You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAF5682345.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAF5682345.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Fusarium circinatum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Nectriaceae; Fusarium; Fusarium circinatum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAF5682345.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | cellobiose dehydrogenase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA8 | 28 | 179 | 4.7e-18 | 0.8846153846153846 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187688 | CDH_like_cytochrome | 9.66e-52 | 23 | 173 | 12 | 168 | Heme-binding cytochrome domain of fungal cellobiose dehydrogenases. Cellobiose dehydrogenase (CellobioseDH or CDH) is an extracellular fungal oxidoreductase that degrades both lignin and cellulose. Specifically, CDHs oxidize cellobiose, cellodextrins, and lactose to corresponding lactones, utilizing a variety of electron acceptors. Class-II CDHs are monomeric hemoflavoenzymes that are comprised of a b-type cytochrome domain linked to a large flavodehydrogenase domain. The cytochrome domain of CDH and related enzymes, which this model describes, folds as a beta sandwich and complexes a heme molecule. It is found at the N-terminus of this family of enzymes, and belongs to the DOMON domain superfamily, a ligand-interacting motif found in all three kingdoms of life. |
| 176490 | Cyt_b561_FRRS1_like | 6.05e-38 | 169 | 357 | 5 | 180 | Eukaryotic cytochrome b(561), including the FRRS1 gene product. Cytochrome b(561), as found in eukaryotes, similar to and including the human FRRS1 gene product (ferric-chelate reductase 1), also called SDR-2 (stromal cell-derived receptor 2). This family comprises a variety of domain architectures, many of which contain dopamine beta-monooxygenase (DOMON) domains. The protein might act as a ferric-chelate reductase, catalyzing the reduction of Fe(3+) to Fe(2+), such as associated with the transport of iron from the endosome to the cytoplasm. It is assumed that this protein uses ascorbate as the electron donor. Belongs to the cytochrome b(561) family, which are secretory vesicle-specific electron transport proteins. Cytochromes b(561) are integral membrane proteins that bind two heme groups non-covalently, and may have six alpha-helical trans-membrane segments. |
| 406418 | CDH-cyt | 1.97e-22 | 23 | 177 | 11 | 174 | Cytochrome domain of cellobiose dehydrogenase. CDH-cyt is the cytochrome domain, at the N-terminus, of cellobiose dehydrogenase. CDH-cyt folds as a beta sandwich with the topology of the antibody Fab V(H) domain and binds iron. The haem iron is ligated by Met83 and His181 in UniProtKB:Q01738. |
| 214769 | B561 | 3.88e-08 | 221 | 339 | 2 | 129 | Cytochrome b-561 / ferric reductase transmembrane domain. Cytochrome b-561 recycles ascorbate for the generation of norepinephrine by dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in the chromaffin vesicles of the adrenal gland. It is a transmembrane heme protein with the two heme groups being bound to conserved histidine residues. A cytochrome b-561 homologue, termed Dcytb, is an iron-regulated ferric reductase in the duodenal mucosa. Other homologues of these are also likely to be ferric reductases. SDR2 is proposed to be important in regulating the metabolism of iron in the onset of neurodegenerative disorders. |
| 187689 | DOMON_DOH | 3.68e-05 | 26 | 114 | 3 | 85 | DOMON-like domain of copper-dependent monooxygenases and related proteins. This diverse family characterizes DOMON domains found in dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), monooxygenase X (MOX), and various other proteins, some of which contain DOMON domains exclusively; the family is not restricted to eukaryotes. DBH is a membrane-bound enzyme that converts dopamine to L-norepinephrine, and plays a central role in the metabolism of catecholamine neurotransmitters. DOMON domains were initially thought to confer protein-protein interactions. They were subsequently found as a heme-binding motif in cellobiose dehydrogenase, an extracellular fungal oxidoreductase that degrades both lignin and cellulose, and in ethylbenzene dehydrogenase, an enzyme that aids in the anaerobic degradation of hydrocarbons. The domain interacts with sugars in the type 9 carbohydrate binding modules (CBM9), which are present in a variety of glycosyl hydrolases, and it can also be found at the N-terminus of sensor histidine kinases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.62e-179 | 1 | 392 | 1 | 404 | |
| 2.66e-130 | 17 | 365 | 19 | 363 | |
| 3.99e-121 | 1 | 367 | 1 | 365 | |
| 6.22e-119 | 5 | 370 | 3 | 393 | |
| 2.23e-101 | 32 | 363 | 39 | 359 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
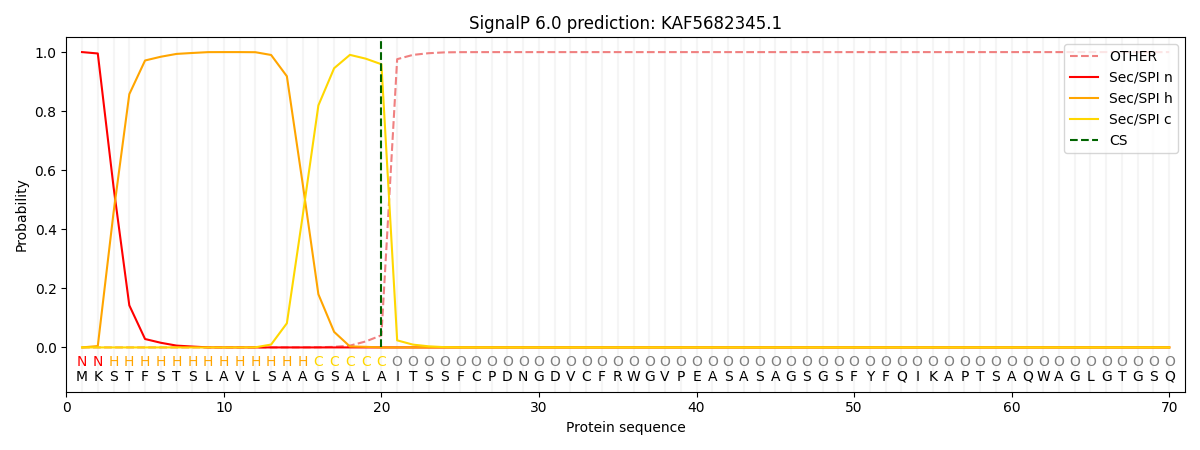
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000255 | 0.999743 | CS pos: 20-21. Pr: 0.9589 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
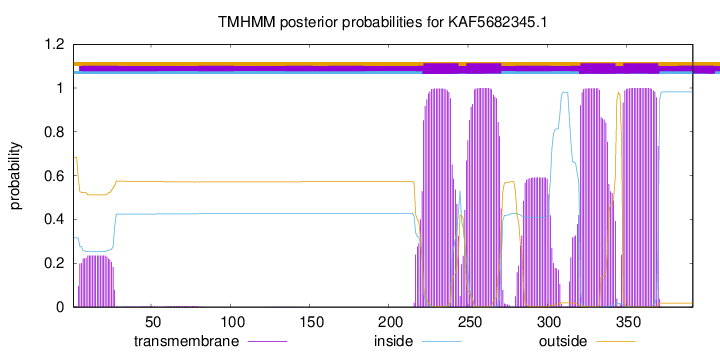
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 222 | 244 |
| 249 | 271 |
| 321 | 343 |
| 348 | 370 |
