You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: H310_04214-t26_2-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: H310_04214-t26_2-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aphanomyces invadans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Saprolegniaceae; Aphanomyces; Aphanomyces invadans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | H310_04214-t26_2-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH31 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein, variant | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.20:38 | 3.2.1.10:16 | 3.2.1.48:16 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH31 | 343 | 831 | 4.3e-146 | 0.9953161592505855 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 269888 | GH31_MGAM_SI_GAA | 0.0 | 362 | 742 | 1 | 367 | maltase-glucoamylase, sucrase-isomaltase, lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase. This subgroup includes the following three closely related glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) enzymes: maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM), sucrase-isomaltase (SI), and lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), also known as acid-maltase. MGAM is one of the two enzymes responsible for catalyzing the last glucose-releasing step in starch digestion. SI is implicated in the digestion of dietary starch and major disaccharides such as sucrose and isomaltose, while GAA degrades glycogen in the lysosome, cleaving both alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages. MGAM and SI are anchored to small-intestinal brush-border epithelial cells. The absence of SI from the brush border membrane or its malfunction is associated with malabsorption disorders such as congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID). The domain architectures of MGAM and SI include two tandem GH31 catalytic domains, an N-terminal domain found near the membrane-bound end, and a C-terminal luminal domain. Both of the tandem GH31 domains of MGAM and SI are included in this family. The domain architecture of GAA includes an N-terminal TFF (trefoil factor family) domain in addition to the GH31 catalytic domain. Deficient GAA expression causes Pompe disease, an autosomal recessive genetic disorder also known as glycogen storage disease type II (GSDII). |
| 395838 | Glyco_hydro_31 | 0.0 | 343 | 831 | 1 | 442 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 31. Glycosyl hydrolases are key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Family 31 comprises of enzymes that are, or similar to, alpha- galactosidases. |
| 224418 | YicI | 7.54e-133 | 119 | 878 | 26 | 709 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 269889 | GH31_GANC_GANAB_alpha | 1.93e-129 | 362 | 878 | 1 | 467 | neutral alpha-glucosidase C, neutral alpha-glucosidase AB. This subgroup includes the closely related glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) isozymes, neutral alpha-glucosidase C (GANC) and the alpha subunit of heterodimeric neutral alpha-glucosidase AB (GANAB). Initially distinguished on the basis of differences in electrophoretic mobility in starch gel, GANC and GANAB have been shown to have other differences, including those of substrate specificity. GANC and GANAB are key enzymes in glycogen metabolism that hydrolyze terminal, non-reducing 1,4-linked alpha-D-glucose residues from glycogen in the endoplasmic reticulum. The GANC/GANAB family includes the alpha-glucosidase II (ModA) from Dictyostelium discoideum as well as the alpha-glucosidase II (GLS2, or ROT2 - Reversal of TOR2 lethality protein 2) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| 269890 | GH31_glucosidase_II_MalA | 1.81e-108 | 362 | 742 | 1 | 336 | Alpha-glucosidase