You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: H257_13937-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: H257_13937-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aphanomyces astaci | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Saprolegniaceae; Aphanomyces; Aphanomyces astaci | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | H257_13937-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT8 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 195777; End:203033 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MSFEGLSIAV TGGAGFIGSS LVTQLLALHA THVMIIDCLT PDYDVAIKRA RIEYALTDER | 60 |
| CSFEQVNICD RARLLDVFRT HQPVVVYHLA AQAGVRRCEL SPALTCATNV EGTASVLHTC | 120 |
| SATPSVKYVV FASSSSVYGN QPTPWNELTT PMDPQSLYAR TKVMGEQLCQ QFGAKHEGNK | 180 |
| SVCILRPFSV YGPQGRPDMA IAKFVRALRH RQPITLIGNT QRDCTFIDDV VQAFVLSALV | 240 |
| QRPHQERYKQ QHQLVSATGE SNINQTPLTR TFNVGTGHTT SMEDVLQQIQ RAMRQVPVEV | 300 |
| LHAPANPVDA IVTRADSVAA SNELGFRASV HLSEGIVKTV ASELHDPPMH IAVVVATTDG | 360 |
| GRFDLLTKRC LPSIWNQTRP PDSIVIVADT SCEDGFTNDL HAFLRNSPGN VMLLFNHRTL | 420 |
| GASGAWNTGI LHVLSAIPPG GDMSRMYIAI CDDDDMWSCD HLALMDRHRS DVVVGGLIRY | 480 |
| ESDEGEGKPL SIPRLPLSSN AFLSGNPHLQ GSNLYVRLLV LLQAGLFDEG LNACTDRDLM | 540 |
| VRVLDLPGVS VECVANGAHS VHHFADASRV RLTTCGHRKQ LALTVFWRKH AHRMTKTVQG | 600 |
| DFMCRAVMLF GWSPPSPQVT PNESTTTSVP TPLISPSCDG RLSQKYALIV GITSDSGSSA | 660 |
| VRGLLEDLVA LSCASLVSTD VVILENGPKA STLQATITTF QESHVLRCLF VPLDQQRQDM | 720 |
| VSGLLPPNQT FDVRASIAET RTRVQLYTSI FAHQLAPQLG SADCIVKPVV WILDDDKRLP | 780 |
| PTFPLQAVLQ AHESDPTIAV VLGVDAQCPP LPPAFCVRTQ LVDMLSHLQL CLHTPPSDPL | 840 |
| GPPQPPGATS LSEKVQGDYY HDLAGYKTLE TPMWMNTMST SLAHFTTLGE CMNQILKGSL | 900 |
| VTRPLASDDD VPPTPTLTLT PSIHRGGCTF VFDLECMLDA NTAPPCHRRS DMVWSLLQRD | 960 |
| VHHKRVVQCR QVCVNHIRQS MPSKTDLIDV AMKDVAGHAL YQALQTVLGD PDMTETPSWV | 1020 |
| ELWPRFWEQY CVTYNRRRTE LRASVERIRG LVYTIKSLLR CQSAWWNSSN NSSDNDVIEG | 1080 |
| AKATLWTALE SLTHRFDSAW EEPLSVDVTN DNTMRELHMW FTAVLPRHRH DDWTRAQLTL | 1140 |
| FHNSVYEPHR IESARACVSI LYQVPPESLE LLGVGYEGVT FHNGKSMDGQ RGCCCFKYMD | 1200 |
| LAALRFPNHV WDSLVALLTE PTKSMLGLRC VRRRGYHVCL ERDYVDGTEL NLNSKRECAP | 1260 |
| EAPLSFLAWC RKANITCRNV KPQNLVVSRE TGQLTLVDIG MDTVVPWTSE GEGHMMRKMY | 1320 |
| LSWAWLHRHD LAALLSASHH SPKMPELQAG FNRFQLAYNH MLTPQACVDD AVALVAQLVP | 1380 |
| PGGGSLLNVT IDWTLHARVQ AILPHAQGAK LVVHPLVQVG KTELTLHNPF DTITCICVVC | 1440 |
| AVDDLTMHRV LLELRAKVAP HGVVVLAMCN PFFVAANPSP HGLSDRFHRC FGRRNDDVVM | 1500 |
| PRPWHVFEHA FWRAGLMVVD MAHTKSADVV AFEPVSDYIV VQLKPVTTLC LSPSVMPAAV | 1560 |
| GGRPSHRGET TLMASCTLLI KTCATEHLTL AARVRHLKEQ LEGPRAFAET LVIVDGYRRD | 1620 |
| NDKSSFGKPE FFEPENELDE EYNDDLDSFV DSTPRPSLDT PLHRDTDKFD LCDGDAVTDE | 1680 |
| LSKCLAVCQE LQQEGWIDRY LHYQPTSAEV VALNSKWFGL HHNNQTHTRT RRGTLVQVAS | 1740 |
| TLAGLEAATS EFILQVDSDL MVGRHSYYHL DDYLGQAMAI FAQDELAISV ALDTFRSQPQ | 1800 |
| GGGRQLPGGP TWCDPDTGTP HRVEVRGCVF SKARLMSKLP MPRPLGPTLA YLKSTTVTQY | 1860 |
| HSVCKVDPQH WLLPWYRAMD IAMQDINWGR SYRVHDGTTF FVHPTDTTKA STDNYGLVLD | 1920 |
| CVATLRLPSA LQHGHVDCQG GVQDWMNALS KRHEDVVVVV LGRNVSPSKI MRCLDSIARQ | 1980 |
