You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: GLOIN_2v1485379-t44_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: GLOIN_2v1485379-t44_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Mucoromycota; Glomeromycetes; ; Glomeraceae; Rhizophagus; Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | GLOIN_2v1485379-t44_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA7 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA7 | 41 | 507 | 9.7e-71 | 0.9716157205240175 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396238 | FAD_binding_4 | 8.84e-34 | 43 | 180 | 1 | 138 | FAD binding domain. This family consists of various enzymes that use FAD as a co-factor, most of the enzymes are similar to oxygen oxidoreductase. One of the enzymes Vanillyl-alcohol oxidase (VAO) has a solved structure, the alignment includes the FAD binding site, called the PP-loop, between residues 99-110. The FAD molecule is covalently bound in the known structure, however the residue that links to the FAD is not in the alignment. VAO catalyzes the oxidation of a wide variety of substrates, ranging form aromatic amines to 4-alkylphenols. Other members of this family include D-lactate dehydrogenase, this enzyme catalyzes the conversion of D-lactate to pyruvate using FAD as a co-factor; mitomycin radical oxidase, this enzyme oxidizes the reduced form of mitomycins and is involved in mitomycin resistance. This family includes MurB an UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase enzyme EC:1.1.1.158. This enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. |
| 223354 | GlcD | 2.29e-28 | 42 | 228 | 31 | 216 | FAD/FMN-containing dehydrogenase [Energy production and conversion]. |
| 369658 | BBE | 5.46e-10 | 462 | 507 | 1 | 44 | Berberine and berberine like. This domain is found in the berberine bridge and berberine bridge- like enzymes which are involved in the biosynthesis of numerous isoquinoline alkaloids. They catalyze the transformation of the N-methyl group of (S)-reticuline into the C-8 berberine bridge carbon of (S)-scoulerine. |
| 273751 | FAD_lactone_ox | 3.54e-07 | 43 | 215 | 15 | 178 | sugar 1,4-lactone oxidases. This model represents a family of at least two different sugar 1,4 lactone oxidases, both involved in synthesizing ascorbic acid or a derivative. These include L-gulonolactone oxidase (EC 1.1.3.8) from rat and D-arabinono-1,4-lactone oxidase (EC 1.1.3.37) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Members are proposed to have the cofactor FAD covalently bound at a site specified by Prosite motif PS00862; OX2_COVAL_FAD; 1. |
| 238734 | vWA_ORF176_type | 0.007 | 611 | 778 | 3 | 165 | VWA ORF176 type: Von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain was originally found in the blood coagulation protein von Willebrand factor (vWF). Typically, the vWA domain is made up of approximately 200 amino acid residues folded into a classic a/b para-rossmann type of fold. The vWA domain, since its discovery, has drawn great interest because of its widespread occurrence and its involvement in a wide variety of important cellular functions. These include basal membrane formation, cell migration, cell differentiation, adhesion, haemostasis, signaling, chromosomal stability, malignant transformation and in immune defenses. In integrins these domains form heterodimers while in vWF it forms multimers. There are different interaction surfaces of this domain as seen by the various molecules it complexes with. Ligand binding in most cases is mediated by the presence of a metal ion dependent adhesion site termed as the MIDAS motif that is a characteristic feature of most, if not all A domains. The members of this subgroup are Eubacterial in origin and have a conserved MIDAS motif. Not much is known about the biochemistry of these. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.36e-25 | 13 | 501 | 34 | 483 | |
| 8.04e-22 | 14 | 237 | 136 | 351 | |
| 1.77e-19 | 16 | 505 | 37 | 488 | |
| 1.01e-18 | 13 | 214 | 35 | 229 | |
| 1.01e-18 | 13 | 214 | 35 | 229 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.18e-24 | 42 | 507 | 53 | 510 | Crystal structure of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase from Cannabis sativa [Cannabis sativa] |
|
| 4.11e-22 | 12 | 507 | 19 | 511 | Chain A, MaDA [Morus alba],6JQH_B Chain B, MaDA [Morus alba] |
|
| 4.05e-19 | 22 | 509 | 28 | 470 | Physcomitrella patens BBE-like 1 variant D396N [Physcomitrium patens],6EO5_B Physcomitrella patens BBE-like 1 variant D396N [Physcomitrium patens] |
|
| 5.39e-19 | 22 | 509 | 28 | 470 | Physcomitrella patens BBE-like 1 wild-type [Physcomitrium patens],6EO4_B Physcomitrella patens BBE-like 1 wild-type [Physcomitrium patens] |
|
| 2.21e-18 | 42 | 512 | 81 | 532 | AtBBE15 [Arabidopsis thaliana],4UD8_B AtBBE15 [Arabidopsis thaliana] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.40e-24 | 42 | 507 | 80 | 537 | Cannabichromenic acid synthase OS=Cannabis sativa OX=3483 GN=CBCAS PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.98e-23 | 42 | 507 | 80 | 537 | Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase OS=Cannabis sativa OX=3483 GN=THCAS PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.13e-21 | 42 | 507 | 76 | 525 | Berberine bridge enzyme-like 12 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=At1g30740 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 5.86e-21 | 42 | 507 | 80 | 537 | Cannabidiolic acid synthase-like 1 OS=Cannabis sativa OX=3483 GN=CBDAS2 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 7.14e-21 | 43 | 507 | 33 | 442 | Uncharacterized FAD-linked oxidoreductase YgaK OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=ygaK PE=3 SV=4 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
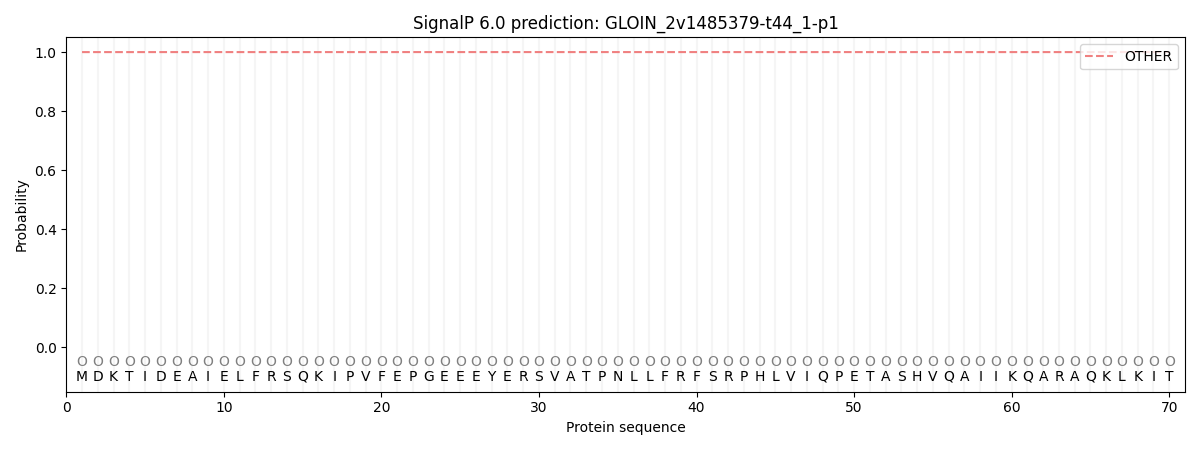
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000051 | 0.000000 |
