You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: GAQ02996.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: GAQ02996.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus lentulus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus lentulus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | GAQ02996.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH55 | 142 | 901 | 1.5e-252 | 0.9702702702702702 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176558 | PI-PLCXDc_like_2 | 2.48e-81 | 1105 | 1400 | 1 | 293 | Catalytic domain of uncharacterized hypothetical proteins similar to eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing proteins. This subfamily corresponds to the catalytic domain present in a group of uncharacterized hypothetical proteins found in bacteria and fungi, which are similar to eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing proteins (PI-PLCXD). The typical eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 3.1.4.11) has a multidomain organization that consists of a PLC catalytic core domain, and various regulatory domains. The catalytic core domain is assembled from two highly conserved X- and Y-regions split by a divergent linker sequence. In contrast, eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain, X domain, and are more closely related to bacterial PI-PLCs, which participate in Ca2+-independent PI metabolism, hydrolyzing the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol (PI) to produce phosphorylated myo-inositol and diacylglycerol (DAG). Although the biological function of eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs still remains unclear, it may distinct from that of typical eukaryotic PI-PLCs. |
| 403800 | Pectate_lyase_3 | 9.81e-73 | 170 | 411 | 1 | 213 | Pectate lyase superfamily protein. This family of proteins possesses a beta helical structure like Pectate lyase. This family is most closely related to glycosyl hydrolase family 28. |
| 176529 | PI-PLCXDc_like | 7.21e-44 | 1106 | 1417 | 2 | 288 | Catalytic domain of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain containing and similar proteins. This family corresponds to the catalytic domain present in phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain containing proteins (PI-PLCXD) which are bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 4.6.1.13) sequence homologs mainly found in eukaryota. The typical eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 3.1.4.11) have a multidomain organization that consists of a PLC catalytic core domain, and various regulatory domains. The catalytic core domain is assembled from two highly conserved X- and Y-regions split by a divergent linker sequence. In contrast, eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs and their bacterial homologs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain, X domain, which is more closely related to that of bacterial PI-PLCs. Although the biological function of eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs still remains unclear, it may be distinct from that of typical eukaryotic PI-PLCs. |
| 176500 | PI-PLCc_bacteria_like | 7.63e-27 | 1106 | 1394 | 2 | 259 | Catalytic domain of bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and similar proteins. This subfamily corresponds to the catalytic domain present in bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC, EC 4.6.1.13) and their sequence homologs found in eukaryota. Bacterial PI-PLCs participate in Ca2+-independent PI metabolism, hydrolyzing the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol (PI) to produce phosphorylated myo-inositol and diacylglycerol (DAG). Although their precise physiological function remains unclear, bacterial PI-PLCs may function as virulence factors in some pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial PI-PLCs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain. Its catalytic mechanism is based on general base