You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAF7625128.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAF7625128.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus flavus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus flavus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAF7625128.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH36 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH131 | 529 | 760 | 2e-94 | 0.9921568627450981 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395036 | Sugar_tr | 5.74e-93 | 28 | 473 | 12 | 452 | Sugar (and other) transporter. |
| 340914 | MFS_HXT | 1.21e-86 | 16 | 473 | 1 | 403 | Fungal Hexose transporter subfamily of the Major Facilitator Superfamily of transporters and similar proteins. The fungal hexose transporter (HXT) subfamily is comprised of functionally redundant proteins that function mainly in the transport of glucose, as well as other sugars such as galactose and fructose. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has 20 genes that encode proteins in this family (HXT1 to HXT17, GAL2, SNF3, and RGT2). Seven of these (HXT1-7) encode functional glucose transporters. Gal2p is a galactose transporter, while Rgt2p and Snf3p act as cell surface glucose receptors that initiate signal transduction in response to glucose, functioning in an induction pathway responsible for glucose uptake. Rgt2p is activated by high levels of glucose and stimulates expression of low affinity glucose transporters such as Hxt1p and Hxt3p, while Snf3p generates a glucose signal in response to low levels of glucose, stimulating the expression of high affinity glucose transporters such as Hxt2p and Hxt4p. Schizosaccharomyces pombe contains eight GHT genes (GHT1-8) belonging to this family. Ght1, Ght2, and Ght5 are high-affinity glucose transporters; Ght3 is a high-affinity gluconate transporter; and Ght6 high-affinity fructose transporter. The substrate specificities for Ght4, Ght7, and Ght8 remain undetermined. The HXT subfamily belongs to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 408085 | GH131_N | 1.58e-79 | 529 | 755 | 1 | 251 | Glycoside hydrolase 131 catalytic N-terminal domain. This is the N-terminal domain found in glycoside hydrolase family 131 (GH131A) protein observed in Coprinopsis cinerea. GH131A exhibits bifunctional exo-beta-1,3-/-1,6- and endo-beta-1,4 activity toward beta-glucan. This domain is catalytic in nature though the catalytic mechanism of C. cinerea GH131A is different from that of typical glycosidases that use a pair of carboxylic acid residues as the catalytic residues. In the case of GH131A, Glu98 and His218 may form a catalytic dyad and Glu98 may activate His218 during catalysis. |
| 273317 | SP | 3.01e-79 | 27 | 469 | 39 | 481 | MFS transporter, sugar porter (SP) family. This model represent the sugar porter subfamily of the major facilitator superfamily (pfam00083) [Transport and binding proteins, Carbohydrates, organic alcohols, and acids] |
| 340916 | MFS_GLUT6_8_Class3_like | 9.65e-67 | 73 | 468 | 48 | 436 | Glucose transporter (GLUT) types 6 and 8, Class 3 GLUTs, and similar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This subfamily is composed of glucose transporter type 6 (GLUT6), GLUT8, plant early dehydration-induced gene ERD6-like proteins, and similar insect proteins including facilitated trehalose transporter Tret1-1. GLUTs, also called Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporters (SLC2A), are a family of proteins that facilitate the transport of hexoses such as glucose and fructose. There are fourteen GLUTs found in humans; they display different substrate specificities and tissue expression. They have been categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class 1 (GLUTs 1-4, 14); Class 2 (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11); and Class 3 (GLUTs 6, 8, 10, 12, and HMIT). Insect Tret1-1 is a low-capacity facilitative transporter for trehalose that mediates the transport of trehalose synthesized in the fat body and the incorporation of trehalose into other tissues that require a carbon source. GLUT proteins are comprised of about 500 amino acid residues, possess a single N-linked oligosaccharide, and have 12 transmembrane segments. They belong to the Glucose transporter -like (GLUT-like) family of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins. MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.13e-172 | 515 | 763 | 1 | 250 | |
| 2.13e-172 | 515 | 763 | 1 | 250 | |
| 2.13e-172 | 515 | 763 | 1 | 250 | |
| 2.13e-172 | 515 | 763 | 1 | 250 | |
| 1.84e-112 | 525 | 758 | 15 | 251 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.30e-85 | 527 | 761 | 1 | 243 | Chain A, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_B Chain B, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_C Chain C, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_D Chain D, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_A Chain A, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_B Chain B, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_C Chain C, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_D Chain D, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina] |
|
| 1.03e-84 | 527 | 763 | 1 | 236 | Chain A, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_B Chain B, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_C Chain C, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_D Chain D, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130] |
|
| 4.88e-47 | 13 | 478 | 4 | 441 | The inward-facing structure of the glucose transporter from Staphylococcus epidermidis [Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228],4LDS_B The inward-facing structure of the glucose transporter from Staphylococcus epidermidis [Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228] |
|
| 1.53e-39 | 19 | 473 | 30 | 489 | Chain A, Sugar transport protein 10 [Arabidopsis thaliana] |
|
| 1.70e-39 | 19 | 473 | 31 | 490 | Crystal Structure of A. thaliana Sugar Transport Protein 10 in complex with glucose in the outward occluded state [Arabidopsis thaliana] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.98e-87 | 2 | 501 | 9 | 509 | MFS-type transporter oryC OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=oryC PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 4.27e-86 | 4 | 496 | 19 | 512 | Sugar transporter STL1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=STL1 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 5.11e-79 | 6 | 499 | 7 | 505 | Major facilitator superfamily transporter mfsA OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=mfsA PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 2.37e-50 | 13 | 507 | 27 | 522 | High-affinity glucose transporter OS=Kluyveromyces lactis (strain ATCC 8585 / CBS 2359 / DSM 70799 / NBRC 1267 / NRRL Y-1140 / WM37) OX=284590 GN=HGT1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 7.83e-49 | 8 | 473 | 80 | 549 | Probable glucose transporter HXT5 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=HXT5 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999709 | 0.000319 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
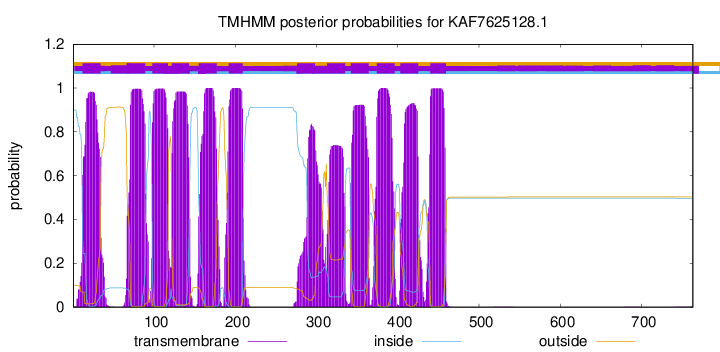
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 12 | 34 |
| 67 | 89 |
| 98 | 117 |
| 122 | 143 |
| 155 | 177 |
| 192 | 209 |
| 276 | 298 |
| 313 | 335 |
| 342 | 364 |
| 374 | 396 |
| 403 | 425 |
| 440 | 459 |
