You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: I311_05813-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: I311_05813-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Cryptococcus gattii VGI | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Arthropoda; Insecta; ; Eriococcidae; Cryptococcus; Cryptococcus gattii VGI | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | I311_05813-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT33 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH18 | 304 | 529 | 2e-19 | 0.652027027027027 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119349 | GH18_chitinase-like | 3.62e-30 | 280 | 538 | 1 | 208 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of beta-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) which is a major component of the cell wall of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitinases have been identified in viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoan parasites, insects, and plants. The structure of the GH18 domain is an eight-stranded beta/alpha barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The GH18 family includes chitotriosidase, chitobiase, hevamine, zymocin-alpha, narbonin, SI-CLP (stabilin-1 interacting chitinase-like protein), IDGF (imaginal disc growth factor), CFLE (cortical fragment-lytic enzyme) spore hydrolase, the type III and type V plant chitinases, the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases, and the chitolectins. The GH85 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 85) ENGases (endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases) are closely related to the GH18 chitinases and are included in this alignment model. |
| 119350 | GH18_chitinase_D-like | 1.46e-16 | 347 | 535 | 83 | 293 | GH18 domain of Chitinase D (ChiD). ChiD, a chitinase found in Bacillus circulans, hydrolyzes the 1,4-beta-linkages of N-acetylglucosamine in chitin and chitodextrins. The domain architecture of ChiD includes a catalytic glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) domain, a chitin-binding domain, and a fibronectin type III domain. The chitin-binding and fibronectin type III domains are located either N-terminal or C-terminal to the catalytic domain. This family includes exochitinase Chi36 from Bacillus cereus. |
| 395573 | Glyco_hydro_18 | 2.87e-12 | 355 | 509 | 83 | 230 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 18. |
| 119363 | GH18_CTS3_chitinase | 9.06e-12 | 339 | 537 | 71 | 253 | GH18 domain of CTS3 (chitinase 3), an uncharacterized protein from the human fungal pathogen Coccidioides posadasii. CTS3 has a chitinase-like glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) domain; and has homologs in bacteria as well as fungi. |
| 226000 | Chi1 | 3.02e-11 | 289 | 539 | 18 | 308 | Chitinase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 552 | 1 | 552 | |
| 2.46e-306 | 1 | 552 | 1 | 629 | |
| 1.02e-272 | 1 | 550 | 1 | 582 | |
| 9.12e-253 | 1 | 550 | 1 | 634 | |
| 9.12e-253 | 1 | 550 | 1 | 634 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.76e-20 | 322 | 540 | 48 | 265 | Crystal structure of a GH18 chitinase from Pseudoalteromonas aurantia [Pseudoalteromonas aurantia],6K7Z_B Crystal structure of a GH18 chitinase from Pseudoalteromonas aurantia [Pseudoalteromonas aurantia],6K7Z_C Crystal structure of a GH18 chitinase from Pseudoalteromonas aurantia [Pseudoalteromonas aurantia],6K7Z_D Crystal structure of a GH18 chitinase from Pseudoalteromonas aurantia [Pseudoalteromonas aurantia] |
|
| 5.16e-07 | 302 | 464 | 29 | 198 | Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of a family GH18 Chitinase from fern, Peteris ryukyuensis [Pteris ryukyuensis],4RL3_B Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of a family GH18 Chitinase from fern, Peteris ryukyuensis [Pteris ryukyuensis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
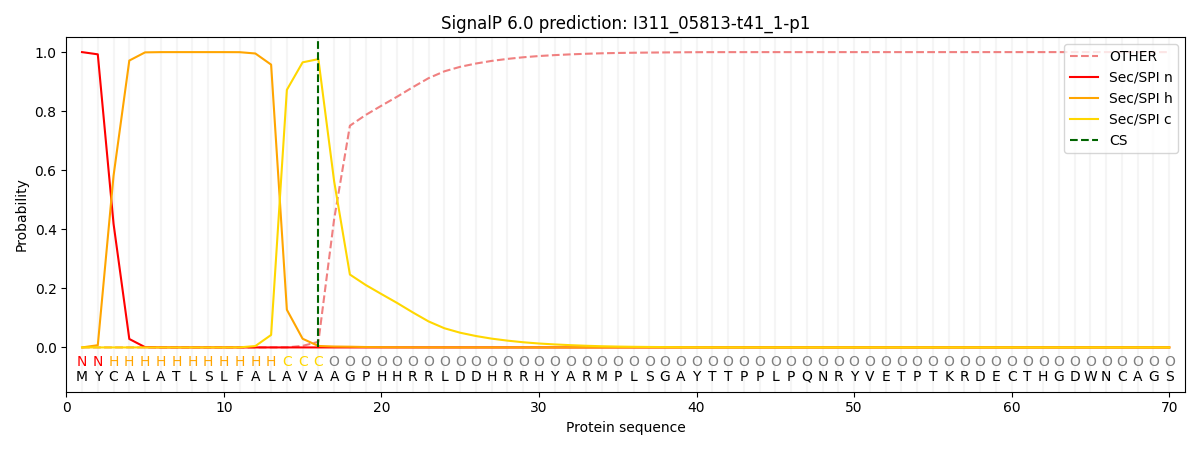
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000365 | 0.999601 | CS pos: 16-17. Pr: 0.9762 |