| HKCPQWTVGV IVVDDASSSH TTAAFLRWYC HPQKNNARPP VTLIQPRFEP RKVGANTVLA | 2040 |
| VEYVCANPMS VVVTLDMDDS LLGMDVWTTL YRYYIQEYAD ATVGGMLRTD KIQPPTSYPG | 2100 |
| ICVNGARRLR GGGNVWMHLR SFRKYLFDRI LDQDLREHAI LDATTLTRGD NGGNPYLTFG | 2160 |
| FDWAMMLPLV EMATKPTVVH EVLYLYEPFG PHKAETDAVA FRLLARPAYS KLRPLIAVVG | 2220 |
| DANLNARHAV VDCAFPGPRA SSEATGAAEK EAVLMALGQA LVDAGYTVLC GGLGGAMLAV | 2280 |
| ARGAHASTEW QEGRVVGLVP GTDRRQANSF IDMPIATGLG IARNCLVAQA DAMVCVGGGS | 2340 |
| GTLSEMALAW SAGRLVIGME SASGVTPQFV GKPLDGRRRY PAEVVPHDQV YRAKDVDQVI | 2400 |
| QLLRAYLPLY AKKRQLPM | 2418 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187563 | UDP_GE_SDE_e | 3.27e-60 | 8 | 341 | 3 | 327 | UDP glucuronic acid epimerase, extended (e) SDRs. This subgroup contains UDP-D-glucuronic acid 4-epimerase, an extended SDR, which catalyzes the conversion of UDP-alpha-D-glucuronic acid to UDP-alpha-D-galacturonic acid. This group has the SDR's canonical catalytic tetrad and the TGxxGxxG NAD-binding motif of the extended SDRs. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
| 187566 | UDP_AE_SDR_e | 3.71e-53 | 8 | 340 | 2 | 301 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase, extended (e) SDRs. This subgroup contains UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, WbpP, an extended SDR, that catalyzes the NAD+ dependent conversion of UDP-GlcNAc and UDPGalNA to UDP-Glc and UDP-Gal. This subgroup has the characteristic active site tetrad and NAD-binding motif of the extended SDRs. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
| 223528 | WcaG | 5.84e-52 | 8 | 345 | 3 | 310 | Nucleoside-diphosphate-sugar epimerase [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 396097 | Epimerase | 1.98e-48 | 8 | 248 | 1 | 235 | NAD dependent epimerase/dehydratase family. This family of proteins utilize NAD as a cofactor. The proteins in this family use nucleotide-sugar substrates for a variety of chemical reactions. |
| 212494 | SDR_e | 1.31e-43 | 8 | 238 | 1 | 187 | extended (e) SDRs. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKU11317.1|GT2 | 2.64e-170 | 322 | 2208 | 3 | 1722 |
| AGB01185.1|GT2 | 8.31e-131 | 350 | 2196 | 3 | 1703 |
| VEJ15080.1|GT2 | 3.83e-103 | 353 | 2412 | 6 | 1782 |
| ACY13523.1|GT2 | 3.13e-75 | 347 | 1083 | 25 | 764 |
| BBM87114.1|GT2 | 1.44e-67 | 351 | 1008 | 8 | 634 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5U4Q_A | 4.43e-32 | 10 | 336 | 8 | 324 | Chain A, dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase [Klebsiella pneumoniae],5U4Q_B Chain B, dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase [Klebsiella pneumoniae] |
| 6KV9_A | 2.06e-24 | 8 | 336 | 21 | 315 | MoeE5 in complex with UDP-glucuronic acid and NAD [Streptomyces viridosporus ATCC 14672],6KVC_A MoeE5 in complex with UDP-glucose and NAD [Streptomyces viridosporus ATCC 14672] |
| 6LTT_A | 2.31e-24 | 10 | 350 | 5 | 315 | Chain A, UDP-glucose 4-epimerase [Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv],6LTT_B Chain B, UDP-glucose 4-epimerase [Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv] |