II-like. Alpha-glucosidase II (alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) enzyme, found in bacteria and plants, which has exo-alpha-1,4-glucosidase and oligo-1,6-glucosidase activities. Alpha-glucosidase II has been characterized in Bacillus thermoamyloliquefaciens where it forms a homohexamer. This subgroup also includes the MalA alpha-glucosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus and the AglA alpha-glucosidase from Picrophilus torridus. MalA is part of the carbohydrate-metabolizing machinery that allows this organism to utilize carbohydrates, such as maltose, as the sole carbon and energy source. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 15 | 936 | 11 | 937 | |
| 0.0 | 27 | 827 | 27 | 837 | |
| 1.08e-236 | 31 | 927 | 44 | 1080 | |
| 4.14e-202 | 75 | 888 | 20 | 796 | |
| 1.11e-199 | 103 | 895 | 49 | 813 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.92e-195 | 22 | 907 | 3 | 817 | Crystal structure of human GAA [Homo sapiens],5KZX_A Crystal structure of human GAA [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 3.88e-195 | 22 | 907 | 1 | 815 | Crystal structure of human lysosomal acid-alpha-glucosidase, GAA, in complex with N-acetyl-cysteine [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 3.88e-195 | 22 | 907 | 1 | 815 | Crystal structure of human lysosomal acid-alpha-glucosidase, GAA [Homo sapiens],5NN5_A Crystal structure of human lysosomal acid-alpha-glucosidase, GAA, in complex with 1-deoxynojirimycin [Homo sapiens],5NN6_A Crystal structure of human lysosomal acid-alpha-glucosidase, GAA, in complex with N-hydroxyethyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [Homo sapiens],5NN8_A Crystal structure of human lysosomal acid-alpha-glucosidase, GAA, in complex with acarbose [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.36e-170 | 75 | 895 | 2 | 792 | Crystral Structure of the N-terminal Subunit of Human Maltase-Glucoamylase [Homo sapiens],2QMJ_A Crystral Structure of the N-terminal Subunit of Human Maltase-Glucoamylase in Complex with Acarbose [Homo sapiens],3CTT_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with Casuarine [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.57e-170 | 75 | 895 | 2 | 792 | Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with BJ2661 [Homo sapiens],3L4U_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with de-O-sulfonated kotalanol [Homo sapiens],3L4V_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with kotalanol [Homo sapiens],3L4W_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with miglitol [Homo sapiens],3L4X_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with NR4-8 [Homo sapiens],3L4Y_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with NR4-8II [Homo sapiens],3L4Z_A Crystal complex of N-terminal Human Maltase-Glucoamylase with Salacinol [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.09e-193 | 22 | 907 | 81 | 895 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=GAA PE=1 SV=4 |
|
| 3.82e-191 | 22 | 907 | 81 | 896 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Gaa PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 1.46e-190 | 22 | 888 | 81 | 874 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Pongo abelii OX=9601 GN=GAA PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 5.12e-188 | 22 | 896 | 81 | 883 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Rattus norvegicus OX=10116 GN=Gaa PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 6.06e-185 | 64 | 910 | 50 | 883 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=GAA PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
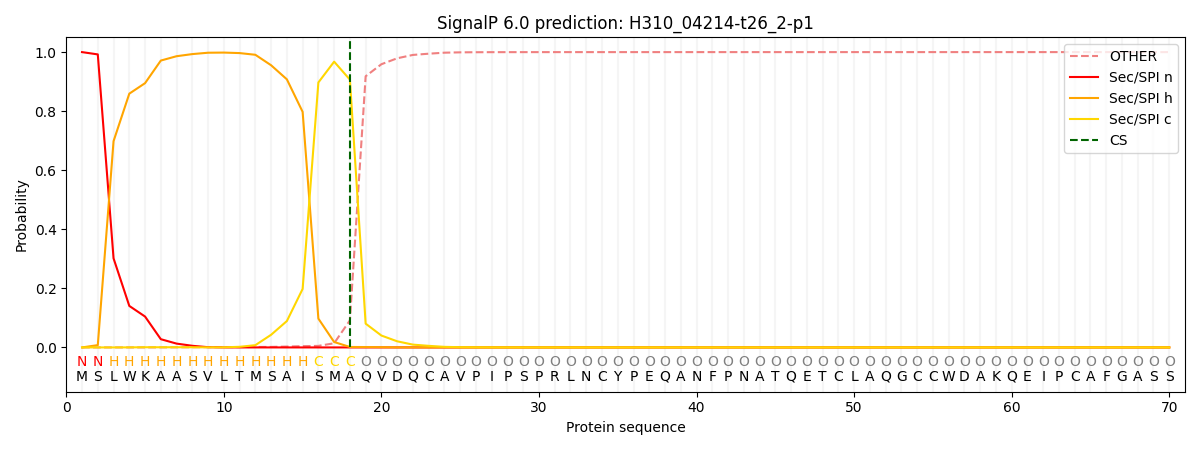
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000594 | 0.999391 | CS pos: 18-19. Pr: 0.9068 |