and acid catalysis utilizing two well conserved histidines, and consists of two steps, a phosphotransfer and a phosphodiesterase reaction. Eukaryotic homologs in this family are named as phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain containing proteins (PI-PLCXD). They are distinct from the typical eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C (PI-PLC, EC 3.1.4.11), which have a multidomain organization that consists of a PLC catalytic core domain, and various regulatory domains. The catalytic core domain is assembled from two highly conserved X- and Y-regions split by a divergent linker sequence. In contrast, eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs contain a single TIM-barrel type catalytic domain, X domain, which is closely related to that of bacterial PI-PLCs. Although the biological function of eukaryotic PI-PLCXDs still remains unclear, it may be distinct from that of typical eukaryotic PI-PLCs. This family also includes a distinctly different type of eukaryotic PLC, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (GPI-PLC), an integral membrane protein characterized in the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei. T. brucei GPI-PLC hydrolyzes the GPI-anchor on the variant specific glycoprotein (VSG), releasing dimyristyl glycerol (DMG), which may facilitate the evasion of the protozoan to the host's immune system. It does not require Ca2+ for its activity and is more closely related to bacterial PI-PLCs, but not mammalian PI-PLCs. |
| 403800 | Pectate_lyase_3 | 7.66e-11 | 543 | 656 | 1 | 122 | Pectate lyase superfamily protein. This family of proteins possesses a beta helical structure like Pectate lyase. This family is most closely related to glycosyl hydrolase family 28. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 45 | 1432 | 54 | 1445 | |
| 0.0 | 45 | 1430 | 63 | 1428 | |
| 0.0 | 335 | 1432 | 8 | 1106 | |
| 0.0 | 32 | 916 | 393 | 1267 | |
| 0.0 | 20 | 918 | 404 | 1297 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.07e-169 | 146 | 897 | 4 | 736 | Chain A, Beta-1,3-glucanase [Thermochaetoides thermophila],5M60_A Chain A, Beta-1,3-glucanase [Thermochaetoides thermophila] |
|
| 2.38e-167 | 148 | 902 | 26 | 743 | Chain A, Glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],3EQN_B Chain B, Glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],3EQO_A Chain A, Glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],3EQO_B Chain B, Glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
|
| 3.07e-08 | 157 | 268 | 13 | 110 | Structure of the Streptococcus pneumoniae surface protein and adhesin PfbA [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4] |
|
| 5.53e-08 | 172 | 268 | 117 | 202 | Crystal structure of PfbA, a surface adhesin of Streptococcus pneumoniae [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6],4MR0_B Crystal structure of PfbA, a surface adhesin of Streptococcus pneumoniae [Streptococcus pneumoniae R6] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.56e-175 | 139 | 902 | 34 | 862 | Probable glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase ARB_02077 OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=ARB_02077 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.31e-137 | 131 | 905 | 34 | 776 | Glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase OS=Cochliobolus carbonum OX=5017 GN=EXG1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.74e-49 | 141 | 867 | 30 | 708 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase BGN13.1 OS=Trichoderma harzianum OX=5544 GN=bgn13.1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.01e-07 | 172 | 268 | 153 | 238 | Plasmin and fibronectin-binding protein A OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) OX=171101 GN=pfbA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
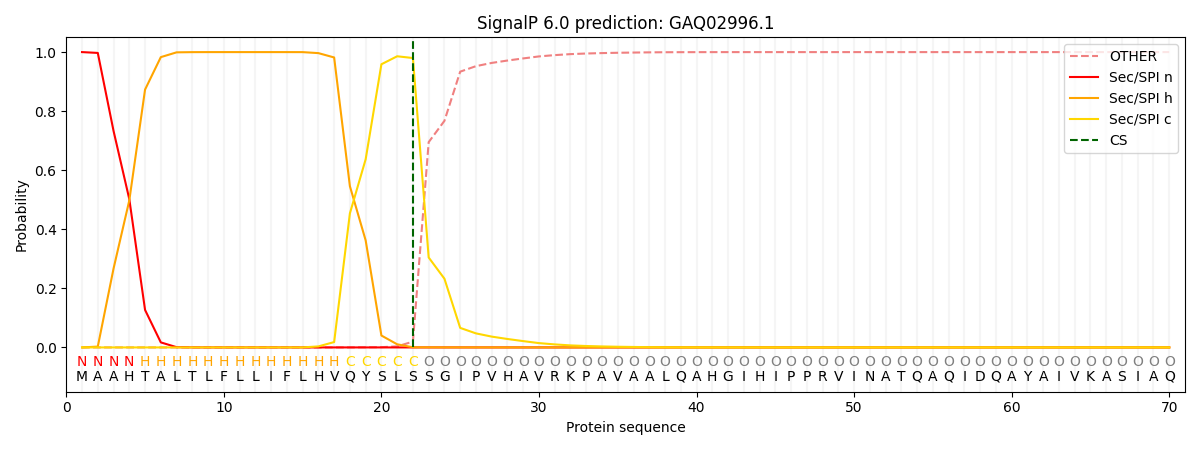
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000212 | 0.999781 | CS pos: 22-23. Pr: 0.9799 |