| 6ZL6_A | 2.16e-23 | 6 | 336 | 1 | 303 | Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZL6_B Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLA_A Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with NAD [Bacillus cereus],6ZLA_B Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with NAD [Bacillus cereus],6ZLA_C Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with NAD [Bacillus cereus],6ZLA_D Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with NAD [Bacillus cereus],6ZLD_A Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLD_B Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLK_A Equilibrium Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid/UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLK_B Equilibrium Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid/UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLK_C Equilibrium Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid/UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLK_D Equilibrium Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Glucuronic acid/UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLL_A Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLL_B Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLL_C Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4],6ZLL_D Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-Galacturonic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus HuA2-4] |
| 6ZLJ_A | 7.17e-23 | 6 | 336 | 1 | 303 | Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase Y149F mutant from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-4-DEOXY-4-FLUORO-Glucuronic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus],6ZLJ_B Crystal Structure of UDP-Glucuronic acid 4-epimerase Y149F mutant from Bacillus cereus in complex with UDP-4-DEOXY-4-FLUORO-Glucuronic acid and NAD [Bacillus cereus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|P39858|CAPI_STAAU | 1.58e-31 | 6 | 243 | 1 | 234 | Protein CapI OS=Staphylococcus aureus OX=1280 GN=capI PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|O81312|GAE3_ARATH | 1.50e-29 | 4 | 338 | 89 | 413 | UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase 3 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=GAE3 PE=2 SV=1 |
| sp|O22141|GAE4_ARATH | 3.05e-29 | 4 | 340 | 95 | 421 | UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase 4 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=GAE4 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q04871|YCL2_ECO11 | 3.67e-29 | 10 | 336 | 5 | 321 | Uncharacterized 37.6 kDa protein in cld 5'region OS=Escherichia coli O111:H- OX=168927 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9LPC1|GAE2_ARATH | 7.07e-29 | 4 | 340 | 90 | 416 | UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase 2 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=GAE2 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
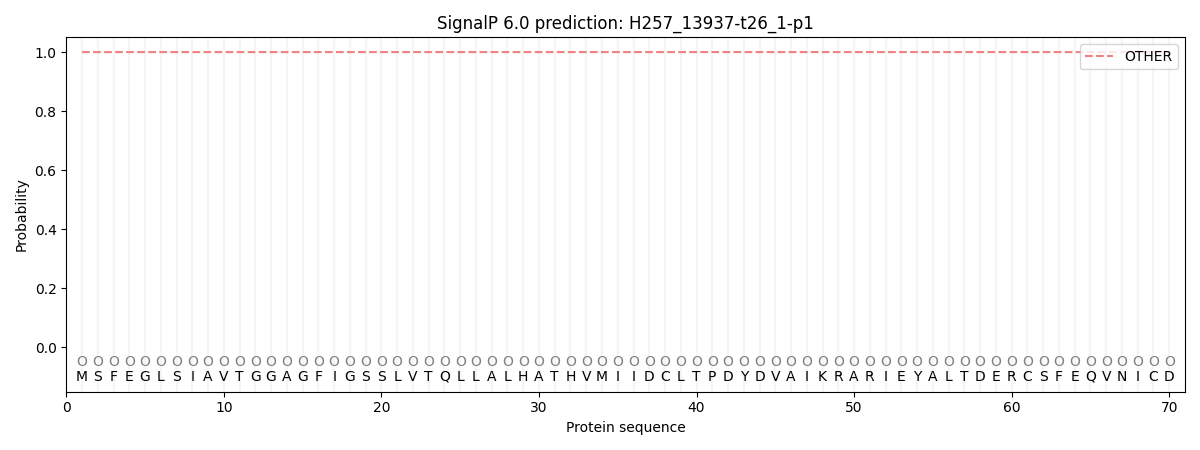
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000028 | 0.000002 |
