You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: KAB8203463.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: KAB8203463.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus parasiticus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus parasiticus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | KAB8203463.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE8 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | putative endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.4:18 | 3.2.1.73:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH7 | 22 | 414 | 4.6e-162 | 0.9855421686746988 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 153432 | GH7_CBH_EG | 0.0 | 24 | 408 | 1 | 386 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 7. Glycosyl hydrolase family 7 contains eukaryotic endoglucanases (EGs) and cellobiohydrolases (CBHs) that hydrolyze glycosidic bonds using a double-displacement mechanism. This leads to a net retention of the conformation at the anomeric carbon. Both enzymes work synergistically in the degradation of cellulose,which is the main component of plant cell wall, and is composed of beta-1,4 linked glycosyl units. EG cleaves the beta-1,4 linkages of cellulose and CBH cleaves off cellobiose disaccharide units from the reducing end of the chain. In general, the O-glycosyl hydrolases are a widespread group of enzymes that hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between two or more carbohydrates, or between a carbohydrate and a non-carbohydrate moiety. A glycosyl hydrolase classification system based on sequence similarity has led to the definition of more than 95 different families inlcuding glycoside hydrolase family 7. |
| 395677 | Glyco_hydro_7 | 0.0 | 20 | 413 | 1 | 434 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 7. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.00e-309 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | |
| 3.00e-309 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | |
| 3.00e-309 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | |
| 3.00e-309 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | |
| 3.00e-309 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.68e-177 | 19 | 415 | 2 | 396 | Chain A, Glucanase [Rasamsonia emersonii],6SU8_B Chain B, Glucanase [Rasamsonia emersonii],6SU8_C Chain C, Glucanase [Rasamsonia emersonii] |
|
| 3.28e-129 | 21 | 415 | 4 | 399 | HUMICOLA INSOLENS ENDOCELLULASE EGI S37W, P39W DOUBLE-MUTANT [Humicola insolens] |
|
| 6.16e-129 | 21 | 415 | 4 | 399 | Chain AAA, Endoglucanase 1 [Humicola insolens],6YOZ_BBB Chain BBB, Endoglucanase 1 [Humicola insolens] |
|
| 6.58e-129 | 21 | 415 | 4 | 399 | Chain AAA, Endoglucanase 1 [Humicola insolens] |
|
| 8.16e-129 | 21 | 414 | 4 | 398 | HUMICOLA INSOLENS ENDOCELLULASE EGI NATIVE STRUCTURE [Humicola insolens],2A39_B HUMICOLA INSOLENS ENDOCELLULASE EGI NATIVE STRUCTURE [Humicola insolens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.33e-310 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=celB PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 5.33e-310 | 1 | 416 | 1 | 416 | Endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=celB PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.31e-226 | 10 | 415 | 11 | 416 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB OS=Aspergillus terreus (strain NIH 2624 / FGSC A1156) OX=341663 GN=celB PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.21e-212 | 10 | 414 | 11 | 412 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=celB PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.22e-188 | 6 | 414 | 7 | 405 | Probable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase celB OS=Neosartorya fischeri (strain ATCC 1020 / DSM 3700 / CBS 544.65 / FGSC A1164 / JCM 1740 / NRRL 181 / WB 181) OX=331117 GN=celB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
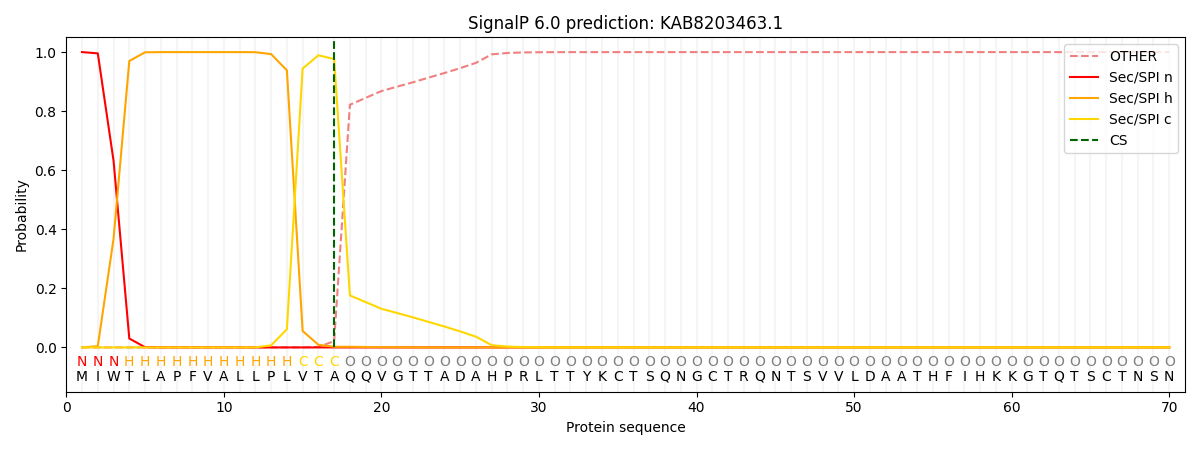
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000197 | 0.999786 | CS pos: 17-18. Pr: 0.9764 |
