists of several eukaryotic proteins that are thought to be involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. For instance, the mouse PTG protein has been shown to interact with glycogen synthase, phosphorylase kinase, phosphorylase a: these three enzymes have key roles in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. PTG also binds the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1C) and localizes it to glycogen. Subsets of similar interactions have been observed with several other members of this family, such as the yeast PIG1, PIG2, GAC1 and GIP2 proteins. While the precise function of these proteins is not known, they may serve a scaffold function, bringing together the key enzymes in glycogen metabolism. This family is a carbohydrate binding domain. |
| 200458 | AmyAc_euk_AmyA | 5.78e-14 | 373 | 530 | 88 | 213 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in eukaryotic Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes eukaryotic alpha-amylases including proteins from fungi, sponges, and protozoans. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGX42980.1|CBM21|GH13 | 0.0 | 19 | 765 | 16 | 789 |
| QRV88491.1|CBM21|GH13 | 3.43e-237 | 41 | 763 | 79 | 840 |
| QRW16798.1|CBM21|GH13 | 1.08e-236 | 1 | 765 | 1 | 783 |
| QRV73700.1|CBM21|GH13 | 3.13e-235 | 41 | 763 | 79 | 840 |
| QRW02641.1|CBM21|GH13 | 3.13e-235 | 41 | 763 | 79 | 840 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PIF_A | 1.22e-43 | 314 | 689 | 13 | 351 | PIG ALPHA-AMYLASE [Sus scrofa],1PIG_A PIG PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE COMPLEXED WITH THE OLIGOSACCHARIDE V-1532 [Sus scrofa],4X0N_A Porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase in complex with helianthamide, a novel proteinaceous inhibitor [Sus scrofa] |
| 1BVN_P | 2.26e-43 | 314 | 689 | 13 | 351 | Pig Pancreatic Alpha-Amylase In Complex With The Proteinaceous Inhibitor Tendamistat [Sus scrofa] |
| 1PPI_A | 2.26e-43 | 314 | 689 | 13 | 351 | THE ACTIVE CENTER OF A MAMMALIAN ALPHA-AMYLASE. THE STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF A PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE WITH A CARBOHYDRATE INHIBITOR REFINED TO 2.2 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION [Sus scrofa] |
| 1JFH_A | 3.07e-43 | 314 | 689 | 13 | 351 | STRUCTURE OF A PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE BOUND TO A SUBSTRATE ANALOGUE AT 2.03 ANGSTROM RESOLUTION [Sus scrofa] |
| 1KXQ_A | 4.18e-43 | 314 | 689 | 13 | 351 | Camelid VHH Domain in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXQ_B Camelid VHH Domain in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXQ_C Camelid VHH Domain in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXQ_D Camelid VHH Domain in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXT_A Camelid VHH Domains in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXT_C Camelid VHH Domains in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXT_E Camelid VHH Domains in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXV_A Camelid VHH Domains in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa],1KXV_B Camelid VHH Domains in Complex with Porcine Pancreatic alpha-Amylase [Sus scrofa] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|O97396|AMY_PHACE | 8.07e-44 | 298 | 635 | 16 | 311 | Alpha-amylase OS=Phaedon cochleariae OX=80249 PE=2 SV=1 |
| sp|P00688|AMYP_MOUSE | 1.65e-43 | 285 | 689 | 5 | 363 | Pancreatic alpha-amylase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Amy2 PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|O77013|AMYR_DROKI | 4.45e-43 | 298 | 682 | 16 | 350 | Alpha-amylase-related protein OS=Drosophila kikkawai OX=30033 GN=Amyrel PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|P19961|AMY2B_HUMAN | 5.96e-43 | 285 | 689 | 5 | 366 | Alpha-amylase 2B OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=AMY2B PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|O77021|AMYR_DRODO | 6.06e-43 | 298 | 682 | 16 | 350 | Alpha-amylase-related protein OS=Drosophila dossoui OX=60716 GN=Amyrel PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
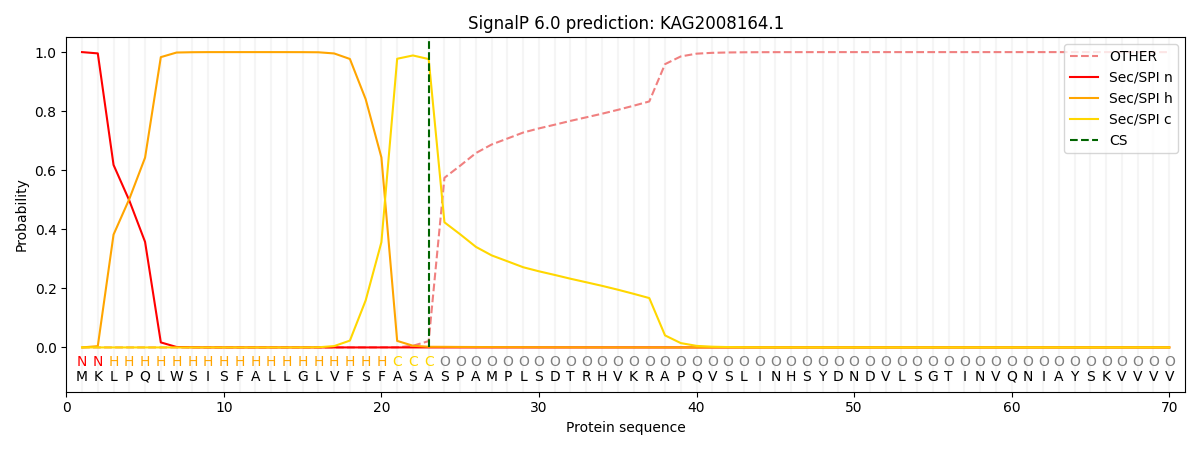
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000401 | 0.999570 | CS pos: 23-24. Pr: 0.9764 |

